برای استفاده از سبکدهی مبتنی بر داده برای مرزها، باید یک شناسه نقشه ایجاد کنید که از نقشه برداری جاوا اسکریپت استفاده میکند. در مرحله بعد، باید یک سبک نقشه جدید ایجاد کنید، لایههای عوارض مرزی را انتخاب کنید و سبک را با شناسه نقشه خود مرتبط کنید.
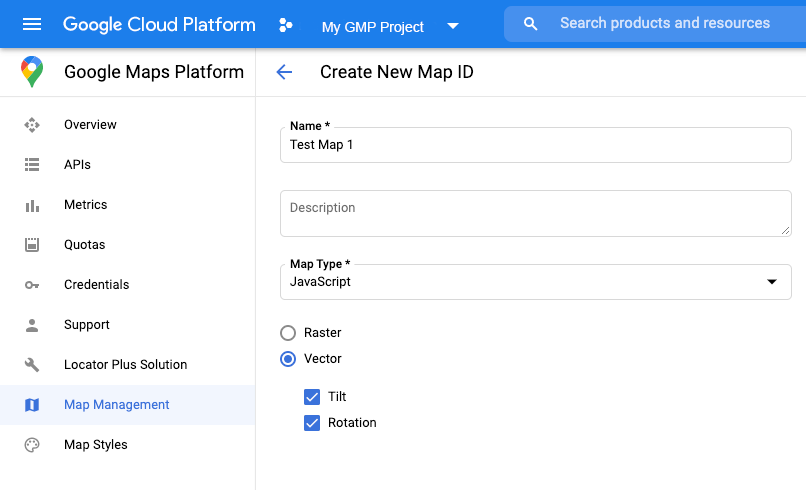
ایجاد شناسه نقشه
برای ایجاد یک شناسه نقشه جدید، مراحل موجود در سفارشیسازی ابری را دنبال کنید. نوع نقشه را روی جاوا اسکریپت تنظیم کنید و گزینه برداری (Vector) را انتخاب کنید. برای فعال کردن کجی و چرخش روی نقشه، گزینه Tilt and Rotation را تیک بزنید. اگر استفاده از کجی یا جهتگیری روی برنامه شما تأثیر منفی میگذارد، تیک گزینه Tilt and Rotation را بردارید تا کاربران نتوانند آنها را تنظیم کنند.
ایجاد یک سبک نقشه جدید
برای ایجاد یک سبک نقشه جدید، دستورالعملهای موجود در مدیریت سبکهای نقشه را برای ایجاد سبک دنبال کنید و سبک را با شناسه نقشهای که اخیراً ایجاد کردهاید مرتبط کنید .
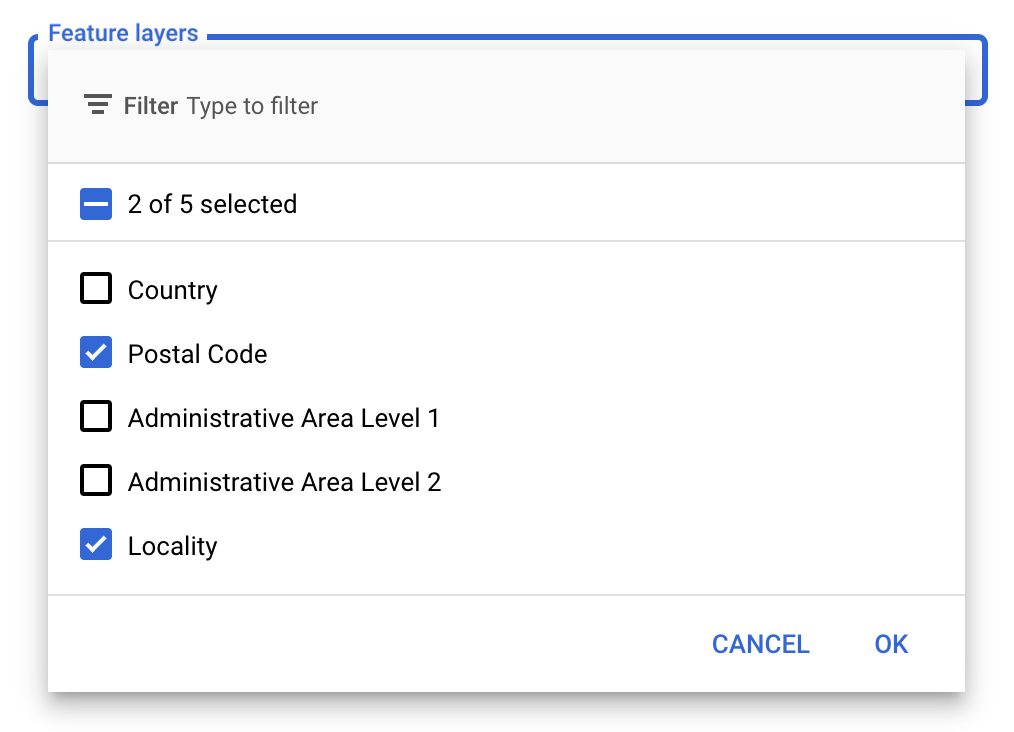
انتخاب لایههای ویژگی
در کنسول API گوگل میتوانید انتخاب کنید که کدام لایههای ویژگی نمایش داده شوند. این تعیین میکند که چه نوع مرزهایی روی نقشه ظاهر شوند (برای مثال، مکانها، ایالتها و غیره).
برای مدیریت لایههای ویژگی
- در کنسول API گوگل، به صفحهی «سبکهای نقشه» (Map Styles) بروید .
- در صورت درخواست، یک پروژه را انتخاب کنید.
- یک سبک نقشه انتخاب کنید.
- برای اضافه کردن یا حذف لایهها، روی منوی کشویی Feature layers کلیک کنید.
- برای ذخیره تغییرات و در دسترس قرار دادن آنها در نقشههایتان، روی ذخیره کلیک کنید.
کد مقداردهی اولیه نقشه خود را بهروزرسانی کنید
این به شناسه نقشهای که ایجاد کردهاید نیاز دارد. میتوانید آن را در صفحه مدیریت نقشههای خود پیدا کنید.
- API جاوا اسکریپت Maps را با اضافه کردن بوتاسترپ لودر درونخطی به کد برنامه خود، همانطور که در قطعه کد زیر نشان داده شده است، بارگذاری کنید:
<script> (g=>{var h,a,k,p="The Google Maps JavaScript API",c="google",l="importLibrary",q="__ib__",m=document,b=window;b=b[c]||(b[c]={});var d=b.maps||(b.maps={}),r=new Set,e=new URLSearchParams,u=()=>h||(h=new Promise(async(f,n)=>{await (a=m.createElement("script"));e.set("libraries",[...r]+"");for(k in g)e.set(k.replace(/[A-Z]/g,t=>"_"+t[0].toLowerCase()),g[k]);e.set("callback",c+".maps."+q);a.src=`https://maps.${c}apis.com/maps/api/js?`+e;d[q]=f;a.onerror=()=>h=n(Error(p+" could not load."));a.nonce=m.querySelector("script[nonce]")?.nonce||"";m.head.append(a)}));d[l]?console.warn(p+" only loads once. Ignoring:",g):d[l]=(f,...n)=>r.add(f)&&u().then(()=>d[l](f,...n))})({ key: "YOUR_API_KEY", v: "weekly", // Use the 'v' parameter to indicate the version to use (weekly, beta, alpha, etc.). // Add other bootstrap parameters as needed, using camel case. }); </script>
هنگام نمونهسازی نقشه با استفاده از ویژگی
mapIdیک شناسه نقشه ارائه دهید. این باید همان شناسه نقشهای باشد که با استفاده از یک سبک نقشه با لایههای ویژگی فعال پیکربندی کردهاید.map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), { center: {lat: -34.397, lng: 150.644}, zoom: 8, mapId: 'MAP_ID' // A map ID using a style with one or more feature layers enabled. });
درباره بارگیری API جاوا اسکریپت Maps بیشتر بدانید.
اضافه کردن لایههای عوارض به نقشه
برای دریافت ارجاع به یک لایه ویژگی روی نقشه خود، هنگام مقداردهی اولیه نقشه، تابع map.getFeatureLayer() را فراخوانی کنید:
function initMap() { map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), { center: { lat: 20.773, lng: -156.01 }, zoom: 12, mapId: 'MAP_ID', }); // Add a feature layer for localities. localityLayer = map.getFeatureLayer('LOCALITY'); ... }
بررسی قابلیتهای نقشه
استایلدهی مبتنی بر داده برای مرزها نیازمند قابلیتهایی است که در کنسول API گوگل فعال شده و با شناسه نقشه مرتبط باشند. از آنجا که شناسههای نقشه موقتی و در معرض تغییر هستند، میتوانید قبل از فراخوانی یک قابلیت خاص (برای مثال استایلدهی مبتنی بر داده) با فراخوانی map.getMapCapabilities() آن را بررسی کنید. این بررسی اختیاری است.
مثال زیر اضافه کردن یک شنونده برای ثبت تغییرات قابلیت نقشه را نشان میدهد:
// subscribe to changes map.addListener('mapcapabilities_changed', () => { const mapCapabilities = map.getMapCapabilities(); if (!mapCapabilities.isDataDrivenStylingAvailable) { // Data-driven styling is *not* available, add a fallback. // Existing feature layers are also unavailable. } });
مراحل بعدی
- یک چندضلعی مرزی را سبکبندی کنید
- یک نقشه کروپلت تهیه کنید
- مدیریت رویدادهای ماوس
- دریافت شناسه مکانی برای یک منطقه
- از APIهای Geocoding و Places با استایلدهی مبتنی بر داده برای مرزها استفاده کنید.

