목표
대량 주소 유효성 검사 튜토리얼에서는 대량 주소 유효성 검사를 사용할 수 있는 다양한 시나리오를 안내했습니다. 이 튜토리얼에서는 Google Cloud Platform 내에서 대량 주소 유효성 검사를 실행하기 위한 다양한 설계 패턴을 소개합니다.
일회성 실행을 위해 Cloud Run, Compute Engine 또는 Google Kubernetes Engine을 사용하여 Google Cloud Platform에서 대량 주소 유효성 검사를 실행하는 방법을 간략하게 살펴보겠습니다. 그런 다음 이 기능을 데이터 파이프라인의 일부로 포함하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
이 도움말을 끝까지 읽으면 Google Cloud 환경에서 주소 유효성 검사를 대량으로 실행하는 다양한 옵션을 잘 이해할 수 있습니다.
Google Cloud Platform의 참조 아키텍처
이 섹션에서는 Google Cloud Platform을 사용한 대량 주소 확인의 다양한 설계 패턴을 자세히 살펴봅니다. Google Cloud Platform에서 실행하면 기존 프로세스 및 데이터 파이프라인과 통합할 수 있습니다.
Google Cloud Platform에서 대량 주소 유효성 검사를 한 번 실행
다음은 일회성 작업이나 테스트에 더 적합한 Google Cloud Platform에서 통합을 빌드하는 방법을 보여주는 참조 아키텍처입니다.
이 경우 CSV 파일을 Cloud Storage 버킷에 업로드하는 것이 좋습니다. 그러면 Cloud Run 환경에서 대량 주소 유효성 검사 스크립트를 실행할 수 있습니다. 하지만 Compute Engine 또는 Google Kubernetes Engine과 같은 다른 런타임 환경에서 실행할 수 있습니다. 출력 CSV를 Cloud Storage 버킷에 업로드할 수도 있습니다.
Google Cloud Platform 데이터 파이프라인으로 실행
이전 섹션에 표시된 배포 패턴은 일회성 사용을 위해 대량 주소 유효성 검사를 빠르게 테스트하는 데 적합합니다. 하지만 데이터 파이프라인의 일부로 정기적으로 사용해야 하는 경우 Google Cloud Platform 네이티브 기능을 활용하여 더 강력하게 만들 수 있습니다. 다음과 같은 사항을 변경할 수 있습니다.
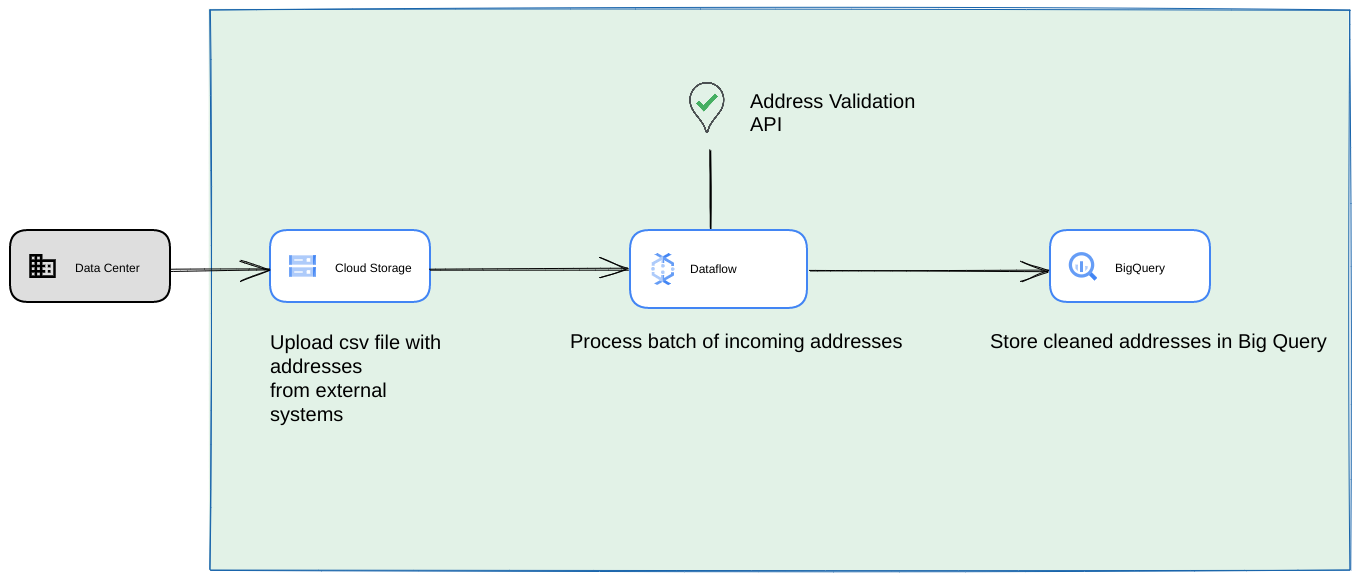
- 이 경우 Cloud Storage 버킷에 CSV 파일을 덤프할 수 있습니다.
- Dataflow 작업은 처리할 주소를 선택한 다음 BigQuery에 캐시할 수 있습니다.
- Dataflow Python 라이브러리를 확장하여 대량 주소 검증을 위한 로직을 포함하여 Dataflow 작업의 주소를 검증할 수 있습니다.
데이터 파이프라인에서 스크립트를 장기 반복 프로세스로 실행
또 다른 일반적인 방법은 스트리밍 데이터 파이프라인의 일부로 주소 일괄 처리를 반복적인 프로세스로 검증하는 것입니다. BigQuery 데이터 스토어에 주소가 있을 수도 있습니다. 이 접근 방식에서는 매일/매주/매월 트리거해야 하는 반복 데이터 파이프라인을 빌드하는 방법을 알아봅니다.
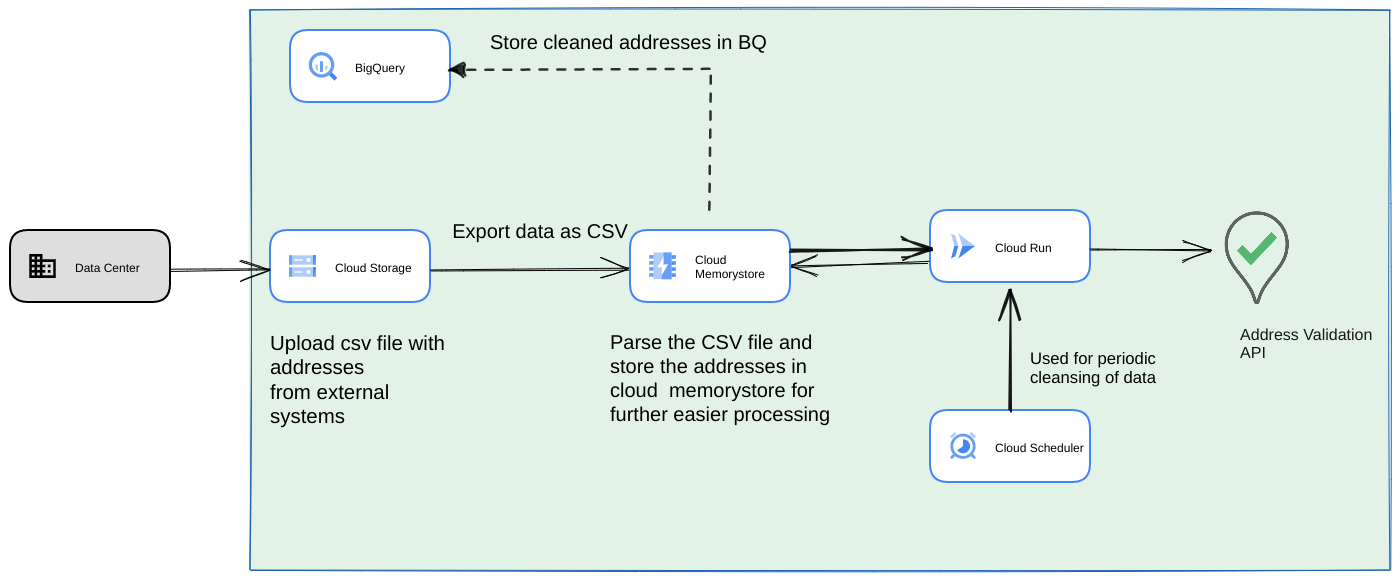
- 초기 CSV 파일을 Cloud Storage 버킷에 업로드합니다.
- Memorystore를 영구 데이터 저장소로 사용하여 장기 실행 프로세스의 중간 상태를 유지합니다.
- BigQuery 데이터 스토어에 최종 주소를 캐시합니다.
- 스크립트를 주기적으로 실행하도록 Cloud Scheduler를 설정합니다.
이 아키텍처에는 다음과 같은 장점이 있습니다.
- Cloud Scheduler를 사용하면 주소 유효성 검사를 주기적으로 실행할 수 있습니다. 주소를 매월 재검증하거나 새 주소를 매월/분기별로 검증하는 것이 좋습니다. 이 아키텍처는 해당 사용 사례를 해결하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
고객 데이터가 BigQuery에 있는 경우 검증된 주소 또는 검증 플래그를 BigQuery에 직접 캐시할 수 있습니다. 참고: 캐시할 수 있는 항목과 방법은 대량 주소 유효성 검사 도움말에 자세히 설명되어 있습니다.
Memorystore를 사용하면 복원력이 향상되고 더 많은 주소를 처리할 수 있습니다. 이 단계에서는 매우 큰 주소 데이터 세트를 처리하는 데 필요한 상태를 전체 처리 파이프라인에 추가합니다. Google Cloud Platform에서 제공하는 Cloud SQL[https://cloud.google.com/sql] 또는 기타 데이터베이스 버전과 같은 다른 데이터베이스 기술도 여기에서 사용할 수 있습니다. 하지만 Memorystore는 확장성과 단순성 요구사항의 균형을 완벽하게 맞추므로 첫 번째 선택이 되어야 합니다.
결론
여기에 설명된 패턴을 적용하면 Google Cloud Platform에서 다양한 사용 사례에 대해 주소 유효성 검사 API를 사용할 수 있습니다.
위에서 설명한 사용 사례를 시작하는 데 도움이 되는 오픈소스 Python 라이브러리가 있습니다. 컴퓨터의 명령줄에서 호출하거나 Google Cloud Platform 또는 다른 클라우드 제공업체에서 호출할 수 있습니다.
이 도움말에서 라이브러리 사용 방법을 자세히 알아보세요.
다음 단계
신뢰할 수 있는 주소로 결제, 배송, 운영 개선 백서를 다운로드하고 주소 확인으로 결제, 배송, 운영 개선 웨비나를 시청하세요.
추천 추가 자료:
참여자
Google에서 이 도움말을 유지관리합니다. 다음 참여자가 원래 작성했습니다.
주요 작성자:
헨리크 밸브 | 솔루션 엔지니어
토마스 앙글라레 | 솔루션 엔지니어
사르탁 강굴리 | 솔루션 엔지니어

