有料検索のデータ
Google の検索ボリューム(GQV)は、メディアと販売の間の重要な交絡因子となることがよくあります。有料検索では特にそうです。予算の上限が妨げにならない場合など、特定のキャンペーン設定において、検索ボリュームによって広告ボリュームが増大することがあるためです。GQV が交絡因子である場合は、交絡するメディアについてバイアスのない因果推定値を得るために、制御する必要があります。GQV を制御しないと、有料検索の因果効果が過大評価される可能性があります。
メリディアンは、GQV データを制御変数として含めることができるソリューションを提供しています。以下の推奨事項を参考にしてください。
GQV データは、地域の人口に基づいてスケーリングすることをおすすめします。これには
control_population_scaling_id引数を使用します。ブランド固有の検索語句をターゲットとする有料検索キャンペーンは、より一般的な商品関連の検索語句をターゲットとするキャンペーンとは大きく異なります。このようなキャンペーンは、モデルに個別のメディア チャネルとして含めることをおすすめします。
ブランド固有のキーワード キャンペーンは、直接のウェブ トラフィックを増やすことを目的としているため、多くの場合クリック数を使用してモデル化されます。他のキャンペーンでは、インプレッションがクリックにつながらなかった場合でも効果的である可能性があるため、インプレッション数を使用してモデル化されることがよくあります。
含める検索語句の数は、モデルに含まれる各有料検索メディア チャネルがターゲットとする検索語句に応じた数にすることをおすすめします。たとえば、ブランド固有の有料検索と一般の有料検索が別々のメディア チャネルとして MMM に含まれている場合は、ブランド固有の GQV と一般の GQV を、2 つの個別のコントロール変数として含めることをおすすめします。
考慮事項について詳しくは、検索ボリュームをコントロール変数として含めるをご覧ください。
組織の GQV、有料検索、フリークエンシーなどの Google 関連データは、Google MMM データ プラットフォームから取得できます。このデータにアクセスする方法については、MMM データ プラットフォームを使用するをご覧ください。
検索広告にクリック数またはインプレッション数を使用する
検索広告にクリック数とインプレッション数のどちらを使用するかを決める際は、次の点を考慮してください。
クリック数とインプレッション数のどちらを使用するかで結果は変わりますが、どの入力が最適であるかについては、測定パートナーの間ではもちろん、測定パートナーの内部でも、見解が一致するわけではありません。
広告主として、細かく制御できるほうを検討してください。このモデルでは、(クリック数またはインプレッション数のどちらで定義されているかにかかわらず)メディア マーケティングが KPI に与える影響を確認できるため、より細かく制御できる変数を使用すると、KPI への影響をより細かく制御できます。
クリック数は KPI と相関が高い傾向があり、インプレッション数は GQV と相関が高い傾向があります。ブランド固有のキーワード キャンペーンは、直接のウェブ トラフィックを増やすことを目的としているため、多くの場合クリック数を使用してモデル化されます。他のキャンペーンでは、インプレッションがクリックにつながらなかった場合でも効果的である可能性があるため、インプレッション数を使用してモデル化されることがよくあります。
検索広告の交絡因子としての検索ボリュームについて
因果推論をマーケティングに応用する際の最大の課題は、広告主様は、商品やサービスの需要が高まっているときにマーケティングに投下する費用を増やす傾向があるという点です。マーケティング費用の因果効果を分析する際の重要ポイントは、KPI の増加がマーケティング費用の増額によるものなのか、それとも本質的な需要の増加によるものなのかを明らかにすることです。
検索広告の場合、本質的な需要とマーケティング費用の強い相関性が特に顕著になります。検索広告は、広告主様がターゲットに設定した特定のキーワードに検索語句が一致した場合にのみ表示されるためです。本質的な需要が高い場合、オーガニック検索ボリュームも多くなるため、検索広告の合計費用も高くなります。そのため、オーガニック検索ボリュームは検索広告にとって重要な交絡因子となります。それを考慮しないと、検索広告に関する効果的な推論を導き出すことは困難です。
これは、検索広告の予算が多い広告主様の場合は特に問題となります。有料検索広告のボリュームは、オーガニック検索ボリュームと密接に連動する傾向があるためです。ただし、このことは、予算が少なく、需要の多い期間に予算を増やす広告主様や、そうした期間にのみ検索キャンペーンを実施する広告主様にも影響します。
メリディアンでは、Google 検索広告の交絡因子として、Google のオーガニック検索ボリューム(GQV)をモデルに含めることができます。通常、Google 以外の検索エンジンからのオーガニック検索ボリュームは利用できません。Google 以外の有料検索広告をモデル化することが目的で、その検索エンジンのオーガニック検索ボリュームのデータを利用できない場合は、次の方法をおすすめします。
GQV が Google 以外の検索ボリュームの適切な代用指標になる場合は、バイアスを軽減できる可能性があります。この仮説を評価することをおすすめします。この仮説を評価する方法の 1 つは、次のようなプロットを作成することです。
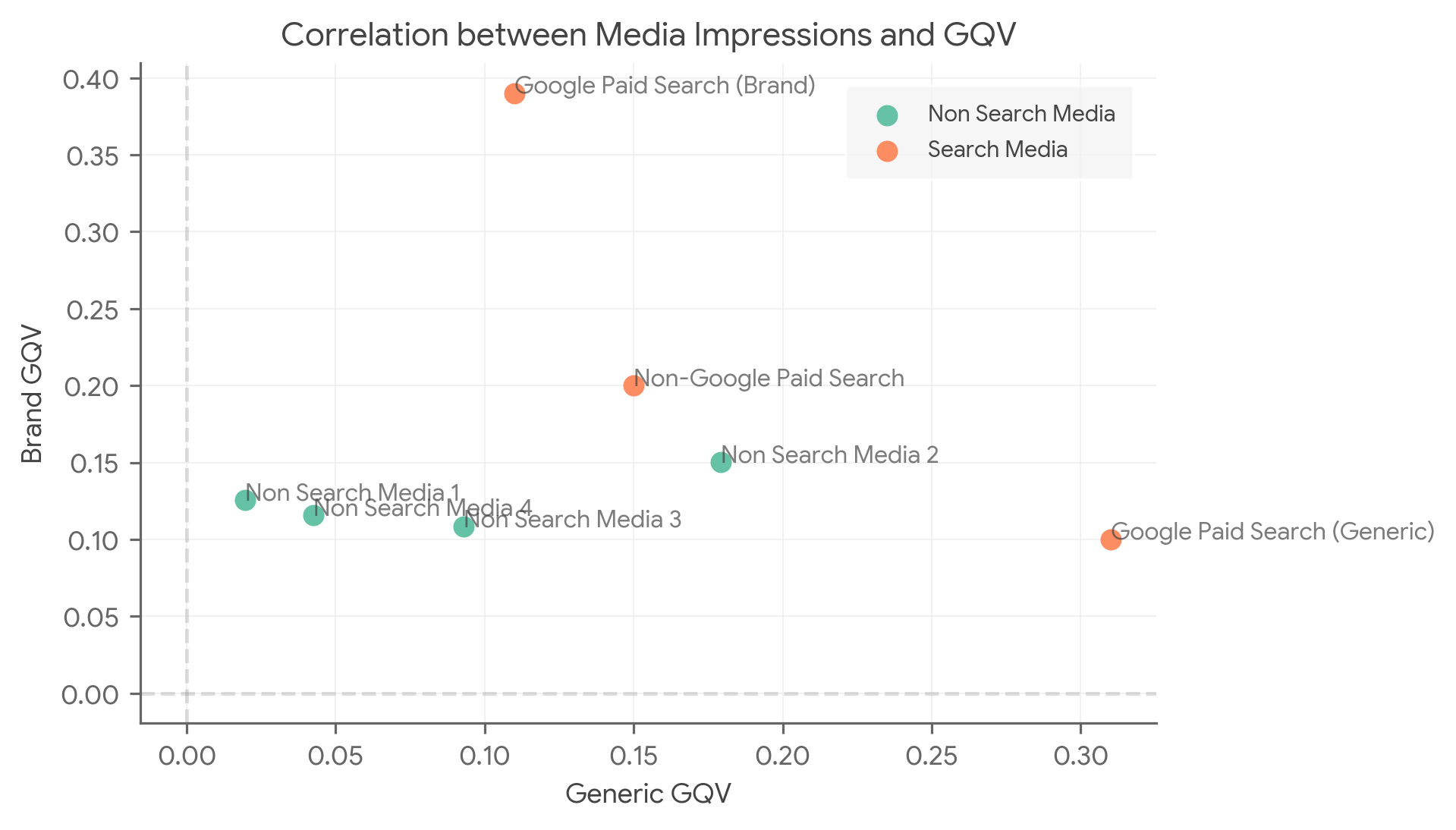
上のグラフは、メディアのインプレッションとブランド名の GQV の相関関係を Y 軸に、メディアのインプレッションと一般的な語句の検索ボリュームの相関関係を X 軸にプロットしています。
GQV が、Google 以外の検索ボリュームの適切な代用指標になるという仮説を拒否する場合は、Google 以外の検索エンジンをモデルから除外する必要があります。
広告のターゲティングによる選択バイアスの問題の詳細については、メディア ミックス モデリングにおける有料検索のバイアス補正をご覧ください。
