PLACES_COUNT 函式會根據指定的搜尋區域和搜尋篩選器,傳回地點的單一計數值。您必須為 PLACES_COUNT 函式指定搜尋區域,並可選擇指定其他篩選參數,例如地點類型、營業狀態、價格等級等。
由於 PLACES_COUNT 函式會傳回單一值,請使用 SELECT 子句呼叫該函式。
輸入參數:
傳回:
- 以
INT64形式表示的單一count值。
- 以
範例:計算搜尋半徑內的商家數量
最簡單的 PLACES_COUNT 函式呼叫會傳回地理區域中所有地點的單一計數。在本例中,您會傳回帝國大廈方圓 1000 公尺內所有營業場所的數量。
這個範例使用 BigQuery ST_GEOGPOINT 函式,從點傳回 GEOGRAPHY 值。
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000 -- Radius in meters ) ) as count;
回應包含單一計數:
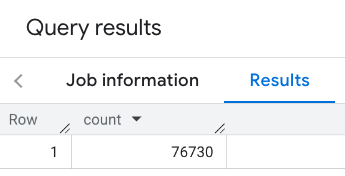
更典型的呼叫會對搜尋區域套用篩選器。下一個範例會使用篩選器,將搜尋範圍限制為只傳回下列項目的計數:
- 類型為
restaurant且評分至少為 3 的地點 - 價格等級為平價或中等
- 目前可正常運作
- 可帶狗入內
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 3, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
篩除的回覆:

請注意,地點資料集查詢會強制執行 5 的最低計數門檻。地點計數函式的優點之一是可傳回任何計數,包括 0。舉例來說,下列呼叫會傳回計數 1:
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 500, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 4.0, 'free_parking_lot', TRUE, 'good_for_watching_sports', TRUE ) ) as count;
示例:使用多邊形計算餐廳數量
您可以使用多邊形指定搜尋區域。使用多邊形時,多邊形的點必須定義封閉迴路,也就是多邊形的第一個點與最後一個點相同。
這個範例使用 BigQuery ST_GEOGFROMTEXT 函式,從多邊形傳回 GEOGRAPHY 值。
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('''POLYGON((-73.985708 40.75773,-73.993324 40.750298, -73.9857 40.7484,-73.9785 40.7575, -73.985708 40.75773))'''); -- NYC viewport SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- viewport 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
可視區域的回應:

示例:使用線條計算餐廳數量
在下一個範例中,您會使用一條由相連點組成的線定義搜尋區域,並以該線為中心,在 100 公尺的半徑範圍內搜尋。這條線類似於 Routes API 計算出的路線。路線可能適用於車輛、自行車或行人:
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('LINESTRING(-73.98903537033028 40.73655649223003,-73.93580216278471 40.80955538843361)'); -- NYC line SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- line 'geography_radius', 100, -- Radius around line 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
該行的回應:
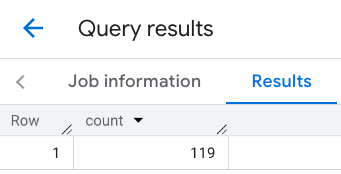
範例:合併多個呼叫的結果
您可以合併多次呼叫 PLACES_COUNT 函式的結果。
舉例來說,您想在特定區域內,取得下列價格範圍的餐廳數量:
PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_MODERATEPRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"
在這個範例中,您會建立迴圈,針對每個價格層級呼叫 PLACES_COUNT 函式,並將每次呼叫的結果插入暫時表格。接著查詢臨時資料表,即可顯示結果:
-- Create a temp table to hold the results. CREATE TEMP TABLE results (type STRING, count INT64); -- Create a loop that calls PLACES_COUNT for each price level. FOR types IN (SELECT type FROM UNNEST(["PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE", "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"]) as type) DO INSERT INTO results VALUES (types.type, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', [types.type] ))); END FOR; -- Query the table of results. SELECT * FROM results;
合併回覆:
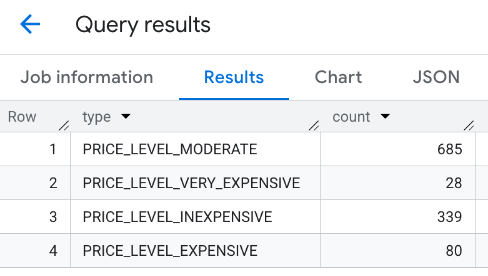
另一種做法是使用 UNION ALL 指令,合併多個 SELECT 陳述式的結果。下列範例顯示的結果與上一個範例相同:
SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count
