借助适用于 Google 文档的 Apps 脚本,您可以访问文档中的任何标签页中的内容。
什么是标签页?
Google 文档有一个称为标签页的组织层。借助 Google 文档,用户可以在单个文档中创建一个或多个标签页,这与 Google 表格中目前的标签页功能类似。每个标签页都有自己的标题和 ID(附加在网址中)。标签页还可以有子标签页,即嵌套在其他标签页下的标签页。
访问标签页
您可以使用 Document.getTabs() 访问标签页属性和内容,该方法会返回 Tab 列表。后续部分将简要介绍 Tab 类;标签页类文档还提供了更多详细信息。
标签页属性
您可以使用 Tab.getId() 和 Tab.getTitle() 等方法检索标签页属性。
标签页内容
可以使用 Tab.asDocumentTab() 检索每个标签页中的文档内容。对文档类结构的更改部分介绍了如何使用此方法。
标签页层次结构
子标签页会通过 Tab.getChildTabs() 在 Google Apps 脚本中公开。若要访问所有标签页中的内容,需要遍历子标签页的“树”。例如,假设有一个文档包含如下标签页层次结构:
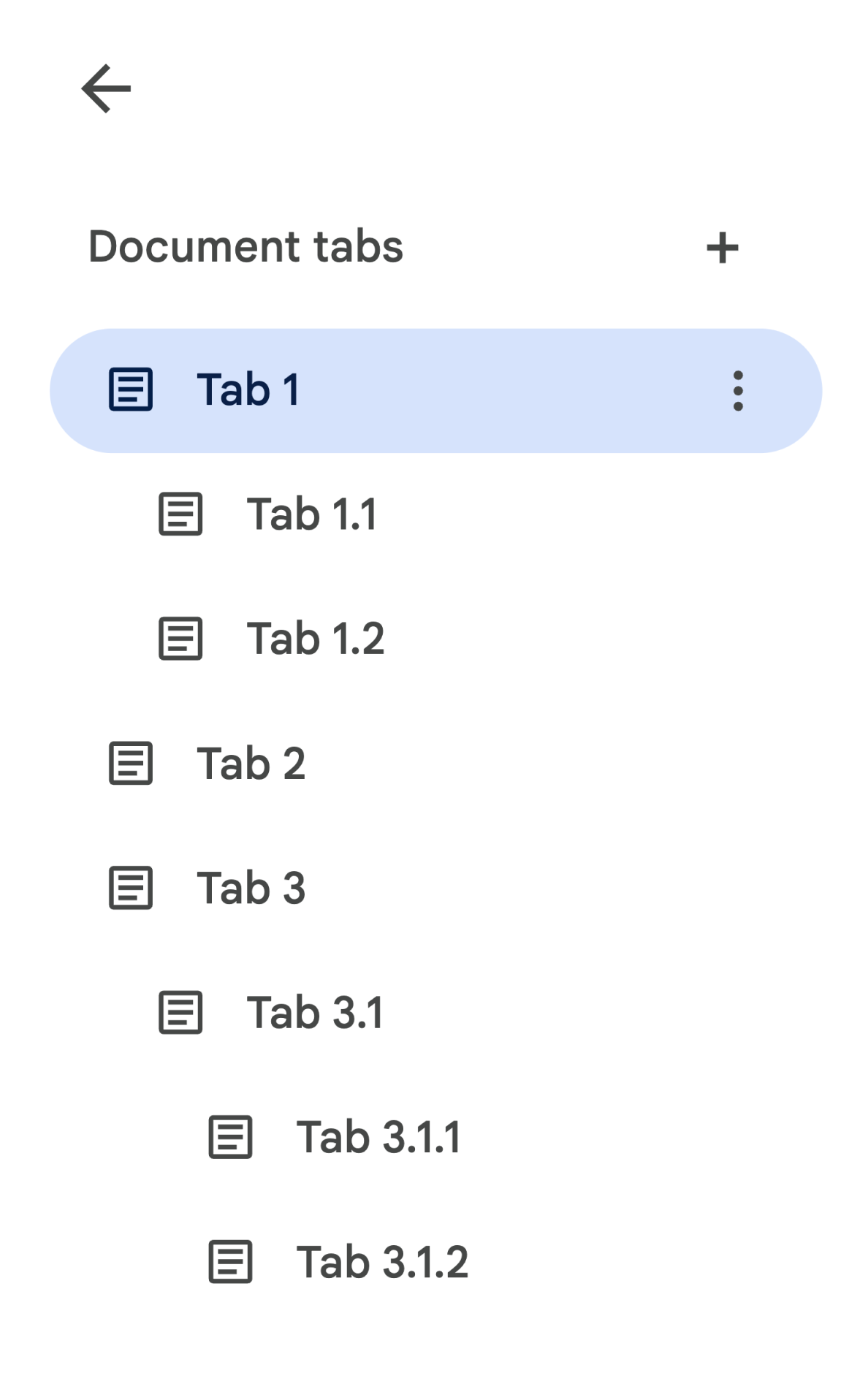
如需访问标签页 3.1.2,您可以执行以下操作:
// Print the ID of Tab 3.1.2. const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const tab = doc.getTabs()[2].getChildTabs()[0].getChildTabs()[1]; console.log(tab.getId());
请参阅后面几部分中的示例代码块,其中提供了用于迭代文档中的所有标签页的示例代码。
检索标签页的其他方式
您还可以通过另外两种方法检索标签页:
Document.getTab(tabId):返回具有指定 ID 的标签页。Document.getActiveTab():返回用户的活跃标签页。仅适用于绑定到文档的脚本。后续部分将对此进行更详细的介绍。
文档类结构的变更
以前,文档没有标签页的概念,因此 Document 类公开了用于直接访问和修改文档文本内容的方法。以下方法属于此类别:
Document.addBookmark(position)Document.addFooter()Document.addHeader()Document.addNamedRange(name, range)Document.getBody()Document.getBookmark(id)Document.getBookmarks()Document.getFooter()Document.getFootnotes()Document.getHeader()Document.getNamedRangeById(id)Document.getNamedRanges()Document.getNamedRanges(name)Document.newPosition(element, offset)Document.newRange()
由于新增了标签页的结构层次,这些方法不再从语义上表示文档中所有标签页的文本内容。文本内容现在将以不同的图层表示;所有上述文本方法都可以通过 DocumentTab 访问。
Document 类中的这些现有方法将访问或修改来自活动标签页(在绑定至特定文档的脚本中)或第一个标签页(如果活动标签页不可用)中的内容。
访问特定标签页中的文本内容
建议改用 DocumentTab 类(通过 Tab.asDocumentTab() 方法提供)提供的方法,而不是使用 Document 提供的文本方法。例如:
// Print the text from the body of the active tab. const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const documentTab = doc.getActiveTab().asDocumentTab(); const body = documentTab.getBody(); console.log(body.getText());
用户选择的变化
文本选择方法
Document 类提供了 getter 和 setter,用于管理用户在有效文档中选择的文本位置。这些方法在运行脚本的用户的活跃标签页上下文中运行。
Document.getCursor():返回用户在活动标签页中的光标位置。Document.getSelection():返回用户在活动标签页中的选择范围。Document.setCursor(position):设置用户在有效文档中的光标位置。如果相应位置位于非活动标签页中,则用户的活动标签页也会切换到与该位置关联的标签页。Document.setSelection(range):设置用户在有效文档中的选择范围。如果范围位于非活动标签页中,则用户的活动标签页也会切换到与该范围关联的标签页。
标签页选择方法和用例
随着标签页的引入,获取和设置运行脚本的用户的活动标签页可能很有用。您可以使用以下方法执行此操作:
Document.getActiveTab():返回有效文档中的用户有效Tab。Document.setActiveTab(tabId):将用户在当前文档中选择的Tab设置为具有指定 ID 的标签页。
用户的整体“选择”由当前标签页以及当前光标位置或选择范围组成。处理活跃选择的两种模式是明确地将用户的活动标签页修改为特定标签页,或者使用用户的活动标签页。
您可以使用 Document.setActiveTab(tabId) 显式更改用户的活动标签页。或者,从非活跃标签页使用 Position 或 Range 调用 Document.setCursor(position) 或 Document.setSelection(range) 将使该标签页重新变为活跃状态。
如果脚本的预期行为是使用用户的活动标签页而不更改它,则不需要 Document.setActiveTab(tabId)。Document.getCursor() 和 Document.getSelection() 方法将根据用户运行脚本时所用的标签页,在活动标签页上运行。
请注意,文档不支持在多个标签页中选择多个标签页,也不支持在不同标签页中选择多个位置或范围。因此,使用 Document.setActiveTab(tabId) 将清除之前的光标位置或选择范围。
特定标签页的位置和范围方法
特定标签页为 Position 和 Range 的文本选择概念赋予了意义。也就是说,只有当脚本知道光标位置或选择范围所在的特定标签页时,光标位置或选择范围才有意义。
为此,您可以使用 DocumentTab.newPosition(element, offset) 和 DocumentTab.newRange() 方法,这些方法会构建一个 Position 或 Range,以定位到调用该方法的特定 DocumentTab。相比之下,Document.newPosition(element, offset) 和 Document.newRange() 将构造一个以活动标签页(或第一个标签页,如果脚本未绑定)为目标的位置或范围。
请参阅后续部分中的示例代码块,其中提供了有关使用选择的示例代码。
标签页的常见使用模式
以下代码示例介绍了与标签页互动的各种方式。
读取文档中所有标签页的内容
通过遍历标签页树并从 Tab 和 DocumentTab(而非 Document)中调用 getter 方法,可以将在标签页功能之前执行此操作的现有代码迁移到支持标签页。以下代码示例部分展示了如何输出文档中每个标签页中的所有文本内容。此标签页遍历代码可适用于许多其他不关心标签页实际结构的用例。
/** Logs all text contents from all tabs in the active document. */ function logAllText() { // Generate a list of all the tabs in the document, including any // nested child tabs. DocumentApp.openById('abc123456') can also // be used instead of DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(). const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const allTabs = getAllTabs(doc); // Log the content from each tab in the document. for (const tab of allTabs) { // Get the DocumentTab from the generic Tab object. const documentTab = tab.asDocumentTab(); // Get the body from the given DocumentTab. const body = documentTab.getBody(); // Get the body text and log it to the console. console.log(body.getText()); } } /** * Returns a flat list of all tabs in the document, in the order * they would appear in the UI (i.e. top-down ordering). Includes * all child tabs. */ function getAllTabs(doc) { const allTabs = []; // Iterate over all tabs and recursively add any child tabs to // generate a flat list of Tabs. for (const tab of doc.getTabs()) { addCurrentAndChildTabs(tab, allTabs); } return allTabs; } /** * Adds the provided tab to the list of all tabs, and recurses * through and adds all child tabs. */ function addCurrentAndChildTabs(tab, allTabs) { allTabs.push(tab); for (const childTab of tab.getChildTabs()) { addCurrentAndChildTabs(childTab, allTabs); } }
读取文档中第一个标签页的内容
这类似于阅读所有标签页。
/** * Logs all text contents from the first tab in the active * document. */ function logAllText() { // Generate a list of all the tabs in the document, including any // nested child tabs. const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const allTabs = getAllTabs(doc); // Log the content from the first tab in the document. const firstTab = allTabs[0]; // Get the DocumentTab from the generic Tab object. const documentTab = firstTab.asDocumentTab(); // Get the body from the DocumentTab. const body = documentTab.getBody(); // Get the body text and log it to the console. console.log(body.getText()); }
更新第一个标签页中的内容
以下代码示例部分展示了如何在进行更新时定位到特定标签页。
/** Inserts text into the first tab of the active document. */ function insertTextInFirstTab() { // Get the first tab's body. const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const firstTab = doc.getTabs()[0]; const firstDocumentTab = firstTab.asDocumentTab(); const firstTabBody = firstDocumentTab.getBody(); // Append a paragraph and a page break to the first tab's body // section. firstTabBody.appendParagraph("A paragraph."); firstTabBody.appendPageBreak(); }
更新活跃标签页或所选标签页中的内容
以下代码段展示了如何在进行更新时定位到活动标签页。
/** * Inserts text into the active/selected tab of the active * document. */ function insertTextInActiveTab() { // Get the active/selected tab's body. const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const activeTab = doc.getActiveTab(); const activeDocumentTab = activeTab.asDocumentTab(); const activeTabBody = activeDocumentTab.getBody(); // Append a paragraph and a page break to the active tab's body // section. activeTabBody.appendParagraph("A paragraph."); activeTabBody.appendPageBreak(); }
在当前标签页中设置光标位置或选择范围
以下代码示例部分展示了如何更新用户活跃标签页中的光标位置或选择范围。这仅在绑定的脚本中相关。
/** * Changes the user's selection to select all tables within the tab * with the provided ID. */ function selectAllTables(tabId) { const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const tab = doc.getTab(tabId); const documentTab = tab.asDocumentTab(); // Build a range that encompasses all tables within the specified // tab. const rangeBuilder = documentTab.newRange(); const tables = documentTab.getBody().getTables(); for (let i = 0; i < tables.length; i++) { rangeBuilder.addElement(tables[i]); } // Set the document's selection to the tables within the specified // tab. Note that this actually switches the user's active tab as // well. doc.setSelection(rangeBuilder.build()); }
设置活动标签页或所选标签页
以下代码段展示了如何更改用户的活动标签页。 这仅与绑定脚本相关。
/** * Changes the user's selected tab to the tab immediately following * the currently selected one. Handles child tabs. * *Only changes the selection if there is a tab following the
* currently selected one. */ function selectNextTab() { const doc = DocumentApp.getActiveDocument(); const allTabs = getAllTabs(doc); const activeTab = doc.getActiveTab(); // Find the index of the currently active tab. let activeTabIndex = -1; for (let i = 0; i < allTabs.length; i++) { if (allTabs[i].getId() === activeTab.getId()) { activeTabIndex = i; } } // Update the user's selected tab if there is a valid next tab. const nextTabIndex = activeTabIndex + 1; if (nextTabIndex < allTabs.length) { doc.setActiveTab(allTabs[nextTabIndex].getId()); } }
