Place Details コンポーネント
Places UI キットの Place Details コンポーネントを使用すると、アプリに場所の詳細を表示する個々の UI コンポーネントを追加できます。このコンポーネントはカスタマイズ可能です。
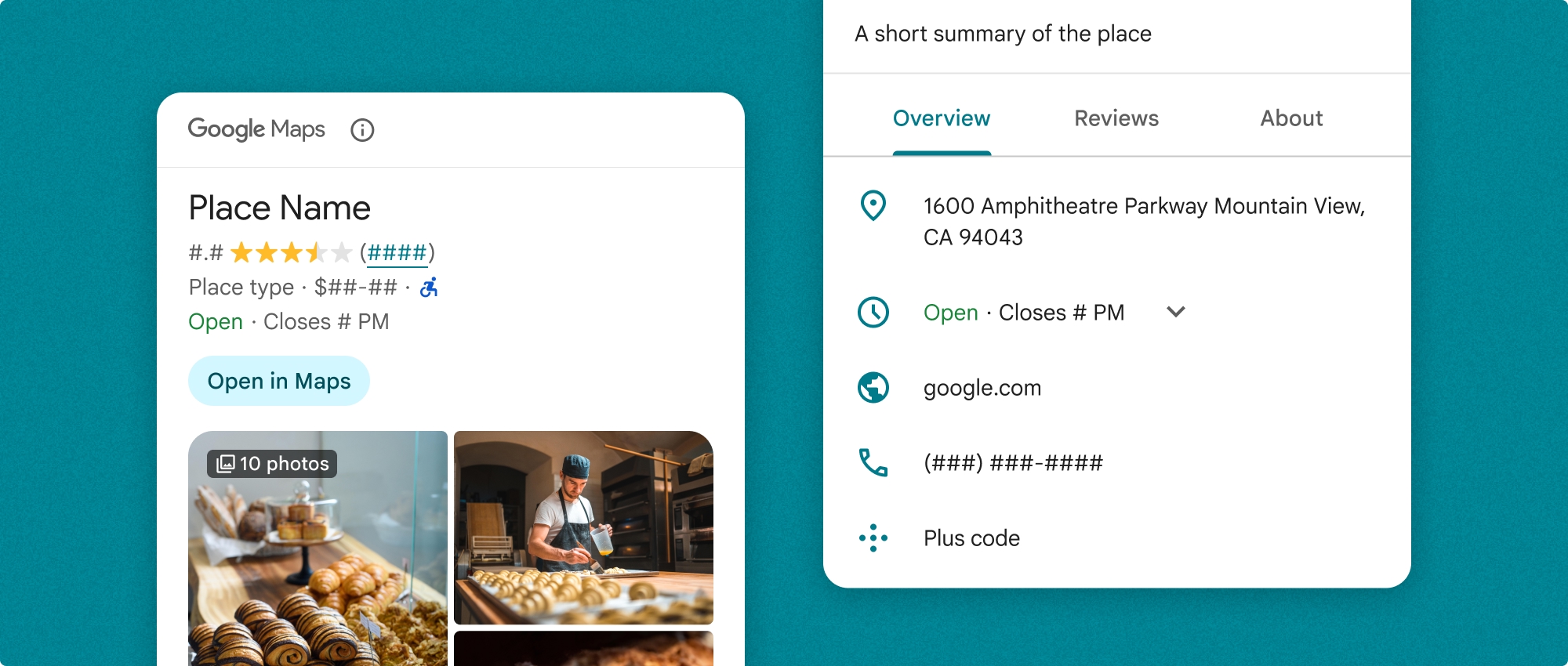
場所の詳細コンポーネントは、単独で使用することも、他の Google Maps Platform API やサービスと組み合わせて使用することもできます。このコンポーネントは、プレイス ID、リソース名、緯度と経度の座標のいずれかを受け取り、レンダリングされた Place Details 情報を返します。
Place Details コンポーネントは完全にテーマ設定可能で、フォント、色、角の丸みをユースケースやビジュアル ブランド ガイドラインに合わせてカスタマイズできます。PlacesMaterialTheme を拡張し、テーマ属性のオーバーライドを提供するテーマを作成することで、場所の詳細の外観をカスタマイズできます。場所に関する詳細情報のどのフィールドを含めるかをカスタマイズすることもできます。そのためには、Content エントリのリストを指定します。各エントリは、場所について表示される情報の 1 つに対応しています。
レイアウト バリエーション
Place Details コンポーネントは、次の 2 つの主要なレイアウト バリエーションをサポートしています。
- コンパクト: 重要な情報をプレビューするためのレイアウト。
- フル: 利用可能なすべての場所の詳細を表示する包括的なレイアウト。
コンパクト レイアウトは、縦向きまたは横向きで表示できます。これにより、コンポーネントをさまざまなデザイン レイアウトや画面サイズに統合できます。完全なレイアウトは縦向きでのみ表示できます。
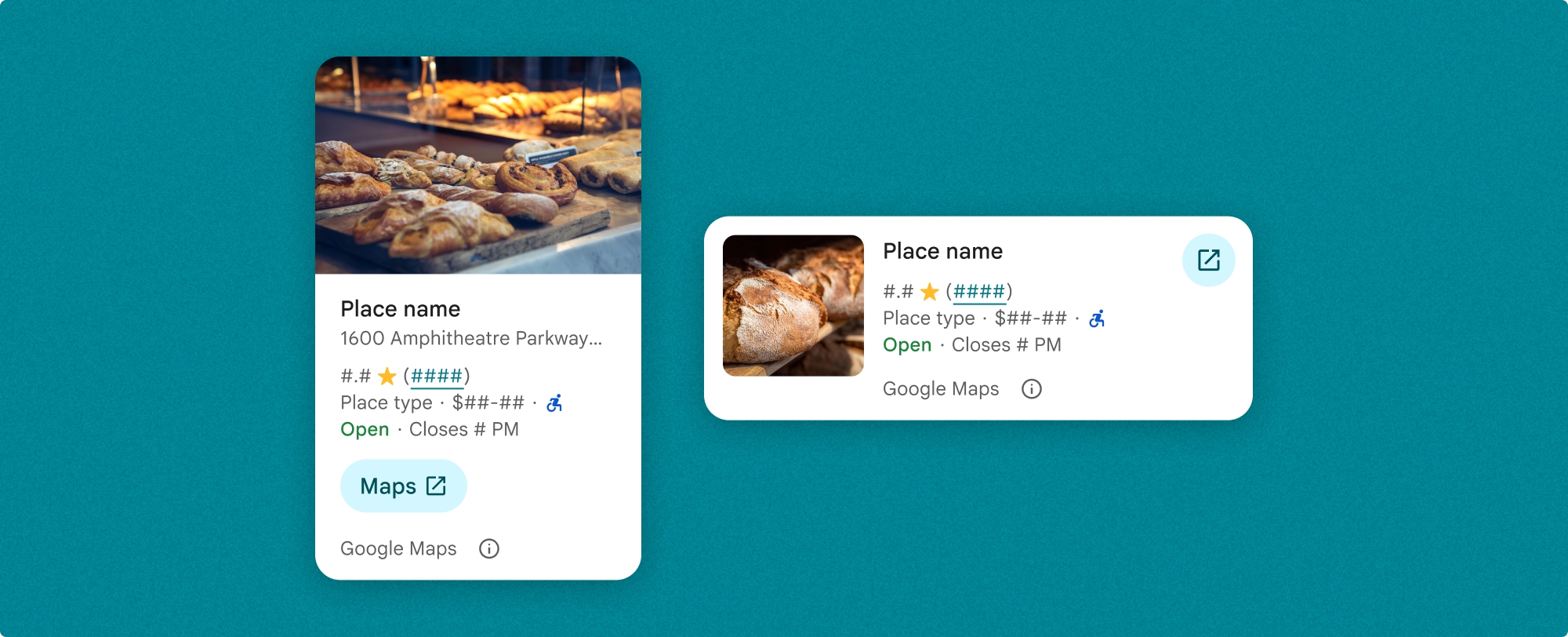
プレイスの詳細コンポーネントを使用すると、コンポーネントに表示されるコンテンツを細かく制御できます。各要素(写真、レビュー、連絡先情報など)は個別に表示または非表示にできるため、コンポーネントの外観と情報密度を正確にカスタマイズできます。
Place Details のコンパクト表示
Place Details コンパクト フラグメント(PlaceDetailsCompactFragment)は、選択した場所の詳細を最小限のスペースでレンダリングします。これは、地図上の場所をハイライト表示する情報ウィンドウ、チャットで位置情報を共有するなどのソーシャル メディア エクスペリエンス、現在地の選択候補、Google マップ上の場所を参照するメディア記事などで役立ちます。
Place Details の全画面表示
Place Details の全画面ビュー(PlaceDetailsFragment)では、プレイスの詳細情報を表示するサーフェスが広くなり、より多くの種類の情報を表示できます。
コンテンツの表示オプション
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.Content または PlaceDetailsFragment.Content の列挙型を使用して、表示するコンテンツを指定できます。
| コンパクト表示 | 全文表示 |
|---|---|
|
|
課金
Place Details UI キットを使用する場合、.loadWithPlaceId()、.loadWithResourceName()、loadWithCoordinates() の各メソッドが呼び出されるたびに課金されます。同じ場所を複数回読み込むと、リクエストごとに課金されます。
複数回課金されないように、Android ライフサイクル メソッドに .loadWithPlaceId() または .loadWithResourceName() を直接追加しないでください。たとえば、onResume() メソッドで .loadWithPlaceId() や .loadWithResourceName() を直接呼び出さないでください。
アプリに場所の詳細を追加する
レイアウトにフラグメントを追加することで、アプリに場所の詳細情報を追加できます。フラグメントをインスタンス化するときに、ニーズに合わせて、アプリの外観に合わせて、プレイスの詳細情報のデザインをカスタマイズできます。カスタマイズの詳細をご覧ください。
Kotlin と Java の両方で、3 つの方法を使用できます。1 つはプレイス ID(loadWithPlaceId())でフラグメントを読み込む方法、1 つはリソース名(loadWithResourceName())でフラグメントを読み込む方法、1 つは緯度/経度座標(loadWithCoordinates())でフラグメントを読み込む方法です。いずれかの方法を選択することも、複数の方法を選択することもできます。
コンパクト ビューのデフォルトの向きは縦向きです。横向きのレイアウトにする場合は、Orientation.HORIZONTAL を指定します。必要に応じて、わかりやすくするために Orientation.VERTICAL を指定することもできます。全画面表示は縦向きでのみ表示できます。
プレイスの詳細コンポーネントの例セクションの例をご覧ください。
外観をカスタマイズする
カスタム スタイル
Place Details コンポーネントの色、タイポグラフィ、間隔、境界線、角をカスタマイズできます。
Places UI キットは、マテリアル デザイン(Google マップ固有の変更がいくつか加えられています)にほぼ基づいた、ビジュアル カスタマイズに対するデザイン システム アプローチを提供します。マテリアル デザインの色とタイポグラフィのリファレンスをご覧ください。デフォルトでは、スタイルは Google マップのビジュアル デザイン言語に準拠しています。
Places UI Kit はデフォルトでダークモードを提供するため、ダークモードとライトモードの両方をカスタマイズする必要がある場合があります。ダークモードをカスタマイズするには、values-night/colors.xml に色のエントリを追加します。
スタイル設定の詳細については、カスタム スタイル設定のセクションをご覧ください。
幅と高さのカスタマイズ
コンパクト ビュー
推奨される幅:
- 縦向き: 180 dp ~ 300 dp。
- 横向き: 180 dp ~ 500 dp。
幅が 160dp 未満の場合、正しく表示されないことがあります。
コンパクト ビューの高さは設定しないことをおすすめします。これにより、ウィンドウ内のコンテンツで高さを設定できるようになり、すべての情報を表示できます。
完全再生数
フルビューの場合、推奨される幅は 250 dp ~ 450 dp です。幅が 250dp 未満の場合、正しく表示されないことがあります。
コンポーネントの高さを設定できます。縦型の Place Details ビューは、割り当てられたスペース内で縦方向にスクロールします。
ベスト プラクティスは、フルビューの高さを設定することです。これにより、ウィンドウ内のコンテンツが適切にスクロールされます。
Place Details コンポーネントの例
コンパクト ビューまたはフルビューを作成する
Kotlin
// We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } }
Java
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( Orientation.HORIZONTAL, Arrays.asList(Content.ADDRESS, Content.TYPE, Content.RATING, Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE_ICON), R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme); fragment.setPlaceLoadListener( new PlaceLoadListener() { @Override public void onSuccess(Place place) { ... } @Override public void onFailure(Exception e) { ... } }); getSupportFragmentManager() .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.fragment_container, fragment) .commitNow(); // Load the fragment with a Place ID. fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId); // Load the fragment with a resource name. fragment.loadWithResourceName(resourceName);
この完全なコードサンプルは、ユーザーのデバイスの構成に基づいてコンパクト ビューの向きをプログラムで決定します。
Kotlin
package com.example.placedetailsuikit import android.Manifest import android.annotation.SuppressLint import android.content.pm.PackageManager import android.content.res.Configuration import android.location.Location import android.os.Bundle import android.util.Log import android.view.View import android.widget.Toast import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge import androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher import androidx.activity.result.contract.ActivityResultContracts import androidx.activity.viewModels import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel import com.example.placedetailsuikit.databinding.ActivityMainBinding import com.google.android.gms.location.FusedLocationProviderClient import com.google.android.gms.location.LocationServices import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PointOfInterest import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.Places import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.Place import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceDetailsCompactFragment import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceLoadListener import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.model.Orientation private const val TAG = "PlacesUiKit" /** * A simple ViewModel to store UI state that needs to survive configuration changes. * In this case, it holds the ID of the selected place. Using a ViewModel is good practice * as it prevents data loss during events like screen rotation, ensuring a * seamless user experience. */ class MainViewModel : ViewModel() { var selectedPlaceId: String? = null } /** * This activity serves as a basic example of integrating the Place Details UI Kit. * It demonstrates the fundamental steps required: * 1. Setting up a Google Map. * 2. Requesting location permissions to center the map. * 3. Handling clicks on Points of Interest (POIs) to get a Place ID. * 4. Using the Place ID to load and display place details in a [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. */ class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPoiClickListener { // ViewBinding provides type-safe access to views defined in the XML layout, // eliminating the need for `findViewById` and preventing null pointer exceptions. private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding private var googleMap: GoogleMap? = null // The FusedLocationProviderClient is the main entry point for interacting with the // fused location provider, which intelligently manages the underlying location technologies. private lateinit var fusedLocationClient: FusedLocationProviderClient // Using registerForActivityResult is the modern, recommended approach for handling // permission requests. It decouples the request from the handling logic, making the // code cleaner and easier to manage compared to the older `onRequestPermissionsResult` callback. private lateinit var requestPermissionLauncher: ActivityResultLauncher<Array<String>> // The `by viewModels()` delegate provides a lazy-initialized ViewModel scoped to this Activity. // This ensures that we get the same ViewModel instance across configuration changes. private val viewModel: MainViewModel by viewModels() override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // The ActivityResultLauncher is initialized here. The lambda defines the callback // that will be executed once the user responds to the permission dialog. requestPermissionLauncher = registerForActivityResult(ActivityResultContracts.RequestMultiplePermissions()) { permissions -> // We check if either fine or coarse location permission was granted. if (permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION] == true || permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION] == true) { Log.d(TAG, "Location permission granted by user.") fetchLastLocation() } else { // If permission is denied, we inform the user and default to a known location. // This ensures the app remains functional even without location access. Log.d(TAG, "Location permission denied by user.") Toast.makeText( this, "Location permission denied. Showing default location.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() moveToSydney() } } // enableEdgeToEdge() allows the app to draw behind the system bars for a more immersive experience. enableEdgeToEdge() binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) setContentView(binding.root) binding.dismissButton.setOnClickListener { dismissPlaceDetails() } // --- Crucial: Initialize Places SDK --- // It's essential to initialize the Places SDK before making any other Places API calls. // This should ideally be done once, for example, in the Application's `onCreate`. val apiKey = BuildConfig.PLACES_API_KEY if (apiKey.isEmpty() || apiKey == "YOUR_API_KEY") { // A valid API key is required for the Places SDK to function. Log.e(TAG, "No api key") Toast.makeText( this, "Add your own API_KEY in local.properties", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() finish() return } // `initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled` is used to opt-in to the new SDK version. Places.initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled(applicationContext, apiKey) fusedLocationClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this) // ------------------------------------ // The SupportMapFragment is the container for the map. `getMapAsync` allows us to // work with the GoogleMap object via a callback once it's fully initialized. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map_fragment) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) // This block handles restoration after a configuration change (e.g., screen rotation). // If a place was selected before the rotation, its ID is stored in the ViewModel. // We use this ID to immediately show the details fragment again. if (viewModel.selectedPlaceId != null) { viewModel.selectedPlaceId?.let { placeId -> Log.d(TAG, "Restoring PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } } } /** * This callback is triggered when the GoogleMap object is ready to be used. * All map setup logic should be placed here. */ override fun onMapReady(map: GoogleMap) { Log.d(TAG, "Map is ready") googleMap = map // Setting the OnPoiClickListener allows us to capture user taps on points of interest. googleMap?.setOnPoiClickListener(this) // After the map is ready, we determine the initial camera position based on location permissions. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fetchLastLocation() } else { requestLocationPermissions() } } /** * A helper function to centralize the check for location permissions. */ private fun isLocationPermissionGranted(): Boolean { return ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED || ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED } /** * This function triggers the permission request flow. The result is handled by the * ActivityResultLauncher defined in `onCreate`. */ private fun requestLocationPermissions() { Log.d(TAG, "Requesting location permissions.") requestPermissionLauncher.launch( arrayOf( Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) ) } /** * Fetches the device's last known location. This is a fast and battery-efficient way * to get a location fix. It should only be called after verifying permissions. */ @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun fetchLastLocation() { // Double-checking permissions here is a good practice, although the call sites are already guarded. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fusedLocationClient.lastLocation .addOnSuccessListener { location: Location? -> if (location != null) { val userLocation = LatLng(location.latitude, location.longitude) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(userLocation, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to user's last known location.") } else { // `lastLocation` can be null if the location has never been recorded. // In this case, we fall back to a default location. Log.d(TAG, "Last known location is null. Falling back to Sydney.") moveToSydney() } } .addOnFailureListener { // This listener handles errors in the location fetching process. Log.e(TAG, "Failed to get location.", it) moveToSydney() } } } /** * Moves the map camera to a default, hardcoded location (Sydney). * This serves as a reliable fallback. */ private fun moveToSydney() { val sydney = LatLng(-33.8688, 151.2093) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(sydney, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to Sydney") } /** * This is the callback for the `OnPoiClickListener`. It's triggered when a user * taps a POI on the map. */ override fun onPoiClick(poi: PointOfInterest) { val placeId = poi.placeId Log.d(TAG, "Place ID: $placeId") // We save the selected place ID to the ViewModel. This is critical for surviving // configuration changes. If the user rotates the screen now, the `onCreate` // method will be able to restore the place details view. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = placeId showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } /** * This function is the core of the integration. It creates, configures, and displays * the [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. * @param placeId The unique identifier for the place to be displayed. */ private fun showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId: String) { Log.d(TAG, "Showing PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") // We manage the visibility of UI elements to provide feedback to the user. // The wrapper is shown, and a loading indicator is displayed while the data is fetched. binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.GONE binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.VISIBLE // The Place Details widget can be displayed vertically or horizontally. // We dynamically choose the orientation based on the device's current configuration. val orientation = if (resources.configuration.orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE) { Orientation.HORIZONTAL } else { Orientation.VERTICAL } // We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } } /** * Hides the place details view and clears the selected place ID from the ViewModel. */ private fun dismissPlaceDetails() { binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.GONE // Clearing the ID in the ViewModel is important so that if the user rotates the // screen after dismissing, the details view doesn't reappear. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = null } override fun onDestroy() { super.onDestroy() // It's a good practice to nullify references to objects that have a lifecycle // tied to the activity, like the GoogleMap object, to prevent potential memory leaks. googleMap = null } }
テーマを作成する
フラグメントをインスタンス化するときに、デフォルトのスタイル属性をオーバーライドするテーマを指定できます。オーバーライドされていないテーマ属性は、デフォルト スタイルを使用します。ダークモードをサポートする場合は、values-night/colors.xml に色のエントリを追加できます。
Places UI Kit はデフォルトでダークモードを提供するため、ダークモードとライトモードの両方をカスタマイズする必要がある場合があります。ダークモードをカスタマイズするには、values-night/colors.xml に色のエントリを追加します。
<style name="CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme" parent="PlacesMaterialTheme"> <item name="placesColorPrimary">@color/app_primary_color</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurface">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurfaceVariant">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesTextAppearanceBodySmall">@style/app_text_appearence_small</item> <item name="placesCornerRadius">20dp</item> </style>
標準コンテンツを使用する
このサンプルでは、標準コンテンツを使用します。
val fragmentStandardContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.STANDARD_CONTENT,
orientation,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)特定のコンテンツをカスタマイズする
このサンプルでは、コンパクト ビューの住所、アクセス可能な入り口、メディア Content オプションのみを選択し、CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme でレンダリングします。
val placeDetailsFragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
listOf(
Content.ADDRESS,
Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE,
Content.MEDIA
),
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)すべてのコンテンツを使用する
このサンプルでは、コンパクト ビューのすべての Content オプションを使用します。
val fragmentAllContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)
