在 Earth Engine 中,从矢量到光栅的插值会根据 FeatureCollection 创建 Image。具体而言,Earth Engine 会使用存储在地图项属性中的数值数据,对地图项之外的新位置插值值。插值会产生连续的 Image,其中包含指定距离范围内的内插值。
反距离加权插值
Earth Engine 中的反距离权重 (IDW) 函数基于 Basso 等人 (1999) 所述的方法。在反距离上添加了额外的控制参数,形式为衰减系数 (gamma)。其他参数包括要插值的属性的平均值和标准差,以及插值的最大范围距离。以下示例创建了
一氧化碳浓度的插值表面,以填补原始栅格数据集中的空间空白。FeatureCollection 是通过对两周的甲烷复合物进行采样生成的。
// Import two weeks of S5P methane and composite by mean. var ch4 = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S5P/OFFL/L3_CH4') .select('CH4_column_volume_mixing_ratio_dry_air') .filterDate('2019-08-01', '2019-08-15') .mean() .rename('ch4'); // Define an area to perform interpolation over. var aoi = ee.Geometry.Polygon( [[[-95.68487605978851, 43.09844605027055], [-95.68487605978851, 37.39358590079781], [-87.96148738791351, 37.39358590079781], [-87.96148738791351, 43.09844605027055]]], null, false); // Sample the methane composite to generate a FeatureCollection. var samples = ch4.addBands(ee.Image.pixelLonLat()) .sample({region: aoi, numPixels: 1500, scale:1000, projection: 'EPSG:4326'}) .map(function(sample) { var lat = sample.get('latitude'); var lon = sample.get('longitude'); var ch4 = sample.get('ch4'); return ee.Feature(ee.Geometry.Point([lon, lat]), {ch4: ch4}); }); // Combine mean and standard deviation reducers for efficiency. var combinedReducer = ee.Reducer.mean().combine({ reducer2: ee.Reducer.stdDev(), sharedInputs: true}); // Estimate global mean and standard deviation from the points. var stats = samples.reduceColumns({ reducer: combinedReducer, selectors: ['ch4']}); // Do the interpolation, valid to 70 kilometers. var interpolated = samples.inverseDistance({ range: 7e4, propertyName: 'ch4', mean: stats.get('mean'), stdDev: stats.get('stdDev'), gamma: 0.3}); // Define visualization arguments. var band_viz = { min: 1800, max: 1900, palette: ['0D0887', '5B02A3', '9A179B', 'CB4678', 'EB7852', 'FBB32F', 'F0F921']}; // Display to map. Map.centerObject(aoi, 7); Map.addLayer(ch4, band_viz, 'CH4'); Map.addLayer(interpolated, band_viz, 'CH4 Interpolated');
请注意,如 range 参数所指定,插值仅在距离最近测量站不超过 70 公里的范围内有效。
Kriging
Kriging 是一种插值方法,它使用半变异的模型估计值来创建插值值的图像,该图像是已知位置值的最佳组合。 Kriging 估算器需要参数来描述拟合到已知数据点的半变异函数的形状。这些参数如图 1 所示。
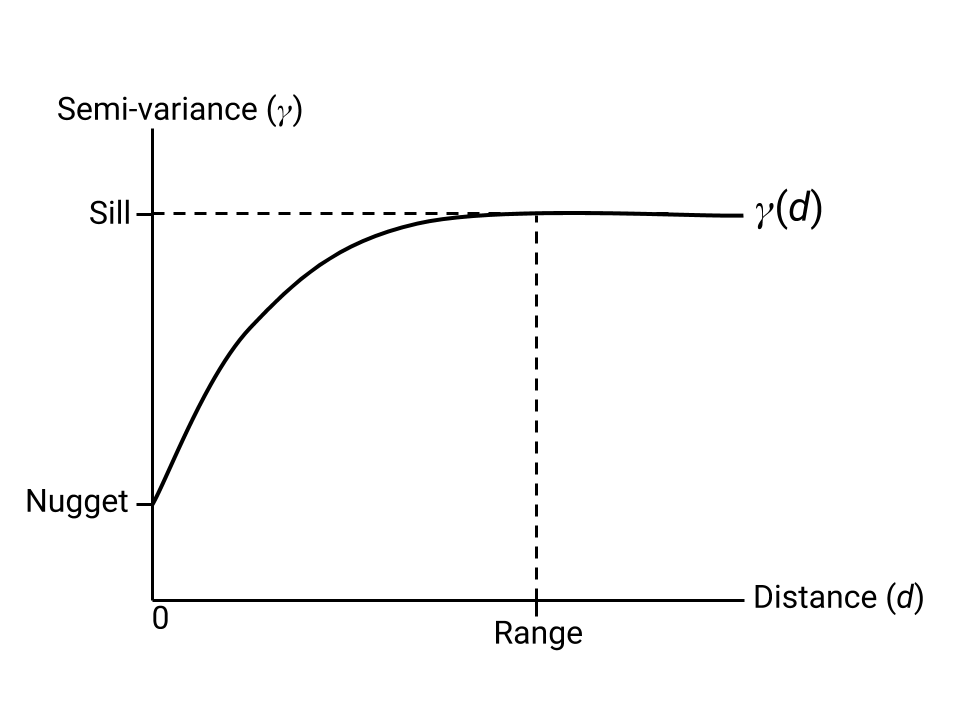
nugget、sill 和 range 参数。
以下示例在随机位置对海表温度 (SST) 图像进行采样,然后使用克里格插值法从样本中插值 SST:
// Load an image of sea surface temperature (SST). var sst = ee.Image('NOAA/AVHRR_Pathfinder_V52_L3/20120802025048') .select('sea_surface_temperature') .rename('sst') .divide(100); // Define a geometry in which to sample points var geometry = ee.Geometry.Rectangle([-65.60, 31.75, -52.18, 43.12]); // Sample the SST image at 1000 random locations. var samples = sst.addBands(ee.Image.pixelLonLat()) .sample({region: geometry, numPixels: 1000}) .map(function(sample) { var lat = sample.get('latitude'); var lon = sample.get('longitude'); var sst = sample.get('sst'); return ee.Feature(ee.Geometry.Point([lon, lat]), {sst: sst}); }); // Interpolate SST from the sampled points. var interpolated = samples.kriging({ propertyName: 'sst', shape: 'exponential', range: 100 * 1000, sill: 1.0, nugget: 0.1, maxDistance: 100 * 1000, reducer: 'mean', }); var colors = ['00007F', '0000FF', '0074FF', '0DFFEA', '8CFF41', 'FFDD00', 'FF3700', 'C30000', '790000']; var vis = {min:-3, max:40, palette: colors}; Map.setCenter(-60.029, 36.457, 5); Map.addLayer(interpolated, vis, 'Interpolated'); Map.addLayer(sst, vis, 'Raw SST'); Map.addLayer(samples, {}, 'Samples', false);
执行插值的邻域的大小由 maxDistance 参数指定。大小越大,输出越流畅,但计算速度越慢。
