इस सेक्शन में मौजूद दस्तावेज़ में, Google Maps की मांग पर यात्रा की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करके यात्राएं बनाने और उन्हें मैनेज करने का तरीका बताया गया है. यह माना जाता है कि आपको इनके बारे में जानकारी है:
- Fleet Engine: आपको Fleet Engine को लागू करने से जुड़ी जानकारी, अनुरोध करने के तरीके, और सुरक्षा के बारे में पता होना चाहिए. इसके लिए, Fleet Engine सेवा क्या है? लेख पढ़ें. साथ ही, Fleet Engine सेट अप करना लेख में सुरक्षा से जुड़े विषय पढ़ें.
- मांग पर उपलब्ध सेवाओं के लिए, वाहन के बारे में बुनियादी जानकारी. वाहनों के बारे में जानकारी देखें.
- अनुरोध पर उपलब्ध सेवाओं के लिए, यात्रा की बुनियादी जानकारी. मांग के हिसाब से यात्राएं देखें.
इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला TripService, gRPC और REST के लिए उपलब्ध है.
आसानी से समझने के लिए, फ़ील्ड रेफ़रंस gRPC के नियमों के मुताबिक होते हैं.
मांग पर उपलब्ध होने वाली सेवाओं के लिए Fleet Engine में, ट्रिप एक तरह की यात्रा होती है. यह आपके उपभोक्ताओं के खाने की डिलीवरी या यात्रा के अनुरोध को पूरा करने के लिए मॉडल तैयार करती है. यात्रा का एक स्टेटस होता है. यात्रा के दौरान, आपको Fleet Engine को इस स्टेटस के बारे में बताना होता है. जैसे, NEW, ENROUTE_TO_PICKUP वगैरह. यात्रा की स्थिति, वाहन को असाइन किए गए जियो-लोकेटेड वेपॉइंट से मेल खाती है. साथ ही, Fleet Engine, यात्रा के हर अपडेट के साथ वाहन के इन वेपॉइंट में बदलाव करता है. यात्राओं और वाहनों के बीच के संबंध के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, Fleet Engine essentials में मांग के हिसाब से यात्राएं देखें.
यात्रा की अवधि
Fleet Engine में हर यात्रा को ट्रैक करने के लिए, आपको सबसे पहले Trip इकाई बनानी होगी. रेफ़रंस के लिए, gRPC या REST देखें.
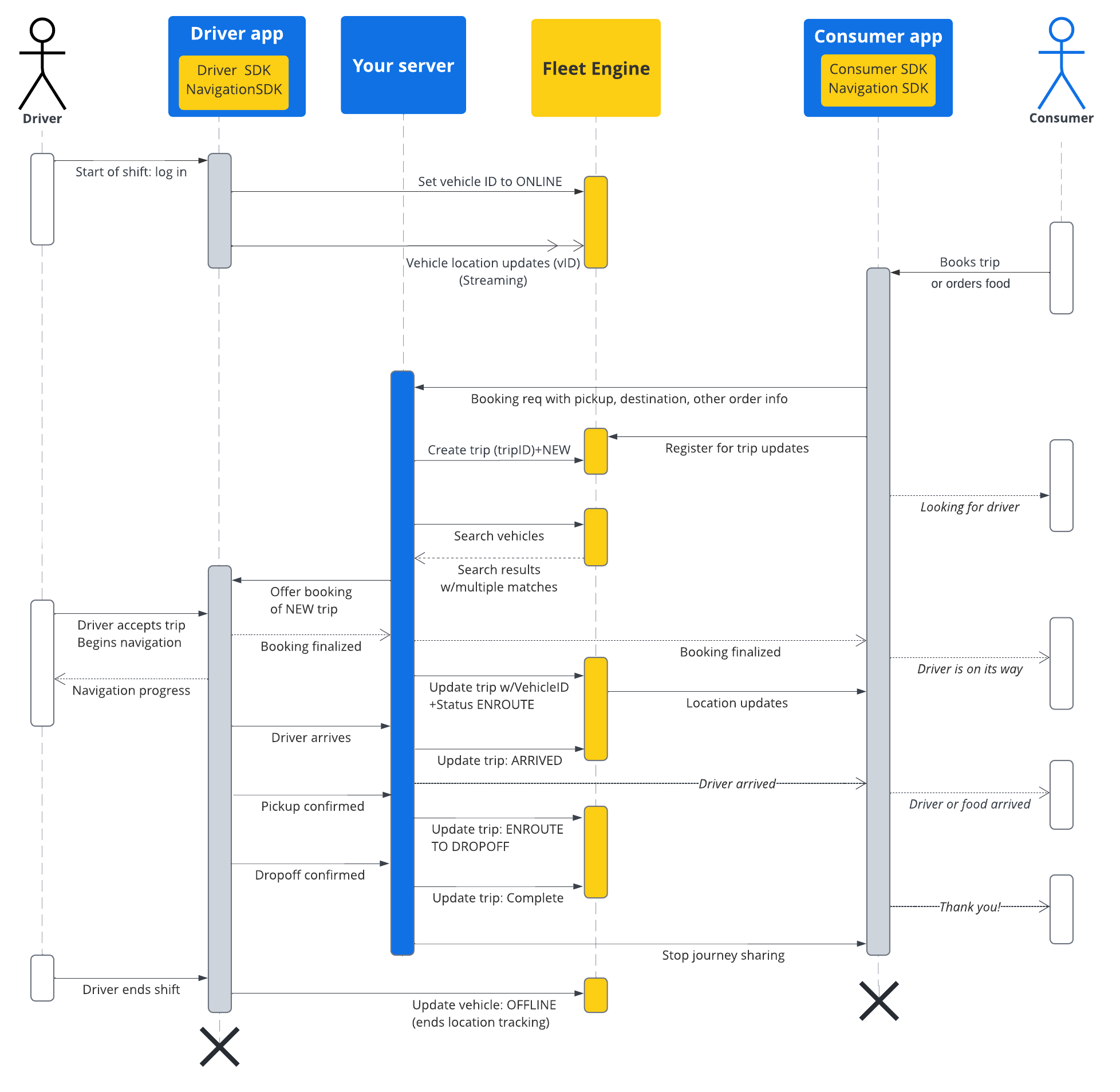
नीचे दी गई टेबल में, आपके सिस्टम में बनाई गई यात्रा के एंड-टू-एंड फ़्लो का उदाहरण दिया गया है. साथ ही, Fleet Engine में यात्रा की लाइफ़साइकल स्टेज के बारे में बताया गया है. इसमें यह माना जाता है कि आपने Fleet Engine सेट अप कर लिया है और आपके पास यात्रा के लिए कोई वाहन है. साथ ही, ड्राइवर ऐप्लिकेशन में जगह की जानकारी के अपडेट चालू हैं. Driver SDK: मांग पर की जाने वाली यात्राएं देखें.
| 1 | बुकिंग का अनुरोध पाना. | Fleet Engine ट्रिप शुरू होने से पहले, आपका बुकिंग सिस्टम सबसे पहले आपके ऐप्लिकेशन या किसी अन्य बुकिंग सिस्टम के ज़रिए, किसी उपभोक्ता से राइड या डिलीवरी का अनुरोध पाता है. इसके बाद, आपका सिस्टम CreateTrip का इस्तेमाल करके ट्रिप की इकाई बनाता है. इसमें पिकअप की जगह जैसी ज़रूरी जानकारी शामिल होती है.
इसके अलावा, इस समय अन्य फ़ील्ड भी सेट किए जा सकते हैं. जैसे, यात्रियों की संख्या और ड्रॉपऑफ़ की जगह. इसके अलावा, वाहन असाइन होने तक इंतज़ार किया जा सकता है. एक डेस्टिनेशन वाली यात्रा बनाना लेख पढ़ें. |
| 2 | वाहन असाइन करें. | आपके पास दो विकल्प हैं. पहला, अपने सिस्टम में सीधे तौर पर यात्राओं के लिए वाहन असाइन करें और Fleet Engine को असाइनमेंट की जानकारी दें. दूसरा, वाहन खोजें सेवा का इस्तेमाल करके वाहन खोजें. इसके लिए, यात्रा और वाहन, दोनों की एट्रिब्यूट के हिसाब से फ़िल्टर करें, ताकि यात्रा पूरी करने के लिए सबसे सही वाहन मिल सके. खोज के दायरे में मौजूद कोई भी वाहन, Driver SDK से मिले जगह की जानकारी के अपडेट के ज़रिए, अपनी दूरी की जानकारी देता है. जब |
| 3 | यात्रा की जानकारी अपडेट करें. | जब ड्राइवर यात्रा का अनुरोध स्वीकार कर लेता है और पिकअप की जगह पर जाने के लिए नेविगेशन शुरू कर देता है, तब आपका सिस्टम यात्रा के स्टेटस को NEW से ENROUTE_TO_PICKUP में बदल देता है. आपको यात्रा के दौरान, वाहन की जगह की जानकारी को लगातार पोल करना होगा. इसके लिए, ऐप्लिकेशन को सीधे तौर पर अपने बैकएंड से कनेक्ट करें या Fleet Engine को पोल करें. Fleet Engine को Driver SDK से, वाहन की जगह की जानकारी के अपडेट लगातार मिलते रहते हैं. इसके बाद, आपका सिस्टम हर यात्रा के माइलस्टोन की जानकारी Fleet Engine को भेजता है. इसके बाद, Fleet Engine वाहन के वेपॉइंट की सूची को अपडेट करता है.
|
| 4 | उपयोगकर्ता के साथ यात्रा की जानकारी शेयर करें. | Fleet Engine, यात्रा की जानकारी और वाहन की जगह की जानकारी को Consumer SDK के लिए उपलब्ध कराता है. Consumer SDK, यात्रा के अपडेट पाने के लिए लिसनर का इस्तेमाल करता है और उन्हें खरीदार के ऐप्लिकेशन में दिखाता है. Fleet Engine, ईटीए, बची हुई दूरी, रास्ते, और वाहन के बचे हुए वेपॉइंट को अपने-आप अपडेट करता है. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, मांग पर उपलब्ध यात्राओं के लिए यात्राएं शेयर करना लेख पढ़ें. |
| 5 | पूरी यात्रा. | जब वाहन यात्रा के डेस्टिनेशन वेपॉइंट पर पहुंच जाता है और आपका ड्राइवर यात्रा पूरी होने की जानकारी देता है, तो आपका सिस्टम Fleet Engine में TripStatus को COMPLETE पर सेट कर देता है. ध्यान रखें कि वाहनों की तरह, यात्रा की इकाइयां भी Fleet Engine में सात दिनों तक सक्रिय रहती हैं. भले ही, उनकी स्थिति कुछ भी हो. इसके बाद, उन्हें हटा दिया जाता है. |
यात्रा के क्रम का फ़्लो
इस डायग्राम में, इस फ़्लो के बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी दी गई है.