ホームページは、1 つ以上のコンテキストに依存しないカードを定義できる Google Workspace アドオンの新しい機能です。コンテキストに依存しないカードは、ユーザーが特定のコンテキストの外部にいるときにユーザー インターフェースを表示するために使用されます。たとえば、ユーザーが Gmail の受信トレイを表示しているが、メールや下書きを開いていないときなどです。
ホームページでは、クイック アクセス サイドパネル の Google アプリ(Keep、カレンダー、ToDo リスト)と同様に、コンテキストに依存しないコンテンツを表示できます。ホームページは、ユーザーがアドオンを初めて開く際の最初の開始点にもなります。また、新しいユーザーにアドオンの操作方法を教えるのにも役立ちます。
アドオンのホームページを定義するには、プロジェクト マニフェストでホームページを指定し、1 つ以上の homepageTrigger 関数を実装します(ホームページの設定をご覧ください)。
アドオンが拡張するホスト アプリケーションごとに 1 つずつ、複数のホームページを設定できます。また、カスタム ホームページを指定していないホストで使用される、共通のデフォルト ホームページを 1 つ定義することもできます。
アドオンのホームページは、次のいずれかの条件が満たされると表示されます。
- ホストでアドオンが初めて開かれたとき(承認後)。
- アドオンが開いているときに、ユーザーがコンテキスト コンテキストから非コンテキスト コンテキストに切り替えた場合。たとえば、カレンダーの予定の編集からメインのカレンダーに移動します。
- ユーザーが [戻る] ボタンを何度かクリックして、内部スタックから他のすべてのカードをポップしたとき。
- コンテキストに依存しないカードの UI 操作で
Navigation.popToRoot()呼び出しが発生した場合。
ホームページの設計は必須ではありませんが、強くおすすめします。ホームページを定義しない場合、ユーザーがホームページに移動するたびに、アドオン名を含む汎用カードが使用されます。
ホームページの設定
Google Workspace アドオンは、addOns.common.homepageTrigger フィールドを使用して、アドオンのマニフェスト内のすべてのホスト アプリケーションのデフォルトのホームページ(コンテキストに依存しない)アドオン コンテンツを構成します。
{
// ...
"addOns": {
// ...
"common": {
// ...
"homepageTrigger": {
"runFunction": "myFunction",
"enabled": true
}
}
}
}
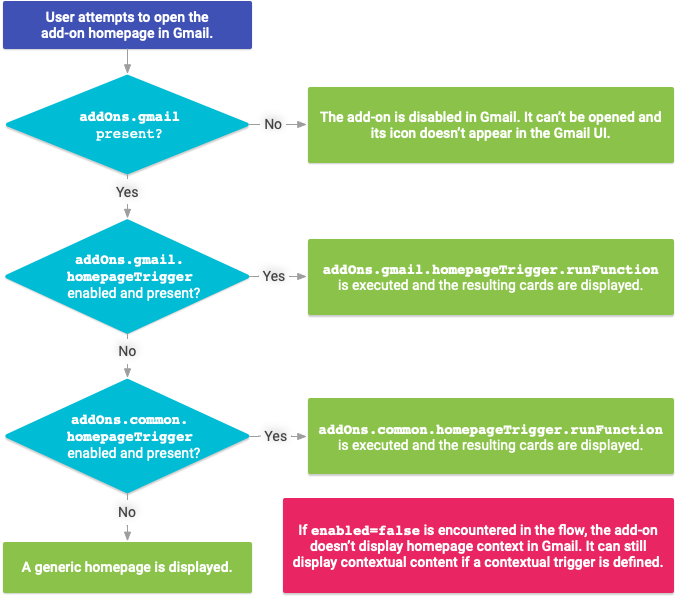
runFunction: Google Workspace アドオン フレームワークがホームページ アドオン カードのレンダリング時に呼び出す Apps Script 関数の名前。この関数はホームページ トリガー関数です。この関数は、ホームページ UI を構成するCardオブジェクトの配列を構築して返す必要があります。複数のカードが返された場合、ホスト アプリケーションには、ユーザーが選択できるカードのヘッダーがリストに表示されます(複数のカードを返すをご覧ください)。enabled: このスコープでホームページ カードを有効にするかどうか。このフィールドは省略可能で、デフォルト値はtrueです。これをfalseに設定すると、すべてのホストでホームページ カードが無効になります(そのホストでオーバーライドしない限り。下記を参照)。
共通の構成に加えて、各ホスト アプリケーションの構成(addOns.gmail.homepageTrigger、addOns.calendar.homepageTrigger など)で使用できる、ホストごとのオーバーライドも同じ構造で存在します。
{
...
"addOns": {
...
"common": {
// By default, call 'buildHomePage' to render homepage content
// in all hosts. Since calendar.homepageTrigger below overrides
// this in Calendar and Drive and the homepageTrigger is disabled
// for Gmail, this homepage function never executes.
"homepageTrigger": { "runFunction": "buildHomePage" }
},
"calendar": {
// Show customized homepage content for Calendar only.
"homepageTrigger": { "runFunction": "buildCalendarHomepage" }
},
"drive": {
// Show customized homepage content for Drive only.
"homepageTrigger": { "runFunction": "buildDriveHomepage" }
}
"gmail": {
// Disable homepage add-on content in Gmail.
"homepageTrigger": { "enabled": false }
},
...
}
}
これは、次のマニフェストの抜粋と同じです。
{
...
"addOns": {
...
"common": { /* ... */ }, // Omitted a default homepageTrigger specification.
"calendar": {
// Show customized homepage content for Calendar only.
"homepageTrigger": { "runFunction": "myCalendarFunction" }
},
"drive": {
// Show customized homepage content for Drive only.
"homepageTrigger": { "runFunction": "myDriveFunction" }
}
"gmail": { /* ... */ },
...
}
}
homepageTrigger セクションはどれも必須ではありません。ただし、特定のホスト プロダクトでアドオンに表示される UI は、対応するマニフェスト フィールドの有無と、関連する homepageTrigger があるかどうかによって異なります。次の例は、さまざまなマニフェスト構成のホームページ UI を作成するために実行されるアドオン トリガー関数(存在する場合)を示しています。
ホームページ イベント オブジェクト
上記のホームページ トリガー関数(runFunction)が呼び出されると、呼び出しコンテキストのデータを含むイベント オブジェクトが渡されます。
ホームページ イベント オブジェクトには、ウィジェットやコンテキスト情報は含まれません。渡される情報は、次の共通イベント オブジェクトのフィールドに限定されます。
commonEventObject.clientPlatformcommonEventObject.hostAppcommonEventObject.userLocaleとcommonEventObject.userTimezone(ただし、制限情報についてはユーザーの言語 / 地域とタイムゾーンへのアクセスをご覧ください)。
詳細については、イベント オブジェクトをご覧ください。
コンテキストに依存しないその他のカード
アドオンの UI には、ホームページではないコンテキストに依存しないカードを追加できます。たとえば、ホームページにボタンがあり、そのボタンをクリックすると [設定] カードが開き、ユーザーがアドオンの設定を調整できる場合、その設定はコンテキストに依存しない(コンテキストに依存しない)設定である可能性があります。
コンテキストに依存しないカードは、他のカードと同様に作成されます。唯一の違いは、カードを生成し表示するアクションまたはイベントです。カード間の遷移を作成する方法については、ナビゲーション メソッドをご覧ください。
