วันจันทร์ที่ 3 พฤษภาคม 2010
ในโพสต์สุดท้ายของซีรีส์การนำ URL ออก เราจะคุยกันเรื่องการติดตามผลของคําขอให้นําออก รวมถึงเรื่องเวลาใดที่ไม่ต้องใช้เครื่องมือนํา URL ออกของ Google เราขอแนะนําให้อ่านโพสต์ก่อนหน้าในซีรีส์นี้หากคุณยังไม่ได้อ่าน
- ส่วนที่ 1: การนํา URL และไดเรกทอรีออก
- ส่วนที่ 2: การนำเนื้อหาที่แคชไว้ออกและการอัปเดต
- ส่วนที่ 3: การนำเนื้อหาที่คุณไม่ได้เป็นเจ้าของออก
- ส่วนที่ 4: การติดตามคำขอ สิ่งที่ไม่ควรนำออก
นอกจากนี้ คุณอาจสนใจอ่านการจัดการข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับตัวคุณที่มีอยู่ทางออนไลน์
ทําความเข้าใจสถานะของคําขอ
เมื่อส่งคําขอให้นําออกแล้ว คําขอดังกล่าวจะปรากฏในรายการคําขอ คุณตรวจสอบสถานะคําขอได้ทุกเมื่อเพื่อดูว่าเนื้อหาถูกนําออกแล้วหรือยัง หรือคําขอยังอยู่ระหว่างรอดําเนินการหรือถูกปฏิเสธ
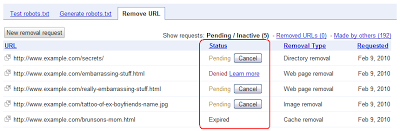
หากคําขอถูกปฏิเสธ คุณจะเห็นลิงก์ "ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม" ข้างคําขอซึ่งจะอธิบายสาเหตุที่คําขอนั้นถูกปฏิเสธ การนําออกต่างประเภทกันมีข้อกําหนดที่ต่างกัน เหตุผลที่คําขอถูกปฏิเสธแต่ละรายการก็อาจแตกต่างกันไป ลิงก์ "ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม" จะช่วยระบุสิ่งที่คุณต้องเปลี่ยนแปลงเพื่อให้คําขอดำเนินการสําเร็จ ตัวอย่างเช่น คุณอาจต้องเปลี่ยน URL ที่เป็นปัญหาเพื่อให้เป็นไปตามข้อกําหนดของประเภทการนําออกที่คุณส่งคําขอ หากดําเนินการไม่ได้ คุณอาจต้องส่งคําขอให้นําออกประเภทอื่น (ซึ่งมีข้อกําหนดที่ตรงกับ URL ของคุณ)
หากมีการทําเครื่องหมายคําขอว่า "นําออกแล้ว" แต่คุณยังคงเห็นเนื้อหาดังกล่าวในผลการค้นหา ให้ตรวจสอบสิ่งต่อไปนี้
-
URL ที่ปรากฏในผลการค้นหาเป็น URL เดียวกันกับที่คุณส่งคำขอให้นําออกไหม เป็นเรื่องปกติที่เนื้อหาเดียวกันหรือคล้ายกันจะปรากฏในหลาย URL ในเว็บไซต์ คุณอาจนํา URL ออกสําเร็จแล้ว 1 รายการ แต่ยังคงเห็น URL อื่นที่มีเนื้อหาเดียวกันนั้นอยู่
วิธีแก้ไข: ขอให้นํา URL อื่นๆ ที่เป็นปัญหาออก โปรดอ่านบทความในศูนย์ช่วยเหลือว่าคุณควรใช้ URL ใดสําหรับคําขอนําออก/บล็อก
-
โปรดทราบว่า URL พิจารณาตัวพิมพ์เล็กและตัวพิมพ์ใหญ่ การส่งคําขอให้นํา
https://www.example.com/embarrassingstuff.htmlออกจึงต่างจากการขอให้นําhttps://www.example.com/EmbarrassingStuff.htmlออกวิธีแก้ไข: ขอให้นํา URL อื่นๆ ที่เป็นปัญหาออก โปรดอ่านบทความในศูนย์ช่วยเหลือว่าคุณควรใช้ URL ใดสําหรับคําขอนําออก/บล็อก
-
เมื่อมีการทําเครื่องหมายคําขอว่า "นําออกแล้ว" นั่นอาจมีความหมายแตกต่างกันไปขึ้นอยู่กับประเภทคําขอที่คุณส่ง หากคุณส่งคําขอให้นํา URL ออกทั้ง URL คำว่า "นําออกแล้ว" จะหมายความว่า URL นั้นทั้งหมดจะไม่ปรากฏในผลการค้นหาของเราอีกต่อไป หากคุณขอให้นําสําเนาที่แคชไว้ของ URL ออก คำว่า "นําออกแล้ว" จะหมายความว่าสําเนาที่แคชไว้ถูกนําออกและจะไม่ปรากฏในผลการค้นหาอีกต่อไป แต่ตัว URL เองอาจยังปรากฏอยู่
วิธีแก้ไข: ตรวจสอบอีกครั้งว่าการนําออกประเภทใดที่คุณต้องการ โดยดูที่คอลัมน์ "ประเภทการนําออก" หากคุณส่งคําขอให้นําแคชออกแต่ต้องการลบ URL ทั้งหมด ให้ตรวจสอบว่า URL เป็นไปตามข้อกําหนดสําหรับการนําออกโดยสมบูรณ์ จากนั้นส่งคําขอใหม่สําหรับการนํา URL ออกโดยสมบูรณ์
เมื่อใดที่ไม่ควรใช้เครื่องมือนํา URL ออก
-
หากต้องการล้างสิ่งที่ไม่ต้องการ อย่างเช่น หน้าเก่าๆ ที่แสดงข้อผิดพลาด
404เครื่องมือนี้มีไว้สําหรับ URL ที่ต้องนําออกอย่างเร่งด่วน เช่น ข้อมูลลับที่เปิดเผยโดยไม่ตั้งใจ หากคุณเพิ่งเปลี่ยนแปลงเว็บไซต์เมื่อไม่นานมานี้และมี URL ที่ล้าสมัยอยู่ในดัชนี Crawler ของ Google จะเห็น URL นี้เมื่อเราทำการ Crawl URL ของคุณอีกครั้ง และหน้าเหล่านั้นจะเลิกแสดงในผลการค้นหาไปเองเมื่อเวลาผ่านไป คุณไม่จําเป็นต้องส่งคําขอให้นําออกโดยด่วนผ่านเครื่องมือนี้ -
หากต้องการนําข้อผิดพลาดที่พบเมื่อทำการ Crawl ออกจากบัญชีเครื่องมือของผู้ดูแลเว็บ เครื่องมือนําออกจะนํา URL ออกจากผลการค้นหาของ Google ไม่ใช่จากบัญชีเครื่องมือของผู้ดูแลเว็บ ขณะนี้ยังไม่มีวิธีให้คุณนํา URL ออกจากรายงานนี้ด้วยตนเอง คุกกี้ดังกล่าวจะหายไปเองเมื่อเวลาผ่านไป เนื่องจากเราหยุดทำการ Crawl URL
404ซ้ำๆ - หากต้องการ "เริ่มใหม่ตั้งแต่ต้น" กับเว็บไซต์ของคุณ หากกังวลว่าเว็บไซต์อาจได้รับโทษหรือคุณต้องการ "เริ่มใหม่ตั้งแต่ต้น" หลังจากซื้อโดเมนจากผู้อื่น เราไม่แนะนําให้ใช้เครื่องมือนํา URL ออก ทั้งเว็บไซต์ แล้ว "เริ่มต้นใหม่" เครื่องมือค้นหาจะรวบรวมข้อมูลจํานวนมากจากเว็บไซต์อื่น (เช่น ผู้ที่ลิงก์มายังคุณ หรือคําที่โปรแกรมใช้อธิบายเว็บไซต์ของคุณ) และใช้ข้อมูลนี้เพื่อช่วยให้เข้าใจเว็บไซต์ แม้ว่าเราจะสามารถลบทุกอย่างที่เราทราบแล้วเกี่ยวกับเว็บไซต์ของคุณ แต่เนื้อหาจํานวนมากจะกลับมาเหมือนเดิมทั้งหมดเมื่อเราทำการ Crawl เว็บไซต์อื่นๆ ทั้งหมดอีกครั้งซึ่งช่วยให้เราเข้าใจเว็บไซต์ของคุณและใส่ไว้ในบริบท หากคุณกังวลว่าโดเมนของคุณมีประวัติที่ไม่ดี เราขอแนะนําให้ยื่นคําขอให้พิจารณาใหม่เพื่อแจ้งให้เราทราบว่าคุณกังวลเกี่ยวกับเรื่องใดและมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงอะไรบ้าง (เช่น คุณได้โดเมนมาจากบุคคลอื่น หรือคุณทําการเปลี่ยนแปลงบางอย่างในเว็บไซต์)
-
หากต้องการทําให้เว็บไซต์ "ออฟไลน์" หลังจากถูกแฮ็ก หากเว็บไซต์ถูกแฮ็กและคุณต้องการกําจัด URL ที่ไม่ดีซึ่งได้รับการจัดทําดัชนีไปแล้ว ให้ใช้เครื่องมือนํา URL ออกเพื่อนํา URL ใหม่ที่แฮ็กเกอร์สร้างขึ้นออกตัวอย่างเช่น
https://www.example.com/buy-cheap-cialis-skq3w598.htmlแต่เราไม่แนะนําให้นําออกทั้งเว็บไซต์ หรือ URL ที่นำออกแล้วก็จะกลับมาอยู่ในดัชนีอีกในท้ายที่สุด คุณเพียงแก้ไขรายการที่โดนแฮ็กและให้เราทำการ Crawl เว็บไซต์อีกครั้ง เพื่อที่เราจะจัดทําดัชนีเนื้อหาใหม่ที่มีการแก้ไขโดยเร็วที่สุด บทความนี้มีรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับวิธีรับมือกับการแฮ็ก -
หากต้องการให้มีการจัดทำดัชนีเว็บไซต์ใน "เวอร์ชัน" ที่ถูกต้อง เมื่อมีการยอมรับคําขอให้นำ
https://www.example.com/tattoo.htmlออก ระบบจะนําhttp://www.example.com/tattoo.htmlออกด้วย เช่นเดียวกับ URL หรือเว็บไซต์เวอร์ชัน www และไม่มี www เนื่องจากเนื้อหาเดิมมักมีอยู่ในแต่ละ URL เหล่านี้และเราพบว่าผู้ดูแลเว็บและผู้ค้นหาส่วนใหญ่ไม่ต้องการให้เนื้อหาที่ซ้ำเหล่านี้ปรากฏในผลการค้นหา สรุปคือ ไม่ควรใช้เครื่องมือนํา URL ออกเป็นเครื่องมือกำหนดหน้า Canonical เพราะเครื่องมือจะไม่เก็บเวอร์ชันที่คุณเลือก แต่จะนํา URL ออกทุกเวอร์ชัน (http/https และ www/ไม่มี www)
เราหวังว่าซีรีส์นี้จะตอบข้อสงสัยของคุณเกี่ยวกับการนำเนื้อหาออกจากผลการค้นหาของ Google และช่วยคุณแก้ปัญหาที่อาจเกิดขึ้นได้ หากยังมีข้อสงสัย โปรดไปที่ฟอรัมความช่วยเหลือ
