本页介绍了如何在 Google 问题跟踪器中使用一个问题屏蔽另一个问题。
如果一个问题会阻止另一个问题,则表示应先解决第一个问题,然后再解决第二个问题。屏蔽功能仅用于跟踪目的。问题跟踪器本身不会强制执行屏蔽操作。即使存在阻止问题解决的待解决问题,您也可以将问题标记为已解决。
屏蔽功能是相互的。如果您将一个问题设置为屏蔽另一个问题,第一个问题会显示在第二个问题的屏蔽对象列表中,而第二个问题会显示在第一个问题的屏蔽列表中。
您必须对包含这两个问题的组件拥有修改问题 权限,才能设置阻塞关系。
已屏蔽的问题
屏蔽问题表示在另一个问题得到解决之前,不应解决该问题。首先需要解决的是屏蔽问题,其次是被屏蔽问题。一个问题可以同时阻止或被多个问题阻止。
屏蔽问题不会对问题施加任何实际限制。也就是说,即使未对导致问题的代码进行任何更改,您仍然可以更新或关闭导致问题的代码。因此,屏蔽功能应被视为跟踪或通知系统。如何回应被屏蔽的问题的决定将交由负责解决此问题的个人和团队。
界面位置
系统会在屏蔽和依赖项标签页中跟踪屏蔽情况。例如,如果您前往问题 A 的页面并将其设置为屏蔽问题 B,则问题 A 的页面会在屏蔽标签页中列出问题 B,而问题 B 的页面会在依赖项标签页的屏蔽程序部分下列出问题 A。
屏蔽和屏蔽程序部分的标题会显示每个部分包含的问题数量。/ 前面的数字是未解决问题的数量,/ 后面的数字是问题总数。例如,如果阻塞标签页显示 2/5,则表示有 5 个问题阻塞了当前问题,但其中只有 2 个问题尚未解决。
点击依赖项或屏蔽标签页,即可显示相关问题的表格。每个问题条目都包含多个部分,包括状态、问题标题和问题 ID。
点击相应行即可前往相应问题。
将某个问题设为被另一个问题屏蔽
若要将某个问题设为因其他问题而被阻塞,请执行以下操作:
前往要屏蔽的问题。
在页面顶部附近的标签页中,点击依赖项。
点击标题为屏蔽程序的部分附近的添加屏蔽程序。
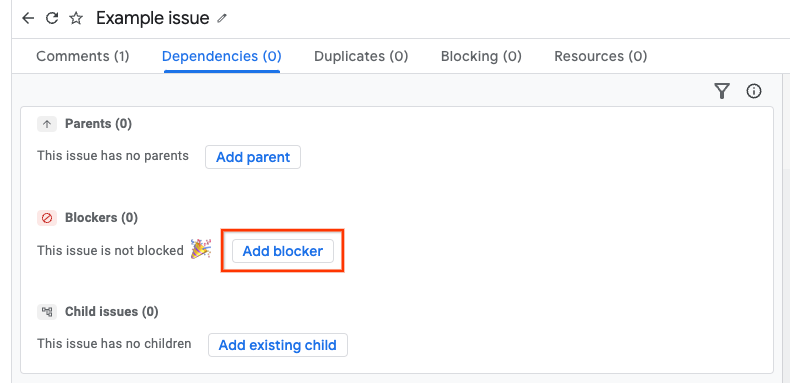
您可以通过以下两种方式输入屏蔽问题。
- 方法 1:按问题进行文本搜索。
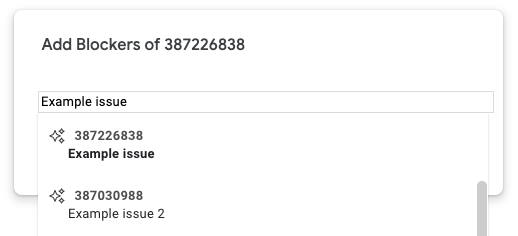
- 方式 2:输入问题 ID。您可以一次添加多个 ID(以英文逗号分隔)。
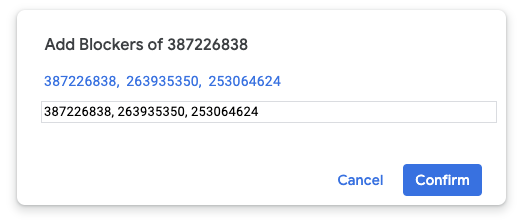
点击确认。
如果成功,屏蔽问题将添加到屏蔽程序列表中。
设置一个问题来屏蔽另一个问题
如需将某个问题设为阻塞另一个问题,请执行以下操作:
前往将被屏蔽的问题。
在页面顶部附近的标签页中,点击屏蔽。
点击添加
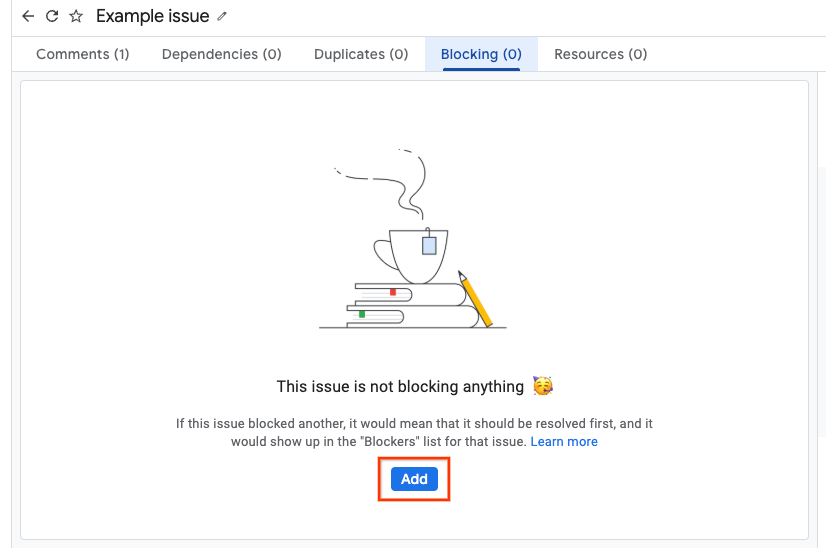
您可以通过以下两种方式输入被屏蔽的问题。
- 方法 1:按问题进行文本搜索。
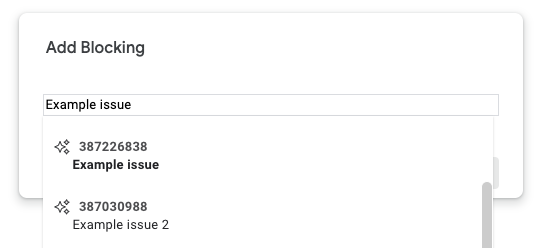
- 方式 2:输入问题 ID。您可以一次添加多个 ID(以英文逗号分隔)。
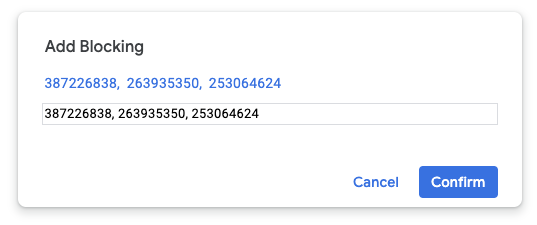
点击确认。
如果成功,系统会将被屏蔽的问题添加到屏蔽列表。