Neste documento, veremos uma visão geral da API Google Tag Manager.
Introdução
A API Google Tag Manager proporciona a um usuário autorizado acesso aos dados de configuração do Gerenciador de tags do Google. Com ela, você pode gerenciar:
- Contas
- Contêineres
- Destinos
- Espaços de trabalho
- Configuração de tag do Google
- Tags
- Gatilhos
- Pastas
- Variáveis incorporadas
- Clientes
- Variáveis
- Versões de contêineres
- Cabeçalhos da versão do contêiner
- Permissões de usuário
- Ambientes
Vamos começar
Quer começar imediatamente? Leia o Guia do desenvolvedor. Cada aplicativo que usa a API precisa passar por duas etapas para concluir o registro, autorizar o usuário e trabalhar com a API. O Guia do desenvolvedor explica cada etapa. Após terminar, você terá um aplicativo personalizável em funcionamento.
Visão geral conceitual
A API expõe várias entidades de configuração do Gerenciador de tags do Google, organizadas hierarquicamente. A conta de cada usuário pode ter um ou mais contêineres, cada com um ou mais espaços de trabalho. No espaço de trabalho, é possível fazer várias modificações simultâneas nas variáveis, variáveis incorporadas, acionadores, pastas e tags de um contêiner. Depois que você fizer as modificações desejadas no espaço de trabalho, poderá criar, visualizar e publicar uma versão. Com um recurso de permissão, você pode gerenciar permissões do usuário no nível da conta. Este diagrama representa as relações pai-filho entre as entidades:
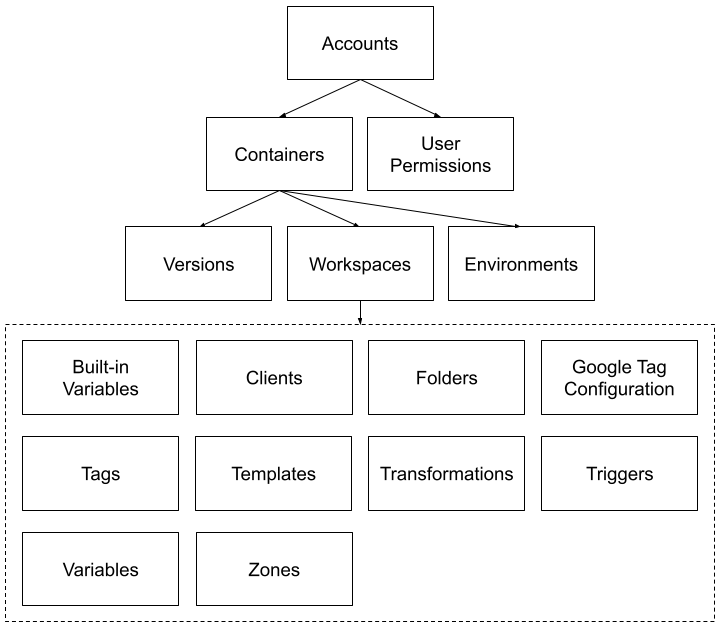
A API Google Tag Manager expõe cada uma das entidades como um recurso. Uma lista de recursos de um tipo específico compõe um conjunto. A API expõe cada conjunto em um URI que pode ser consultado para retornar a lista de entidades contidas nele.
Consulte a referência da API Tag Manager para ver uma descrição detalhada dos métodos na API e os dados que eles retornam.
Políticas de cotas
A API Google Tag Manager processa milhões de operações. Para impedir que o sistema receba mais operações do que pode processar e garantir uma distribuição equitativa dos respectivos recursos, é necessário empregar um sistema de cotas. Consulte o guia Limites e cotas para ver os limites específicos.
Próximas etapas
Recursos para saber mais sobre a API:
- Leia o guia do desenvolvedor para saber como trabalhar com a API.
- Consulte a Referência da API Tag Manager para se familiarizar com os recursos do Gerenciador de tags e as operações disponíveis.