يقدّم هذا الدليل نظرة عامة على مفاهيم "عروض الأسعار في الوقت الفعلي" (RTB) اللازمة لكتابة تطبيقات عروض الأسعار التي يمكنها المشاركة في ميزة "عروض الأسعار في الوقت الفعلي" ضمن برنامج "الشراة المعتمَدون".
الأساسيات
يمكن لتطبيق مقدّم العروض التواصل مع Google باستخدام أحد بروتوكولات عروض الأسعار في الوقت الفعلي المتوافقة. يقدّم طلب عرض السعر الذي يتم إرساله إلى أحد التطبيقات سياقًا حول فرصة إعلان واحدة على الأقل، وذلك لكي يتمكّن مقدّم عرض السعر من تحديد التصميم الأمثل ومبلغ عرض السعر (إن وُجد) لكل مرّة ظهور. يمكن مقدّم العروض الردّ بعرض أسعار لوضع عرض واحد على الأقل وتحديد تصميم الإعلان الذي سيتم عرضه في فرص الإعلان المُرسَلة في الطلب.
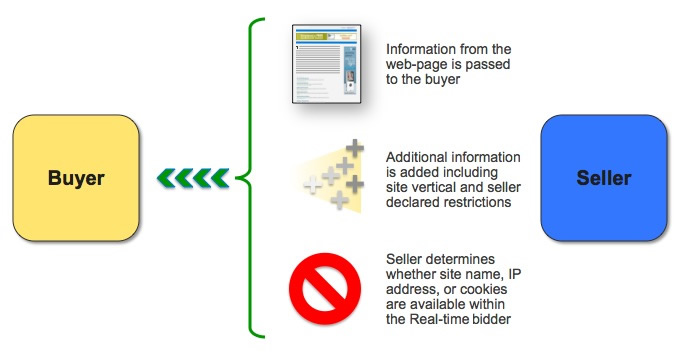
في ما يلي أحد السيناريوهات المحتملة للتفاعل بين تطبيق مقدّم عروض الأسعار و"المشترون المعتمَدون":
- ترسل Google إلى تطبيق مقدّم عروض الأسعار طلب عرض سعر يصف مرّة ظهور يتم المزايدة عليها. تم ضبط حساب مقدّم العروض لاستخدام OpenRTB بتنسيق Protobuf، وبالتالي يصل الطلب كسلسلة
BidRequestكما هو موضّح في openrtb.proto. لمعرفة كيف يجب أن يفسّر تطبيقك طلب عروض الأسعار، راجِع معالجة الطلب. -
يحلّل تطبيق مقدّم عروض الأسعار الطلب ويطبّق منطق عروض الأسعار الخاص به لإنشاء
BidResponseيتضمّن عرض سعر وتصميم إعلان لفرصة عرض الإعلان. بعد ذلك، يحوّل التطبيق استجابة عرض السعر إلى سلسلة ويرسلها إلى Google. للتعرّف على كيفية إنشاء تطبيقك لردّ على عرض سعر وإرجاعه، راجِع إنشاء الردّ. -
يتم تلقّي ردّ عرض السعر ويدخل عرضه المزاد المفتوح، حيث يفوز بمرّة الظهور لأنّه أعلى عرض سعر. نتيجةً لذلك، يتم وضع التصميم الإعلاني المحدّد في الردّ.
اختيار بروتوكول
يحدّد بروتوكول عروض الأسعار في الوقت الفعلي الإشارات التي يمكن أن يستخدمها تطبيقك لتقييم كل مرّة ظهور يتم إرسالها في طلب وتقديم عرض سعر لها، بالإضافة إلى كيفية إنشاء ردّ. هناك طريقتان لتعديل البروتوكول المرتبط بتطبيق مقدّم عروض الأسعار:
- يمكنك التواصل مع المدير الفني للحساب لتغييره يدويًا.
- استخدِم Authorized Buyers REST API لتغييرها آليًا.
البروتوكولات المتوافقة
يتوافق "الشراة المعتمَدون" مع بروتوكولَين لعرض الأسعار في الوقت الفعلي:
- OpenRTB (Protobuf)
تنفيذ لمواصفات OpenRTB باستخدام Protobuf
- OpenRTB (JSON)
هي عملية تنفيذ لمواصفات OpenRTB باستخدام JSON.
لمحة عن Protocol Buffers
Protobuf هو تنسيق مفتوح المصدر لتمثيل المعلومات المنظَّمة وتسلسلها.
إذا أردت استخدام OpenRTB Protobuf، عليك تثبيت برنامج تجميع البروتوكول ووقت تشغيل Protobuf للغة التي اخترتها. يمكنك بعد ذلك
تنزيل ملفات proto التي
تنوي استخدامها وتشغيل برنامج التجميع لإنشاء مكتبة يمكنها تسلسل الرسائل أو إلغاء تسلسلها المحددة في ملف proto، مثل BidRequest أو
BidResponse. يوضّح مرجع Protobuf كيفية إجراء ذلك لعدة لغات.
تعديلات البروتوكول
سيتم تعديل بروتوكولات عروض الأسعار في الوقت الفعلي عندما تضيف Google ميزات جديدة وتوقف ميزات أخرى. سيتم الإعلان عن التغييرات قبل وقت كافٍ من تطبيقها، ما يتيح لك الوقت الكافي لإزالة أي تبعيات قد يتضمّنها تطبيقك على الحقول التي سيتم إيقافها نهائيًا. لمزيد من المعلومات حول التعامل مع الحقول المتوقّفة نهائيًا، يُرجى الاطّلاع على التكيّف مع إيقاف حقول BidRequest نهائيًا.
الخطوات التالية
يقدّم المحتوى التالي المزيد من التفاصيل حول مفاهيم عروض الأسعار في الوقت الفعلي:
- معالجة الطلب: كيفية تحليل الإشارات وتفسيرها في معظم طلبات عروض الأسعار
- إنشاء الرد: كيفية إنشاء رد على طلب عرض سعر، والحقول التي يتم تحديدها عادةً في الرد
- دليل OpenRTB: مرجع لتنفيذ مواصفات OpenRTB في "الشراة المعتمَدون"، بالإضافة إلى الإضافات الخاصة بـ "الشراة المعتمَدون". تقدّم هذه السمة تفاصيل حول الحالات الحدّية والقيود الخاصة بهذا التنفيذ، وتحدّد الحقول المكافئة في بروتوكول Google.
- متطلبات عرض الإعلانات التابعة لجهات خارجية: تحدّد هذه السياسات التي يجب أن يلتزم بها مقدّمو عروض الأسعار لاستخدام أشكال الإعلانات المختلفة، بالإضافة إلى المواصفات الفنية لهذه الأشكال.
- الاستهداف المُسبَق: كيفية ضبط تطبيق مقدّم عروض الأسعار لتلقّي مرّات الظهور التي تتطابق فقط مع معايير الاستهداف.
- مطابقة ملفات تعريف الارتباط: مرجع لخدمة "مطابقة ملفات تعريف الارتباط" والخدمات الأخرى ذات الصلة، والتي تُستخدَم لتجديد النشاط التسويقي.
- القيود المفروضة على وقت الاستجابة والربط المباشر: تفاصيل حول المواقع الجغرافية التي يمكن التداول فيها وكيفية تقليل وقت الاستجابة، مثلاً من خلال الربط المباشر
- اختبار تطبيق مقدّم عروض الأسعار وإصداره: تفاصيل حول كيفية بدء اختبار تطبيق مقدّم عروض الأسعار باستخدام الزيارات التي ترسلها Google على نطاق واسع.

