Interactive Canvas는 개발자가 대화 작업에 시각적 몰입형 환경을 추가할 수 있도록 Google 어시스턴트를 기반으로 빌드된 프레임워크입니다. 이 시각적 환경은 대화에서 어시스턴트가 사용자에게 응답으로 전송하는 대화형 웹 앱입니다. 어시스턴트 대화에서 인라인으로 존재하는 리치 응답과 달리 Interactive Canvas 웹 앱은 전체 화면 웹 뷰로 렌더링됩니다.
작업에서 다음 중 하나를 실행하려면 Interactive Canvas를 사용하세요.
- 전체 화면 이미지 만들기
- 맞춤 애니메이션 및 전환 만들기
- 데이터 시각화 수행
- 맞춤 레이아웃 및 GUI 만들기
지원되는 기기
Interactive Canvas는 현재 다음 기기에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 스마트 디스플레이
- Android 휴대기기
작동 방식
Interactive Canvas를 사용하는 작업은 두 가지 기본 구성요소로 구성됩니다.
- 대화형 작업: 대화형 인터페이스를 사용하여 사용자 요청을 처리하는 작업입니다. Actions Builder 또는 Actions SDK를 사용하여 대화를 빌드할 수 있습니다.
- 웹 앱: 대화 중에 사용자에게 응답으로 응답으로 전송하는 맞춤설정된 시각 요소가 있는 프런트엔드 웹 앱입니다. HTML, 자바스크립트, CSS와 같은 웹 기술을 사용하여 웹 앱을 빌드합니다.
Interactive Canvas 작업과 상호작용하는 사용자는 목표를 달성하기 위해 Google 어시스턴트와 연락을 주고받습니다. 그러나 Interactive Canvas의 경우 이 대화의 대부분은 웹 앱 컨텍스트 내에서 발생합니다. 대화형 작업을 웹 앱에 연결할 때 웹 앱 코드에 Interactive Canvas API를 포함해야 합니다.
- 대화형 캔버스 라이브러리: API를 사용하여 웹 앱과 대화 작업 간의 통신을 사용 설정하기 위해 웹 앱에 포함하는 자바스크립트 라이브러리입니다. 자세한 내용은 Interactive Canvas API 문서를 참고하세요.
Interactive Canvas 라이브러리를 포함하는 것 외에도 대화에서 Canvas 응답 유형을 반환하여 사용자 기기에서 웹 앱을 열어야 합니다. Canvas 응답을 사용하여 사용자 입력을 기반으로 웹 앱을 업데이트할 수도 있습니다.
Canvas: 웹 앱의 URL과 이를 전달할 데이터가 포함된 응답입니다. Actions Builder는 일치하는 인텐트와 현재 장면 데이터로Canvas응답을 자동으로 채워 웹 앱을 업데이트할 수 있습니다. 또는 Node.js 처리 라이브러리를 사용하여 웹훅에서Canvas응답을 전송할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 캔버스 메시지를 참고하세요.
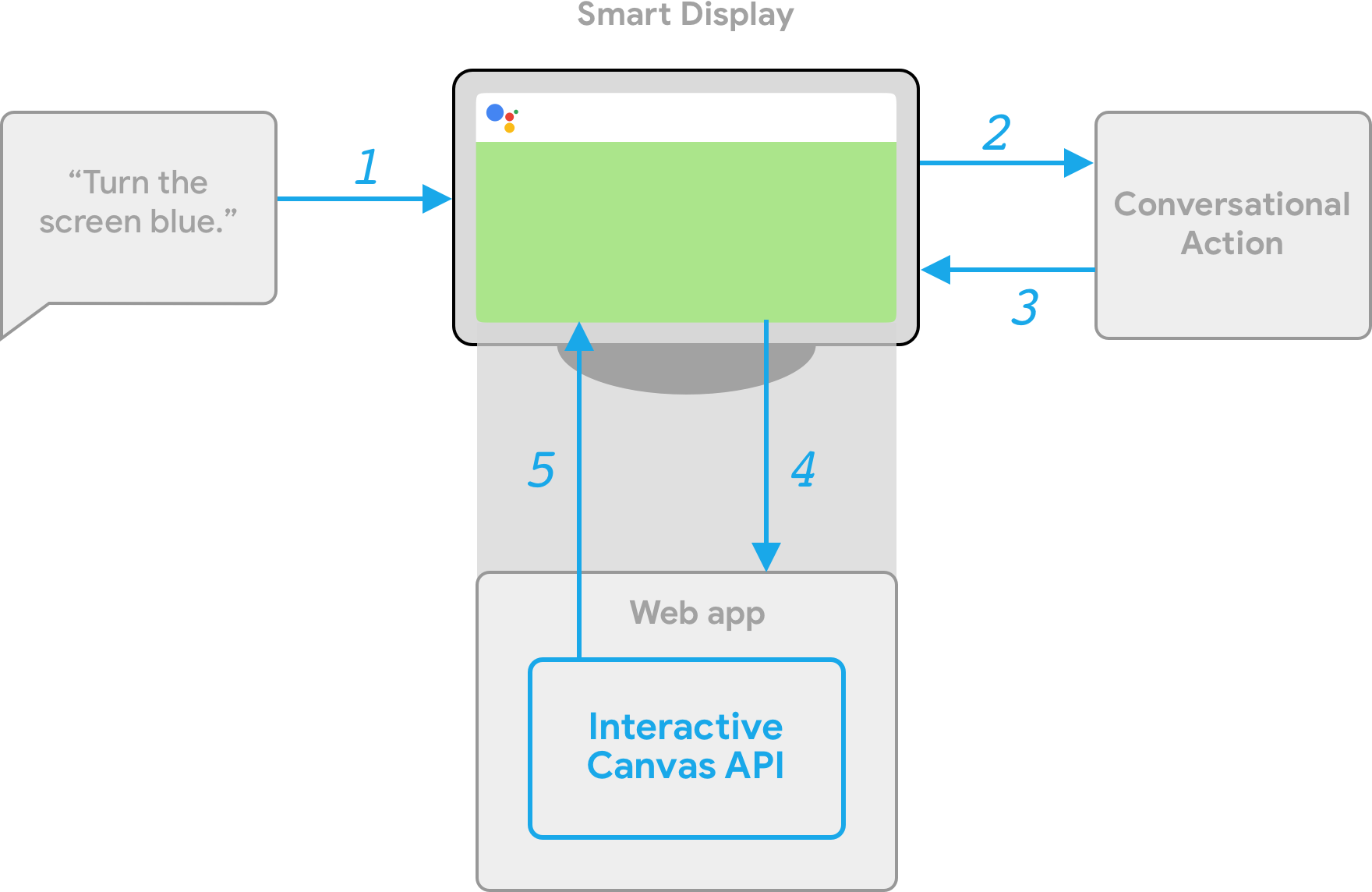
Interactive Canvas의 작동 방식을 보여주기 위해 기기 화면 색상을 사용자가 지정하는 색상으로 변경하는 Cool Colors라는 가상의 작업이 있다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 사용자가 작업을 호출하면 다음 흐름이 발생합니다.
- 사용자가 어시스턴트 기기에 "화면을 파란색으로 켜 줘"라고 말합니다.
- Actions on Google 플랫폼은 사용자의 요청을 대화 로직으로 라우팅하여 인텐트를 일치시킵니다.
- 플랫폼은 인텐트를 이벤트와 일치시켜 이벤트를 트리거하고, 기기에
Canvas응답을 전송합니다. 기기는 응답에 제공된 URL을 사용하여 웹 앱을 로드합니다 (아직 로드되지 않은 경우). - 웹 앱이 로드되면 Interactive Canvas API에 콜백을 등록합니다.
캔버스 응답에
data필드가 포함된 경우data필드의 객체 값이 웹 앱의 등록된onUpdate콜백에 전달됩니다. 이 예에서 대화형 로직은 값이blue인 변수를 포함하는 데이터 필드와 함께Canvas응답을 전송합니다. Canvas응답의data값을 수신하면onUpdate콜백이 웹 앱의 맞춤 로직을 실행하고 정의된 변경사항을 적용할 수 있습니다. 이 예에서onUpdate콜백은data에서 색상을 읽고 화면을 파란색으로 바꿉니다.
클라이언트 측 및 서버 측 처리
Interactive Canvas 작업을 빌드할 때 서버 처리 또는 클라이언트 처리 중에서 선택할 수 있습니다. 서버 처리에서는 주로 웹훅이 필요한 API를 사용합니다. 클라이언트 처리를 사용하면 클라이언트 측 API와 필요한 경우 캔버스가 아닌 기능 (예: 계정 연결)에 웹훅이 필요한 API를 사용할 수 있습니다.
프로젝트 생성 단계에서 서버 웹훅 처리를 사용하여 빌드하려는 경우 대화형 로직과 클라이언트 측 자바스크립트를 처리하는 웹훅을 배포하여 웹 앱을 업데이트하고 둘 사이의 통신을 관리해야 합니다.
클라이언트 처리(현재 개발자 프리뷰에서 사용 가능)로 빌드하려는 경우 새로운 클라이언트 측 API를 사용하여 웹 앱에만 있는 작업 로직을 빌드할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 개발 환경이 간소화되고 대화 차례 간의 지연 시간이 줄어들며 기기 내 기능을 사용할 수 있게 됩니다. 필요한 경우 클라이언트에서 서버 측 로직으로 전환할 수도 있습니다.
클라이언트 측 기능에 대한 자세한 내용은 클라이언트 측 처리를 사용하여 빌드를 참조하세요.
다음 단계
Interactive Canvas용 웹 앱을 빌드하는 방법을 알아보려면 웹 앱을 참고하세요.
전체 Interactive Canvas 작업의 코드는 GitHub 샘플을 참고하세요.