مكوّن "تفاصيل المكان"
يتيح لك مكوّن "تفاصيل المكان" في Places UI Kit إضافة مكوّن فردي لواجهة المستخدم يعرض تفاصيل المكان في تطبيقك. ويمكن تخصيص هذا المكوّن.
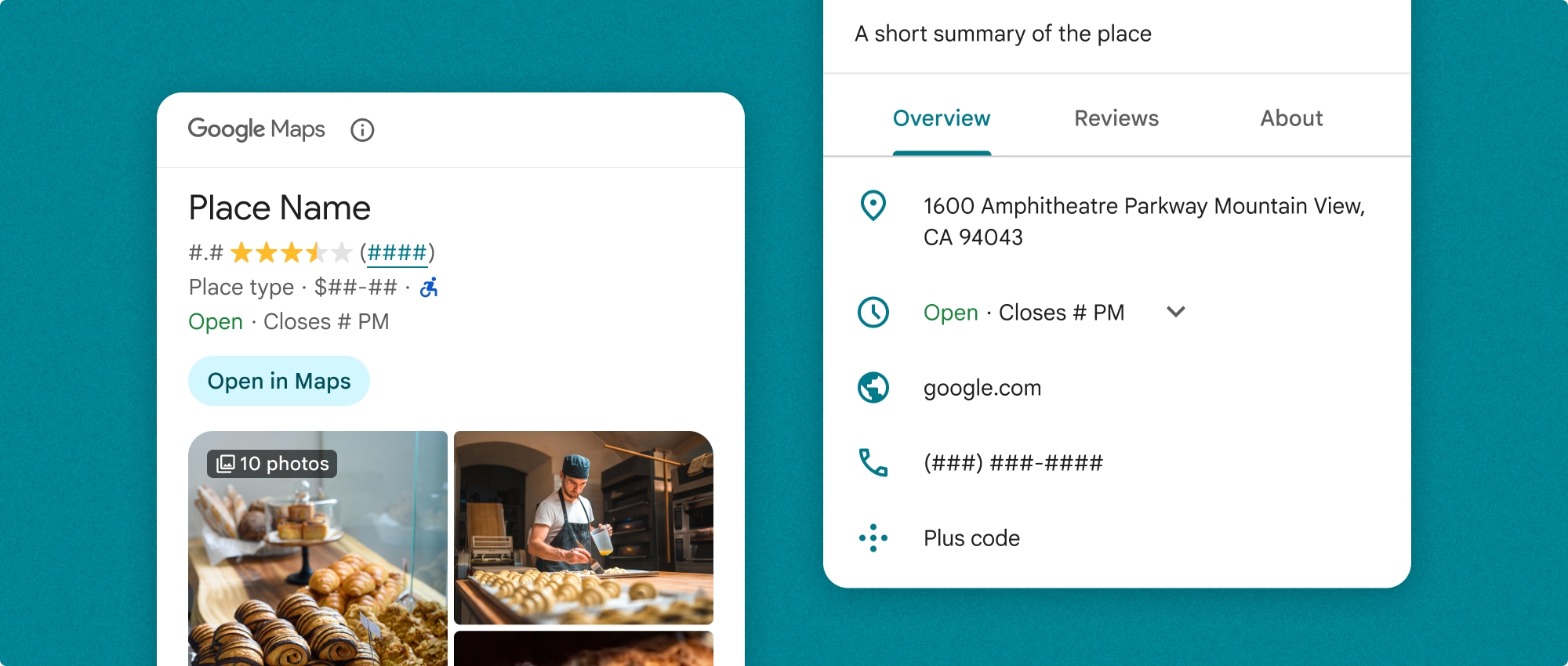
يمكن استخدام مكوّن "تفاصيل المكان" بشكل مستقل أو بالاشتراك مع واجهات برمجة التطبيقات والخدمات الأخرى في "منصة خرائط Google". يتلقّى المكوّن رقم تعريف المكان أو اسم المورد أو إحداثيات خطوط الطول والعرض، ويعرض معلومات تفاصيل المكان.
يمكن تخصيص مظهر مكوّن "تفاصيل المكان" بالكامل، ما يتيح لك تخصيص الخطوط والألوان ونصف قطر الزوايا بما يتوافق مع حالة الاستخدام وإرشادات العلامة التجارية المرئية. يمكنك تخصيص مظهر تفاصيل المكان من خلال إنشاء مظهر يوسّع PlacesMaterialTheme ويوفّر عمليات إلغاء لسمات المظهر. يمكنك أيضًا تخصيص حقول تفاصيل المكان التي يتم تضمينها من خلال تحديد قائمة بإدخالات المحتوى، ويتوافق كل منها مع جزء من المعلومات المعروضة حول المكان.
أشكال التصميم
يتيح مكوّن "تفاصيل المكان" نوعَين رئيسيَين من التصميم:
- مدمج: تخطيط لمعاينة المعلومات الأساسية.
- كامل: تخطيط شامل يعرض جميع تفاصيل المكان المتاحة
يمكن عرض التنسيق المكثّف في الاتجاه العمودي أو الأفقي. يتيح لك ذلك دمج المكوّن في مختلف تخطيطات التصميم وأحجام الشاشات. لا يمكن عرض التنسيق الكامل إلا عموديًا.
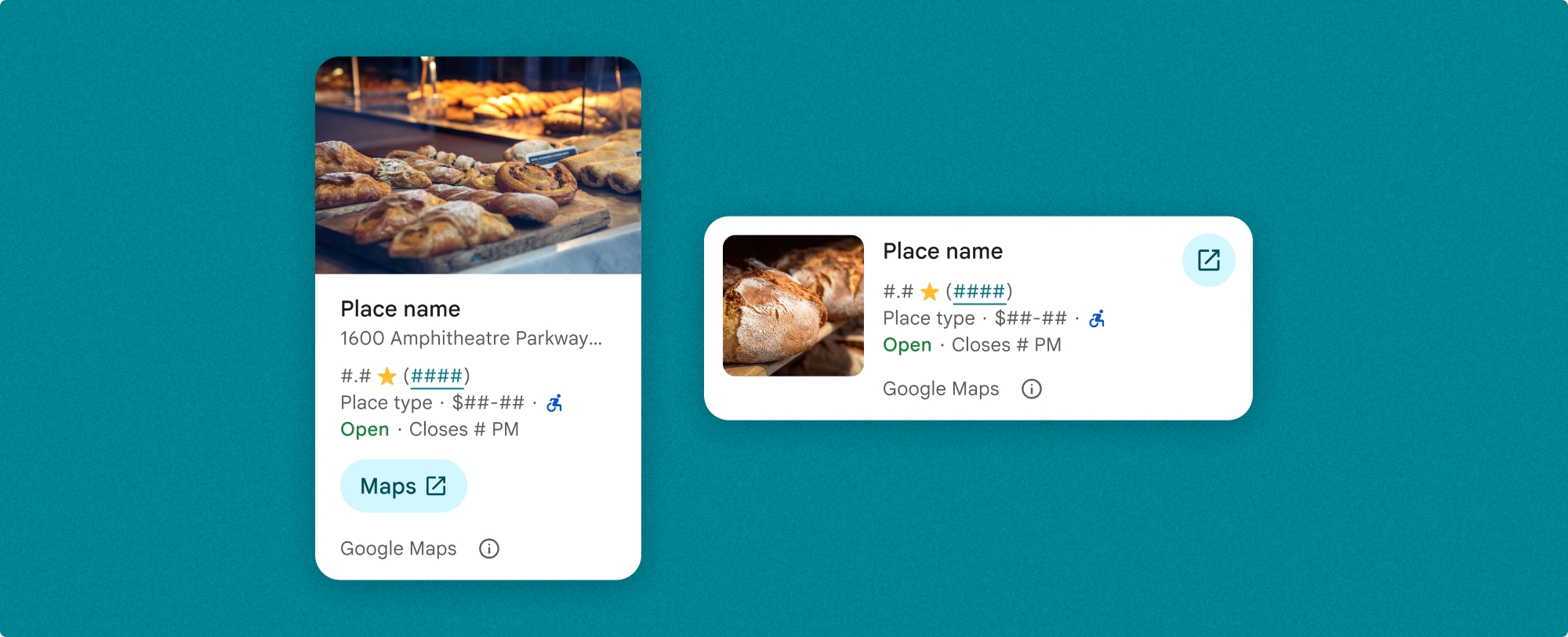
يمنحك مكوّن "تفاصيل المكان" تحكّمًا دقيقًا في المحتوى المعروض في المكوّن. يمكن عرض كل عنصر (مثل الصور والمراجعات ومعلومات الاتصال) أو إخفاؤه بشكل فردي، ما يتيح تخصيصًا دقيقًا لمظهر المكوّنات وكثافة المعلومات.
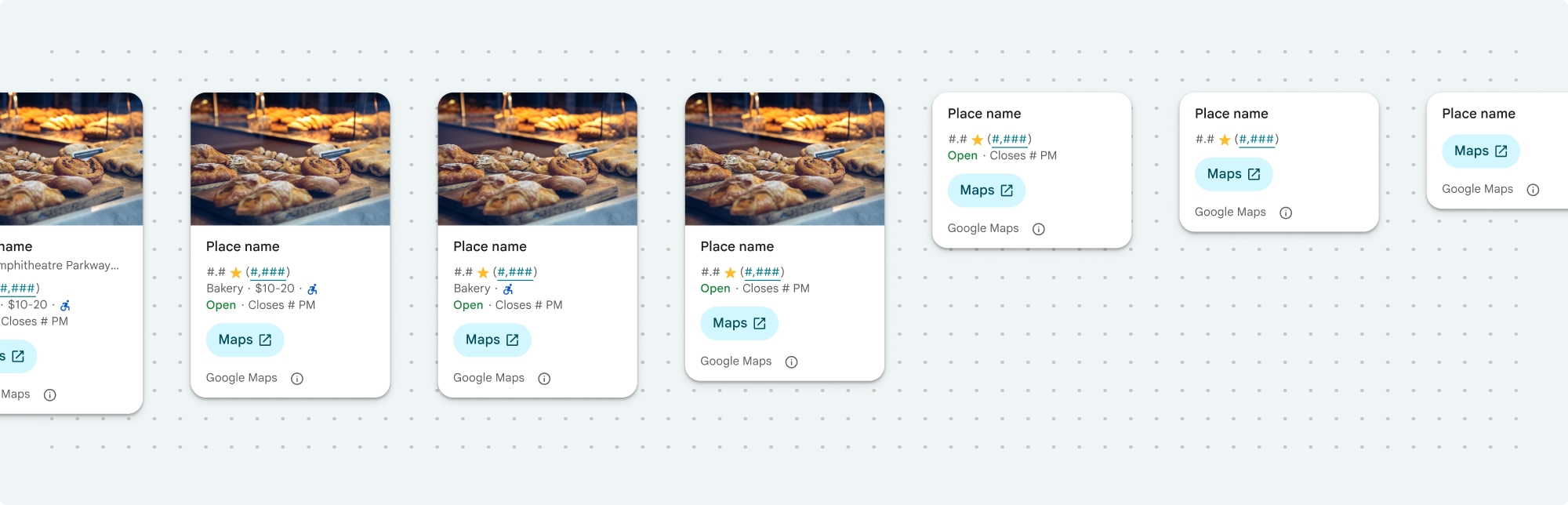
العرض المصغّر لتفاصيل المكان
تعرض "القطعة المدمجة لتفاصيل المكان" (PlaceDetailsCompactFragment) تفاصيل مكان محدّد باستخدام مساحة صغيرة. قد يكون هذا مفيدًا في نافذة معلومات تسلّط الضوء على مكان ما على الخريطة، أو في تجربة على وسائل التواصل الاجتماعي مثل مشاركة موقع جغرافي في محادثة، أو كاقتراح لاختيار موقعك الجغرافي الحالي، أو في مقالة إعلامية للإشارة إلى المكان على "خرائط Google".
عرض تفاصيل المكان بالكامل
يوفّر العرض الكامل لتفاصيل المكان (PlaceDetailsFragment) مساحة أكبر لعرض معلومات تفاصيل المكان، ويتيح لك عرض المزيد من أنواع المعلومات.
خيارات عرض المحتوى
يمكنك تحديد المحتوى الذي تريد عرضه باستخدام القيم التعدادية في PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.Content أو PlaceDetailsFragment.Content.
| العرض المكثّف | عرض كامل |
|---|---|
|
|
الفوترة
عند استخدام حزمة أدوات Place Details UI Kit، يتم تحصيل رسوم منك في كل مرة يتم فيها استدعاء الطريقة .loadWithPlaceId() أو .loadWithResourceName() أو loadWithCoordinates(). في حال تحميل المكان نفسه عدة مرات، يتم تحرير فاتورة لك مقابل كل طلب.
لتجنُّب تحصيل الرسوم منك عدة مرات، لا تُضِف .loadWithPlaceId() أو .loadWithResourceName() مباشرةً في طرق دورة حياة Android. على سبيل المثال، لا تستدعِ .loadWithPlaceId() أو .loadWithResourceName() مباشرةً في طريقة onResume().
إضافة تفاصيل الأماكن إلى تطبيقك
يمكنك إضافة تفاصيل عن الأماكن إلى تطبيقك من خلال إضافة جزء إلى التنسيق. عند إنشاء مثيل للجزء، يمكنك تخصيص مظهر معلومات تفاصيل المكان لتناسب احتياجاتك وتتطابق مع مظهر تطبيقك. مزيد من المعلومات عن التخصيص
تتوفّر ثلاث طرق في كلّ من Kotlin وJava: طريقة لتحميل الجزء باستخدام رقم تعريف المكان (loadWithPlaceId())، وطريقة لتحميل الجزء باستخدام اسم المورد (loadWithResourceName())، وطريقة لتحميل الجزء باستخدام إحداثيات خطوط الطول والعرض (loadWithCoordinates()). يمكنك اختيار أي طريقة أو عدّة طرق.
يكون الوضع التلقائي للعرض المضغوط عموديًا. إذا كنت تريد تخطيطًا أفقيًا، حدِّد Orientation.HORIZONTAL. يمكنك أيضًا تحديد Orientation.VERTICAL اختياريًا لتوضيح المعنى. لا يمكن عرض العرض الكامل إلا عموديًا.
يمكنك الاطّلاع على أمثلة في قسم أمثلة على مكوّن "تفاصيل المكان".
تخصيص المظهر المرئي
تخصيص الأنماط
يمكنك تخصيص ألوان ومظهر الخطوط والمسافات والحدود والزوايا لمكوّن "تفاصيل المكان".
تقدّم حزمة أدوات واجهة المستخدم الخاصة بالأماكن أسلوبًا لنظام التصميم يستند إلى التخصيص المرئي استنادًا إلى تصميم Material Design (مع بعض التعديلات الخاصة بـ "خرائط Google"). يمكنك الاطّلاع على مرجع Material Design الخاص باللون وأسلوب الخط. يتوافق النمط تلقائيًا مع لغة التصميم المرئي في "خرائط Google".
توفّر حزمة Places UI Kit مظهرًا داكنًا تلقائيًا، لذا قد تحتاج إلى تخصيص المظهرين الداكن والفاتح. لتخصيص المظهر الداكن، أضِف إدخالاً للون في values-night/colors.xml.
راجِع قسم التصميم المخصّص لمزيد من المعلومات عن التصميم.
تخصيص العرض والارتفاع
طُرق العرض المصغّرة
العروض المقترَحة:
- الاتجاه العمودي: بين 180 و300 وحدة بكسل مستقلة الكثافة
- الاتجاه الأفقي: بين 180 و500 وحدة بكسل مستقلة الكثافة
قد لا يتم عرض العروض الأصغر من 160 وحدة بكسل مستقل بشكل صحيح.
من أفضل الممارسات عدم ضبط ارتفاع للعروض المضغوطة. سيسمح ذلك للمحتوى في النافذة بتحديد الارتفاع، ما يتيح عرض جميع المعلومات.
مرات المشاهدة الكاملة
بالنسبة إلى العروض الكاملة، يتراوح العرض المقترَح بين 250 و450 وحدة بكسل مستقلة الكثافة. قد لا يتم عرض العرض الأقل من 250 وحدة بكسل مستقلة عن الكثافة بشكل صحيح.
يمكنك ضبط ارتفاع المكوّن: سيتم التمرير عموديًا في عرض "تفاصيل المكان" العمودي ضمن المساحة المخصّصة.
من أفضل الممارسات ضبط ارتفاع للعروض الكاملة. سيتيح ذلك التنقّل بشكل صحيح بين المحتوى في النافذة.
أمثلة على مكوّن "تفاصيل المكان"
إنشاء عرض مكثّف أو عرض كامل
Kotlin
// We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } }
Java
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( Orientation.HORIZONTAL, Arrays.asList(Content.ADDRESS, Content.TYPE, Content.RATING, Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE_ICON), R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme); fragment.setPlaceLoadListener( new PlaceLoadListener() { @Override public void onSuccess(Place place) { ... } @Override public void onFailure(Exception e) { ... } }); getSupportFragmentManager() .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.fragment_container, fragment) .commitNow(); // Load the fragment with a Place ID. fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId); // Load the fragment with a resource name. fragment.loadWithResourceName(resourceName);
يحدّد نموذج الرمز الكامل هذا اتجاه العرض المضغوط آليًا استنادًا إلى إعدادات جهاز المستخدم.
Kotlin
package com.example.placedetailsuikit import android.Manifest import android.annotation.SuppressLint import android.content.pm.PackageManager import android.content.res.Configuration import android.location.Location import android.os.Bundle import android.util.Log import android.view.View import android.widget.Toast import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge import androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher import androidx.activity.result.contract.ActivityResultContracts import androidx.activity.viewModels import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel import com.example.placedetailsuikit.databinding.ActivityMainBinding import com.google.android.gms.location.FusedLocationProviderClient import com.google.android.gms.location.LocationServices import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PointOfInterest import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.Places import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.Place import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceDetailsCompactFragment import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceLoadListener import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.model.Orientation private const val TAG = "PlacesUiKit" /** * A simple ViewModel to store UI state that needs to survive configuration changes. * In this case, it holds the ID of the selected place. Using a ViewModel is good practice * as it prevents data loss during events like screen rotation, ensuring a * seamless user experience. */ class MainViewModel : ViewModel() { var selectedPlaceId: String? = null } /** * This activity serves as a basic example of integrating the Place Details UI Kit. * It demonstrates the fundamental steps required: * 1. Setting up a Google Map. * 2. Requesting location permissions to center the map. * 3. Handling clicks on Points of Interest (POIs) to get a Place ID. * 4. Using the Place ID to load and display place details in a [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. */ class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPoiClickListener { // ViewBinding provides type-safe access to views defined in the XML layout, // eliminating the need for `findViewById` and preventing null pointer exceptions. private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding private var googleMap: GoogleMap? = null // The FusedLocationProviderClient is the main entry point for interacting with the // fused location provider, which intelligently manages the underlying location technologies. private lateinit var fusedLocationClient: FusedLocationProviderClient // Using registerForActivityResult is the modern, recommended approach for handling // permission requests. It decouples the request from the handling logic, making the // code cleaner and easier to manage compared to the older `onRequestPermissionsResult` callback. private lateinit var requestPermissionLauncher: ActivityResultLauncher<Array<String>> // The `by viewModels()` delegate provides a lazy-initialized ViewModel scoped to this Activity. // This ensures that we get the same ViewModel instance across configuration changes. private val viewModel: MainViewModel by viewModels() override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // The ActivityResultLauncher is initialized here. The lambda defines the callback // that will be executed once the user responds to the permission dialog. requestPermissionLauncher = registerForActivityResult(ActivityResultContracts.RequestMultiplePermissions()) { permissions -> // We check if either fine or coarse location permission was granted. if (permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION] == true || permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION] == true) { Log.d(TAG, "Location permission granted by user.") fetchLastLocation() } else { // If permission is denied, we inform the user and default to a known location. // This ensures the app remains functional even without location access. Log.d(TAG, "Location permission denied by user.") Toast.makeText( this, "Location permission denied. Showing default location.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() moveToSydney() } } // enableEdgeToEdge() allows the app to draw behind the system bars for a more immersive experience. enableEdgeToEdge() binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) setContentView(binding.root) binding.dismissButton.setOnClickListener { dismissPlaceDetails() } // --- Crucial: Initialize Places SDK --- // It's essential to initialize the Places SDK before making any other Places API calls. // This should ideally be done once, for example, in the Application's `onCreate`. val apiKey = BuildConfig.PLACES_API_KEY if (apiKey.isEmpty() || apiKey == "YOUR_API_KEY") { // A valid API key is required for the Places SDK to function. Log.e(TAG, "No api key") Toast.makeText( this, "Add your own API_KEY in local.properties", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() finish() return } // `initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled` is used to opt-in to the new SDK version. Places.initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled(applicationContext, apiKey) fusedLocationClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this) // ------------------------------------ // The SupportMapFragment is the container for the map. `getMapAsync` allows us to // work with the GoogleMap object via a callback once it's fully initialized. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map_fragment) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) // This block handles restoration after a configuration change (e.g., screen rotation). // If a place was selected before the rotation, its ID is stored in the ViewModel. // We use this ID to immediately show the details fragment again. if (viewModel.selectedPlaceId != null) { viewModel.selectedPlaceId?.let { placeId -> Log.d(TAG, "Restoring PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } } } /** * This callback is triggered when the GoogleMap object is ready to be used. * All map setup logic should be placed here. */ override fun onMapReady(map: GoogleMap) { Log.d(TAG, "Map is ready") googleMap = map // Setting the OnPoiClickListener allows us to capture user taps on points of interest. googleMap?.setOnPoiClickListener(this) // After the map is ready, we determine the initial camera position based on location permissions. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fetchLastLocation() } else { requestLocationPermissions() } } /** * A helper function to centralize the check for location permissions. */ private fun isLocationPermissionGranted(): Boolean { return ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED || ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED } /** * This function triggers the permission request flow. The result is handled by the * ActivityResultLauncher defined in `onCreate`. */ private fun requestLocationPermissions() { Log.d(TAG, "Requesting location permissions.") requestPermissionLauncher.launch( arrayOf( Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) ) } /** * Fetches the device's last known location. This is a fast and battery-efficient way * to get a location fix. It should only be called after verifying permissions. */ @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun fetchLastLocation() { // Double-checking permissions here is a good practice, although the call sites are already guarded. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fusedLocationClient.lastLocation .addOnSuccessListener { location: Location? -> if (location != null) { val userLocation = LatLng(location.latitude, location.longitude) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(userLocation, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to user's last known location.") } else { // `lastLocation` can be null if the location has never been recorded. // In this case, we fall back to a default location. Log.d(TAG, "Last known location is null. Falling back to Sydney.") moveToSydney() } } .addOnFailureListener { // This listener handles errors in the location fetching process. Log.e(TAG, "Failed to get location.", it) moveToSydney() } } } /** * Moves the map camera to a default, hardcoded location (Sydney). * This serves as a reliable fallback. */ private fun moveToSydney() { val sydney = LatLng(-33.8688, 151.2093) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(sydney, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to Sydney") } /** * This is the callback for the `OnPoiClickListener`. It's triggered when a user * taps a POI on the map. */ override fun onPoiClick(poi: PointOfInterest) { val placeId = poi.placeId Log.d(TAG, "Place ID: $placeId") // We save the selected place ID to the ViewModel. This is critical for surviving // configuration changes. If the user rotates the screen now, the `onCreate` // method will be able to restore the place details view. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = placeId showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } /** * This function is the core of the integration. It creates, configures, and displays * the [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. * @param placeId The unique identifier for the place to be displayed. */ private fun showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId: String) { Log.d(TAG, "Showing PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") // We manage the visibility of UI elements to provide feedback to the user. // The wrapper is shown, and a loading indicator is displayed while the data is fetched. binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.GONE binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.VISIBLE // The Place Details widget can be displayed vertically or horizontally. // We dynamically choose the orientation based on the device's current configuration. val orientation = if (resources.configuration.orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE) { Orientation.HORIZONTAL } else { Orientation.VERTICAL } // We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } } /** * Hides the place details view and clears the selected place ID from the ViewModel. */ private fun dismissPlaceDetails() { binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.GONE // Clearing the ID in the ViewModel is important so that if the user rotates the // screen after dismissing, the details view doesn't reappear. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = null } override fun onDestroy() { super.onDestroy() // It's a good practice to nullify references to objects that have a lifecycle // tied to the activity, like the GoogleMap object, to prevent potential memory leaks. googleMap = null } }
إنشاء مظهر
عند إنشاء مثيل لجزء، يمكنك تحديد مظهر يلغي أيًّا من سمات النمط التلقائي. تستخدم أي سمات للمظهر لم يتم إلغاؤها الأنماط التلقائية. إذا أردت توفير مظهر داكن، يمكنك إضافة إدخال للون في values-night/colors.xml.
توفّر حزمة Places UI Kit مظهرًا داكنًا تلقائيًا، لذا قد تحتاج إلى تخصيص المظهرين الداكن والفاتح. لتخصيص المظهر الداكن، أضِف إدخالاً للون في values-night/colors.xml.
<style name="CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme" parent="PlacesMaterialTheme"> <item name="placesColorPrimary">@color/app_primary_color</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurface">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurfaceVariant">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesTextAppearanceBodySmall">@style/app_text_appearence_small</item> <item name="placesCornerRadius">20dp</item> </style>
استخدام محتوى عادي
يستخدم هذا النموذج المحتوى العادي.
val fragmentStandardContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.STANDARD_CONTENT,
orientation,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)تخصيص محتوى معيّن
يختار هذا النموذج خيارات العنوان والمدخل المناسب لذوي الاحتياجات الخاصة والوسائط Content فقط لعرض مضغوط، ويعرضها باستخدام CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme.
val placeDetailsFragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
listOf(
Content.ADDRESS,
Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE,
Content.MEDIA
),
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)استخدام كل المحتوى
يستخدم هذا النموذج جميع خيارات Content للعرض المضغوط.
val fragmentAllContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)
