Questo documento fornisce una panoramica generale dell'API Google Tag Manager.
Introduzione
L'API Google Tag Manager consente a un utente autorizzato di accedere ai dati di configurazione di Google Tag Manager. Con questa API puoi gestire:
- Account
- Container
- Destinazioni
- Aree di lavoro
- Configurazione tag Google
- Tag
- Trigger
- Cartelle
- Variabili integrate
- Client
- Variabili
- Versioni contenitore
- Intestazioni delle versioni del contenitore
- Autorizzazioni utente
- Ambienti
Per iniziare
Vuoi iniziare subito? Leggi la Guida per gli sviluppatori. Ogni applicazione che utilizza l'API dovrà seguire un paio di passaggi per registrare, autorizzare l'utente e utilizzare l'API. La guida per gli sviluppatori illustra ogni passaggio e, alla fine, avrai un'applicazione funzionante che potrai personalizzare.
Panoramica concettuale
L'API espone più entità di configurazione di Google Tag Manager, organizzate in modo gerarchico. L'account di ogni utente può avere uno o più contenitori, ognuno dei quali può avere una o più aree di lavoro. Un'area di lavoro consente di apportare più modifiche simultanee a variabili, variabili integrate, attivatori, cartelle e tag di un contenitore. Dopo aver apportato le modifiche desiderate all'area di lavoro, puoi creare, visualizzare l'anteprima e pubblicare una versione. Una risorsa Autorizzazioni consente di gestire le autorizzazioni utente a livello di Account. Il seguente diagramma rappresenta le relazioni padre-figlio tra le entità:
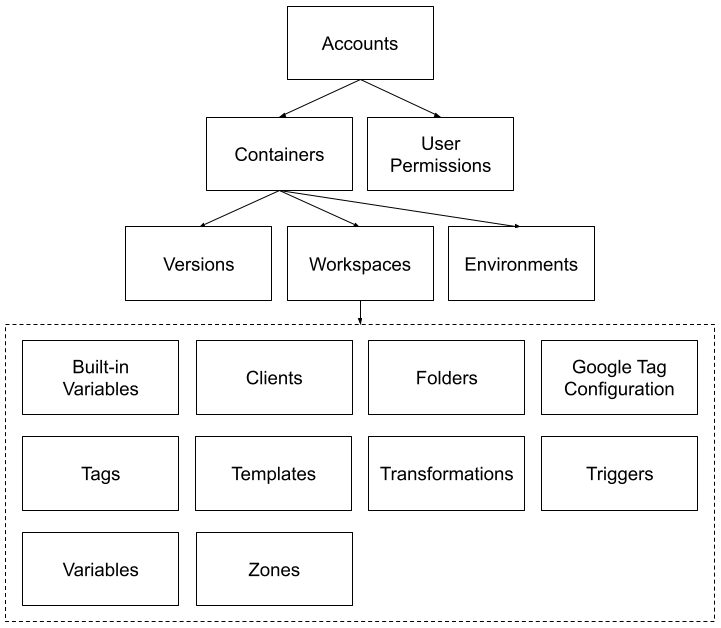
L'API di Google Tag Manager espone ciascuna delle entità come risorsa. Un elenco di risorse di un certo tipo costituisce una raccolta. L'API espone ogni raccolta in un URI su cui è possibile eseguire query per restituire l'elenco delle entità al suo interno.
Consulta il riferimento dell'API Tag Manager per una descrizione dettagliata dei metodi nell'API e dei dati che restituiscono.
Criteri per le quote
L'API Google Tag Manager gestisce milioni di operazioni. Per evitare che il sistema riceva più operazioni di quante ne sia in grado di gestire e per garantire una distribuzione equa delle risorse di sistema, è necessario impiegare un sistema di quote. Per conoscere i limiti specifici, consulta la guida su limiti e quote.
Passaggi successivi
Risorse utili per saperne di più sull'API:
- Leggi la Guida per gli sviluppatori per scoprire come utilizzare l'API.
- Consulta la documentazione di riferimento sull'API Tag Manager per acquisire familiarità con le risorse e le operazioni disponibili di Tag Manager.