Una vez que hayas compilado la entrega de webhook, impleméntala en producción y conéctala. a tu Action. En los siguientes pasos, se muestra cómo configurar tu entorno a fin de implementarlos en Cloud Functions para Firebase para el hosting de producción. Sin embargo, puedes elegir cualquier plataforma de hosting web que admita solicitudes HTTPS y para alojar tu entrega.
Si ya implementaste tu webhook en una plataforma de hosting web, puedes hacer lo siguiente: ve directamente a Conecta el webhook a tu Acción. Ten en cuenta que la última los pasos del proceso que se indican a continuación difieren en función de si usas Dialogflow o SDK de Actions.
Realiza la implementación en Cloud Functions para Firebase
- Descarga y, luego, instala Node.js.
Configura y, luego, inicializa Firebase CLI. Si el siguiente comando falla con un error
EACCES, es posible que debas cambiar los permisos de npm.npm install -g firebase-toolsAutentica la herramienta de Firebase con tu Cuenta de Google:
firebase loginNavega al directorio de tu proyecto de acción y, luego, inicializa Firebase. Serás que selecciones las funciones de Firebase CLI que quieres configurar para tu Proyecto de acciones. Elige
Functionsy otras funciones que quieras usar. como Firestore, luego presiona Intro para confirmar y continuar:cd <cloud_function_dir> firebase initSelecciona la herramienta de Firebase con tu proyecto de acciones para asociarla con las teclas de flecha para navegar por la lista de proyectos:
Después de elegir el proyecto, la herramienta de Firebase inicia la configuración de Functions. y te pregunta qué idioma quieres usar. Selecciona con las teclas de flecha y presiona Intro para continuar.
=== Functions Setup
A functions directory will be created in your project with a Node.js package pre-configured. Functions can be deployed with firebase deploy. ? What language would you like to use to write Cloud Functions? (Use arrow keys) > JavaScript TypeScriptElige si deseas usar ESLint para detectar posibles errores y aplicar estilo Escribe
YoN:? Do you want to use ESLint to catch probable bugs and enforce style? (Y/n)
Para obtener las dependencias del proyecto, escribe
Yen el mensaje:? Do you want to install dependencies with npm now? (Y/n)
Cuando finalice la configuración, verás un resultado similar al siguiente:
✔ Firebase initialization complete!
Instala la dependencia actions-on-google:
cd <cloud_function_dir>/functions npm install actions-on-googleObtén las dependencias de entrega y, luego, implementa la función de entrega:
npm install firebase deploy --only functionsLa implementación tarda unos minutos. Cuando termines, verás el resultado similares a los siguientes. Necesitarás la URL de la función para ingresar Dialogflow
✔ Deploy complete!
Project Console: https://console.firebase.google.com/project/exampleproject-123/overview Function URL (cloudFunctionName): https://us-central1-exampleproject-123.cloudfunctions.net/cloudFunctionName
Conecta el webhook a tu acción
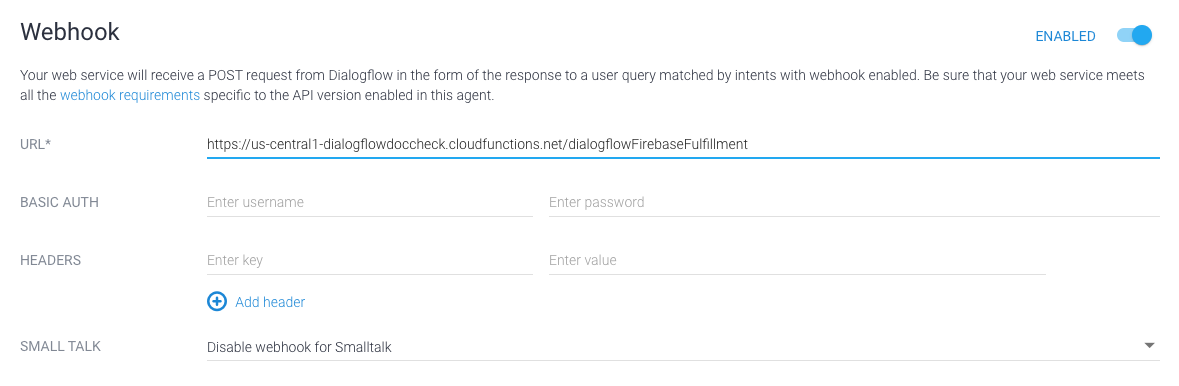
Si usas Dialogflow, haz lo siguiente: Consola de Dialogflow, ve a Fulfillment, cambia el botón Webhook a HABILITADO y reemplaza el la URL en el campo URL con la URL de función.
Si usas el SDK de Actions, crea un objeto.
dentro del objeto conversations para declarar tu entrega en tu acción
paquete:
{
"actions": [
{
"description": "Default Welcome Intent",
"name": "MAIN",
"fulfillment": {
"conversationName": "myFulfillmentFunction"
},
"intent": {
"name": "actions.intent.MAIN",
"trigger": {
"queryPatterns": [
"talk to myFulfillmentFunction"
]
}
}
}
],
"conversations": {
"myFulfillmentFunction": {
"name": "myFulfillmentFunction",
"url": "https://us-central1-myprojectname-ab123.cloudfunctions.net/cloudFunctionName"
}
},
"locale": "en"
}