2010 年 8 月 6 日(金曜日)
状況の変化に伴い、URL の削除に関する以前の投稿で説明したように、サイトからページを完全にブロックまたは削除することが必要になる場合があります。ページの一部のみを変更することや、特定のテキストを削除することが必要になる場合もあります。ページがクロールされる頻度によっては、こうした変更が Google の検索結果に反映されるまで時間がかかることがあります。このブログ投稿では、削除済みの古いコンテンツが、「スニペット」または検索結果からリンクされるキャッシュ ページという形で、検索結果に引き続き表示される場合に実施できる手順について説明します。これは、速やかに削除する必要がある機密情報が古いコンテンツに含まれている場合に役立ちます。ウェブサイトを通常どおりに更新するだけの場合、この手順を実施する必要はありません。
例として、次の架空の検索結果をご覧ください。
| Walter E. Coyote | < タイトル |
|
Chief Development Officer at Acme Corp 1948-2003: worked on the top |
< スニペット |
| www.example.com/about/waltercoyote - Cached | < URL + キャッシュ ページへのリンク |
スニペット(またはリンクされているキャッシュ ページ)に表示されるコンテンツを変更するには、まず実際のページ(ライブページ)のコンテンツを変更する必要があります。ページで一般に公開されているコンテンツが変更されない限り、Google の自動プロセスによって元のコンテンツの一部が引き続き検索結果に表示されます。
ページのコンテンツを変更したら、いくつかの方法で Google の検索結果に変更を反映させることができます。
-
Googlebot がページを再クロールしてインデックスに再登録するのを待ちます。これは、Google でほとんどのコンテンツが更新される自然な方法です。Googlebot が該当のページをクロールする頻度によっては、かなり長い時間がかかる場合があります。Google がページを再クロールしてインデックスに再登録すると、古いコンテンツは現在のコンテンツに置き換えられるため、通常は検索結果に表示されなくなります。Googlebot による該当ページのクロールが(robots.txt によって、またはサーバーに適切にアクセスできないことによって)ブロックされていなければ、何か特別なことをしなくてもそのような結果になります。これらのプロセスは完全に自動化されており、また多くの外的要因に依存しているため、通常、クロールとインデックス登録を早めることはできません。
-
Google の公開 URL 削除ツールを使用して、他の人のウェブページから削除されたコンテンツの削除をリクエストします。このツールを使用する場合は、変更されたページの正確な URL を入力し、[コンテンツはすでにページから削除されました] オプションを選択して、そのページから完全に削除された単語を 1 つ以上指定する必要があります。
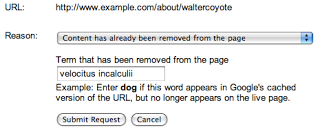
なお、入力する単語はいずれもページに表示されていてはなりません。ある単語がページの特定の部分から削除されていても、ページの別の部分に表示されていれば、リクエストは拒否されます。ページのどこにも表示されなくなった単語を 1 つ以上選択してください。上記の例で「top secret velocitus incalculii capturing device」を削除した場合は、「my project」のような語句ではなく、それらの単語を送信する必要があります。しかし、「top」または「device」という単語がページのどこかに存在していると、リクエストは拒否されます。ほとんどの場合、リクエストの成功率を最大限に高める簡単な方法は、ページのどこにも表示されなくなったことが確実な単語を 1 つだけ指定することです。
リクエストが処理され、送信した単語がページに表示されなくなっていることが確認されると、スニペットが検索結果に表示されなくなり、キャッシュ ページもアクセスできなくなります。ページのタイトルと URL は引き続き表示されます。また、指定した単語がスニペットに表示されなくなっても、削除されたコンテンツに関連する検索(例: velocitus incalculii の検索)の検索結果にエントリが引き続き表示される可能性があります。しかし、ページが再クロールされてインデックスに再登録されると、新しいスニペットとキャッシュ ページが検索結果に表示されます。
Google が単語の削除を確認するには、ページを参照する必要があることにご注意ください。ページがすでに存在せず、サーバーが適切な HTTP 結果コード
404または410を返す場合は、Google がページを参照できないため、完全にページを削除するようリクエストする方が適切です。 - Google ウェブマスター ツールの URL 削除ツールを使用して、ウェブサイトからページの情報を削除するようリクエストします。該当のウェブサイトにアクセスすることができ、かつ Google ウェブマスター ツールでウェブサイトの所有権を確認済みである場合は、そのサイトで URL 削除ツールを使用して([サイト設定] > [クローラ アクセス])、ページが再クロールされるまでスニペットとキャッシュ ページが削除されるようリクエストできます。このツールを使用するために必要なのは、ページの正確な URL を送信することだけです(削除された単語を指定する必要はありません)。リクエストが処理されると、スニペットとキャッシュ ページが検索結果から削除されます。ページのタイトルと URL は引き続き表示されます。また、削除されたコンテンツに関連するクエリの検索結果にページが引き続き表示される可能性があります。ページが再クロールされてインデックスに再登録されると、新しいコンテンツに基づいて更新されたスニペットとキャッシュ ページが検索結果に表示されます。
Google は、ページのコンテンツだけでなく、その他の外的要因(URL への外部からのリンクなど)にも基づいて、アイテムをインデックスに登録し、ランク付けしています。このため、ページが再クロールされてインデックスに再登録された後でも、ページからなくなったコンテンツの検索結果に URL が引き続き表示される可能性があります。URL 削除ツールを使用した場合、スニペットとキャッシュ ページを検索結果から削除することはできますが、検索結果のタイトルは変更または削除されず、表示される URL は変更されません。また、現在あるいは過去のコンテンツに基づいてページが検索結果に表示されることは防止できません。それが重要な場合は、URL が Google の検索結果からの完全な削除の要件を満たすことを確認してください。
非 HTML コンテンツの削除
変更されたコンテンツが HTML または XHTML 形式でない場合(たとえば画像、Flash ファイル、PDF ファイルが変更された場合)、キャッシュ削除ツールは使用できません。したがって、古いコンテンツを検索結果から削除することが重要な場合、最も迅速な解決策は、ファイルの URL を変更して元の URL が HTTP 結果コード 404 を返すようにし、URL 削除ツールを使用して元の URL を削除することです。そうしないで、Google がページの情報を自然に更新するのを待つことにした場合、再クロールの後、非 HTML コンテンツ(PDF ファイルのクイックビュー リンクなど)のプレビューの更新にかかる時間が通常の HTML ページより長くなる可能性があります。
スニペットまたはキャッシュ バージョンの表示を積極的に防止する
自身がウェブマスターである場合は、Google の削除ツールを使用せずに、robots meta タグを使用して、スニペットまたはキャッシュ バージョンの表示を積極的に防止できます。「nosnippet」robots meta タグを使用すると、スニペットの表示を防止できます。また、「noarchive」robots meta タグを使用すると、ページのキャッシュ保存を無効にできます。ただし、これらはデフォルトのアプローチとしてはおすすめしません(スニペットがあると、ユーザーは関連性の高い検索結果をすばやく認識できます。また、キャッシュに保存されたページがあると、予期しないイベントでサーバーが利用できなくなったときでも、ユーザーはコンテンツを参照できます)。なお、すでに Google に認識されている既存のページでこのような変更を行った場合、Googlebot がページを再クロールしてインデックスに再登録するまで、変更は検索結果に反映されません。
このブログ投稿が、更新したページに関する URL 削除ツールのプロセスの仕組みを理解するために少しでもお役に立てば幸いです。次回のブログ投稿では、自身が所有していないコンテンツの削除をリクエストする方法について説明します。更新をお待ちください。
ウェブマスター ヘルプ フォーラムでは、皆様からのご意見やご質問をお待ちしております。
このシリーズの他の投稿
- パート I: URL とディレクトリの削除
- パート II: キャッシュに保存されたコンテンツの削除と更新
- パート III: 自身が所有していないコンテンツの削除
- パート IV: リクエストのトラッキング、削除すべきでない場合
オンラインで利用可能な情報の管理もお読みになることをおすすめします。
