Mối quan hệ của cha mẹ-con
Sử dụng bộ sưu tập để sắp xếp ngăn nắp các trang
Lưu và phân loại nội dung dựa trên lựa chọn ưu tiên của bạn.
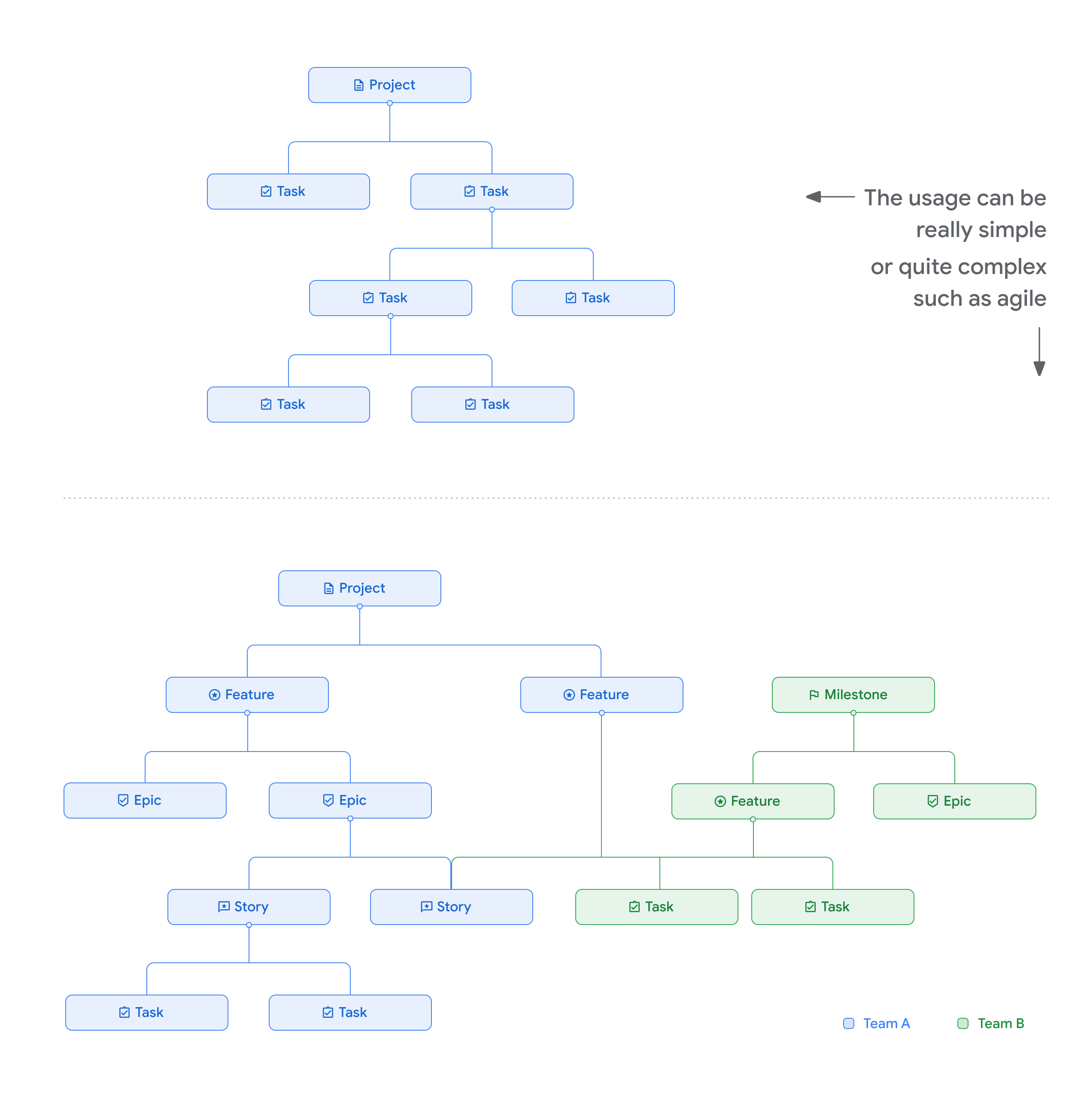
Công cụ theo dõi lỗi của Google hỗ trợ mối quan hệ mẹ con. Mối quan hệ mẹ con thường được dùng để thể hiện bảng chi tiết công việc trong một nỗ lực nhất định. Một phần tử mẹ có thể có nhiều phần tử con và một phần tử con có thể có nhiều phần tử mẹ.
Mối quan hệ mẹ con có các đặc điểm sau:
| Đặc điểm |
Thông tin chi tiết |
| Mối quan hệ |
N:N |
| Sắp xếp |
Hỗ trợ thứ tự của phần tử con trong phần tử mẹ. |
| Phát hiện chu kỳ |
Hệ thống ngăn chặn các phần phụ thuộc tuần hoàn. |
| Số mục con trực tiếp tối đa |
500 |
| Tối đa hoá thành phần cấp trên |
1000 |
Ví dụ
Hình ảnh sau đây cho thấy một số mối quan hệ mẹ con mẫu.
Mối quan hệ mẹ con và chặn
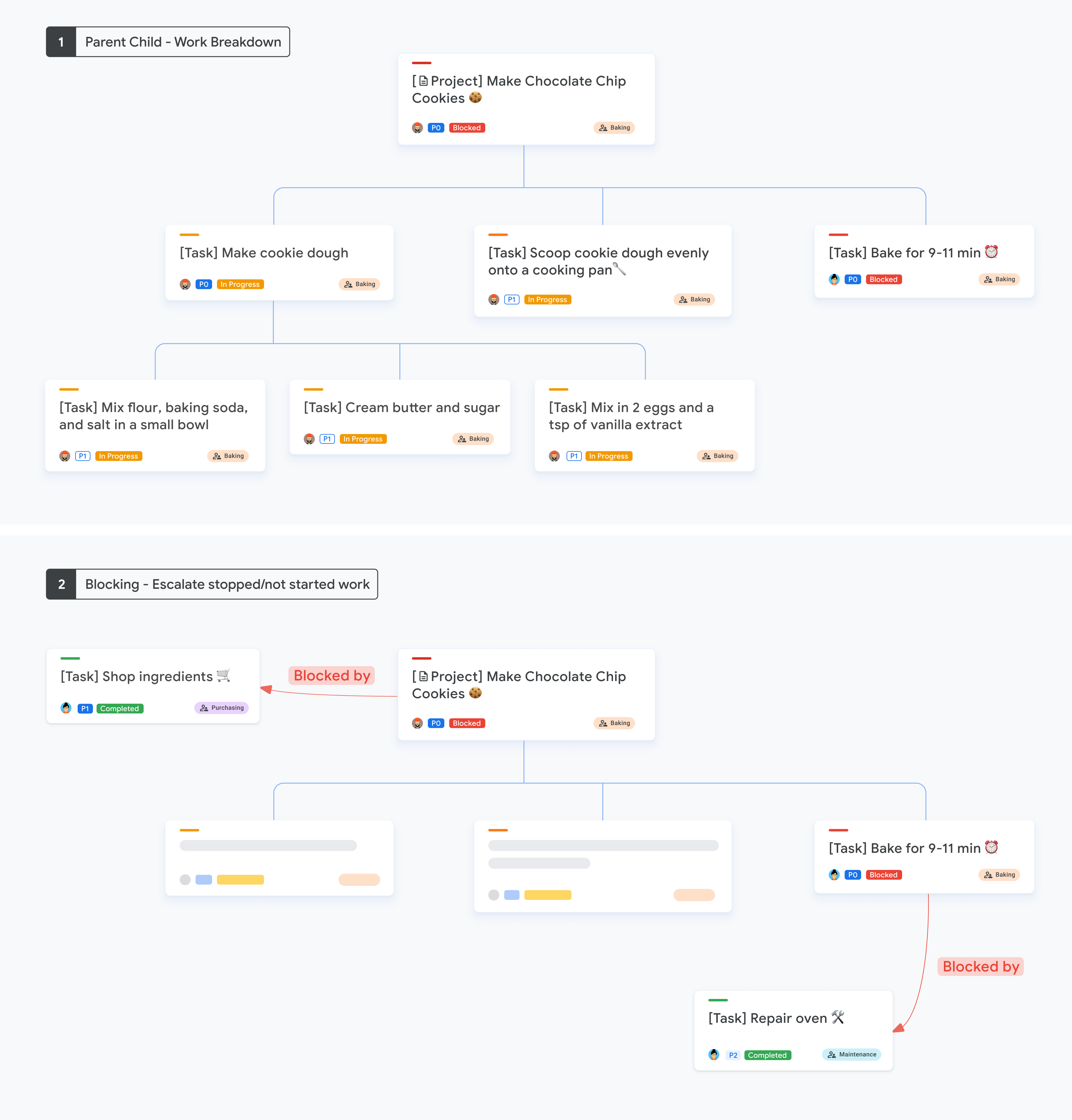
Các mối quan hệ Chặn và Bị chặn hiện có vẫn được hỗ trợ khi bạn sử dụng mối quan hệ mẹ con. Khi bạn kết hợp mối quan hệ mẹ con với tính năng chặn:
- Sử dụng mối quan hệ mẹ con để chia nhỏ công việc thành các đơn vị nhỏ hơn.
- Sử dụng chặn và bị chặn bởi khi thời gian và trình tự là quan trọng, đồng thời bạn muốn cung cấp các chỉ báo rõ ràng trong giao diện người dùng để chuyển công việc đã dừng hoặc chưa bắt đầu lên cấp trên.
Hình ảnh sau đây cho thấy ví dụ về bảng chi tiết công việc chặn và mẹ con.
Mọi quyền được bảo lưu. Java là một nhãn hiệu đã đăng ký của Oracle và/hoặc chi nhánh của Oracle.
Cập nhật lần gần đây nhất: 2025-07-25 UTC.
[null,null,["Cập nhật lần gần đây nhất: 2025-07-25 UTC."],[[["\u003cp\u003eGoogle Issue Tracker enables the creation of parent-child relationships to represent the hierarchical breakdown of work within a project.\u003c/p\u003e\n"],["\u003cp\u003eIssues can have multiple parents and children, but the system prevents circular dependencies and limits the number of direct children to 500 and total ancestors to 1000.\u003c/p\u003e\n"],["\u003cp\u003eWhile parent-child relationships are ideal for structuring tasks, "Blocking" and "Blocked by" relationships should be used to indicate critical timing and sequencing dependencies.\u003c/p\u003e\n"],["\u003cp\u003eUsers are encouraged to leverage both relationship types to manage work effectively, using parent-child for work breakdown and blocking for highlighting time-sensitive dependencies.\u003c/p\u003e\n"]]],[],null,["# Parent-Child Relationships\n\nGoogle Issue Tracker supports parent-child relationships. A parent-child\nrelationship is typically used to represent the breakdown of work within a given\neffort. A parent can have multiple children, and a child can have multiple\nparents.\n\nThe parent-child relationship has the following characteristics:\n\n| Characteristic | Details |\n|-------------------------|----------------------------------------------------|\n| **Relationship** | N:N |\n| **Ordering** | Ordering of children within a parent is supported. |\n| **Cycle detection** | Cyclic dependencies are prevented by the system. |\n| **Max direct children** | 500 |\n| **Max ancestors** | 1000 |\n\nExamples\n--------\n\nThe following graphic shows some sample parent-child relationships.\n\nParent-child relationships and blocking\n---------------------------------------\n\nThe existing **Blocking** and **Blocked by** relationships are still supported\nwhen you use parent-child relationships. When you're combining parent-child\nrelationships with blocking:\n\n- Use **parent-child** relationships to break down work into smaller units.\n- Use **blocking** and **blocked by** when timing and sequence are critical, and you want to provide clear indications in the UI to escalate stopped or not started work.\n\nThe following graphic shows examples of parent-child and blocking work\nbreakdowns."]]
![]()
![]()
