Earth Engine 中有多种光谱转换方法。这些方法包括针对图片的实例方法,例如 normalizedDifference()、unmix()、rgbToHsv() 和 hsvToRgb()。
平移锐化
通过分辨率更高的相应全色图像提供的增强功能,全景锐化可提高多波段图像的分辨率。
rgbToHsv() 和 hsvToRgb() 方法对平移锐化很有用。
Code Editor (JavaScript)
// Load a Landsat 8 top-of-atmosphere reflectance image. var image = ee.Image('LANDSAT/LC08/C02/T1_TOA/LC08_044034_20140318'); Map.addLayer( image, {bands: ['B4', 'B3', 'B2'], min: 0, max: 0.25, gamma: [1.1, 1.1, 1]}, 'rgb'); // Convert the RGB bands to the HSV color space. var hsv = image.select(['B4', 'B3', 'B2']).rgbToHsv(); // Swap in the panchromatic band and convert back to RGB. var sharpened = ee.Image.cat([ hsv.select('hue'), hsv.select('saturation'), image.select('B8') ]).hsvToRgb(); // Display the pan-sharpened result. Map.setCenter(-122.44829, 37.76664, 13); Map.addLayer(sharpened, {min: 0, max: 0.25, gamma: [1.3, 1.3, 1.3]}, 'pan-sharpened');
import ee import geemap.core as geemap
Colab (Python)
# Load a Landsat 8 top-of-atmosphere reflectance image. image = ee.Image('LANDSAT/LC08/C02/T1_TOA/LC08_044034_20140318') # Convert the RGB bands to the HSV color space. hsv = image.select(['B4', 'B3', 'B2']).rgbToHsv() # Swap in the panchromatic band and convert back to RGB. sharpened = ee.Image.cat( [hsv.select('hue'), hsv.select('saturation'), image.select('B8')] ).hsvToRgb() # Define a map centered on San Francisco, California. map_sharpened = geemap.Map(center=[37.76664, -122.44829], zoom=13) # Add the image layers to the map and display it. map_sharpened.add_layer( image, { 'bands': ['B4', 'B3', 'B2'], 'min': 0, 'max': 0.25, 'gamma': [1.1, 1.1, 1], }, 'rgb', ) map_sharpened.add_layer( sharpened, {'min': 0, 'max': 0.25, 'gamma': [1.3, 1.3, 1.3]}, 'pan-sharpened', ) display(map_sharpened)
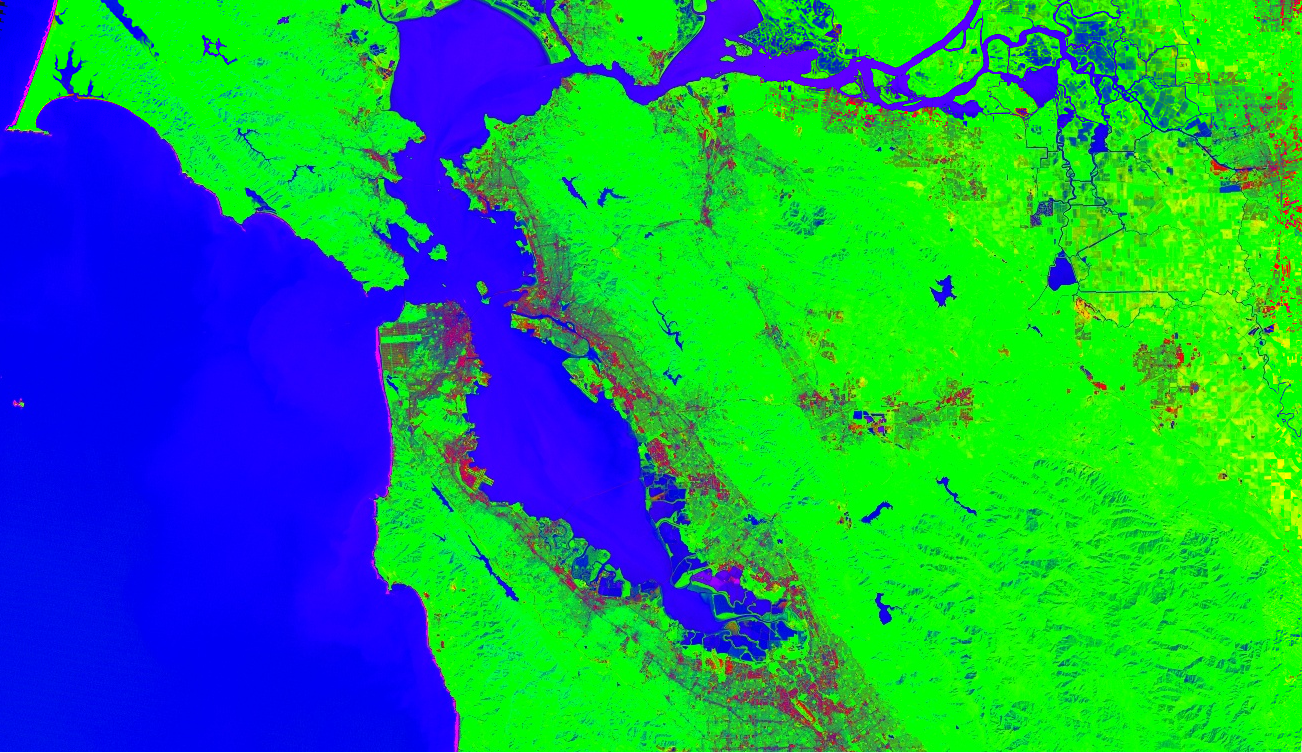
光谱分离
在 Earth Engine 中,光谱分解是作为 image.unmix() 方法实现的。
(如需了解更灵活的方法,请参阅“数组转换”页面)。以下是使用预先确定的城市、植被和水端元解混 Landsat 5 数据的示例:
Code Editor (JavaScript)
// Load a Landsat 5 image and select the bands we want to unmix. var bands = ['B1', 'B2', 'B3', 'B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7']; var image = ee.Image('LANDSAT/LT05/C02/T1/LT05_044034_20080214') .select(bands); Map.setCenter(-122.1899, 37.5010, 10); // San Francisco Bay Map.addLayer(image, {bands: ['B4', 'B3', 'B2'], min: 0, max: 128}, 'image'); // Define spectral endmembers. var urban = [88, 42, 48, 38, 86, 115, 59]; var veg = [50, 21, 20, 35, 50, 110, 23]; var water = [51, 20, 14, 9, 7, 116, 4]; // Unmix the image. var fractions = image.unmix([urban, veg, water]); Map.addLayer(fractions, {}, 'unmixed');
import ee import geemap.core as geemap
Colab (Python)
# Load a Landsat 5 image and select the bands we want to unmix. bands = ['B1', 'B2', 'B3', 'B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7'] image = ee.Image('LANDSAT/LT05/C02/T1/LT05_044034_20080214').select(bands) # Define spectral endmembers. urban = [88, 42, 48, 38, 86, 115, 59] veg = [50, 21, 20, 35, 50, 110, 23] water = [51, 20, 14, 9, 7, 116, 4] # Unmix the image. fractions = image.unmix([urban, veg, water]) # Define a map centered on San Francisco Bay. map_fractions = geemap.Map(center=[37.5010, -122.1899], zoom=10) # Add the image layers to the map and display it. map_fractions.add_layer( image, {'bands': ['B4', 'B3', 'B2'], 'min': 0, 'max': 128}, 'image' ) map_fractions.add_layer(fractions, None, 'unmixed') display(map_fractions)

 在 Google Colab 中运行
在 Google Colab 中运行
 在 GitHub 上查看源代码
在 GitHub 上查看源代码