2010 年 4 月 20 日,星期二
欢迎观看网址移除系列视频的第三集!在第 1 集和第 2 集中,我们讨论了如何加快移除由您控制的内容和请求加速移除缓存内容。今天,我们将介绍当内容源自并非由您控制的网站时,如何使用 Google 的公开网址移除工具请求从 Google 搜索结果中移除该内容。
Google 提供了两种工具来请求加速移除内容:
- 验证过的网址移除工具:用于在以下情况下请求从 Google 搜索结果中移除内容:该内容发布在某个网站上,您在网站站长工具中是该网站的经验证所有者(例如您的博客或公司网站)
- 公开网址移除工具:用于在以下情况下请求从 Google 搜索结果中移除内容:该内容发布在您无法验证所有权的网站上(例如朋友的博客)
有时,您要移除的信息可能来自不归您所有或您无法控制的网站。由于每个网站站长分别控制其网站和网站内容,因此更新或移除 Google 搜索结果的最佳方式是让网站所有者(即发布内容的网站)禁止抓取相应网址、修改内容来源或彻底移除该网页。如果内容没有发生变化,我们下次抓取该内容时,它只会重新显示在搜索结果中。因此,如需移除不归您所有的网站托管的内容,请先与网站所有者联系,请求对方移除或屏蔽相关内容。
已移除或屏蔽的内容
如果网站所有者移除了网页,对已移除网页的请求应返回 404 Not Found 响应或 410 Gone 响应。如果他们选择阻止搜索引擎访问该网页,则应在相应网站的 robots.txt 文件中禁止访问该网页,或者包含 noindex meta 标记。满足其中一项要求后,您就可以使用“Webmaster has already blocked the page”选项提交移除要求。
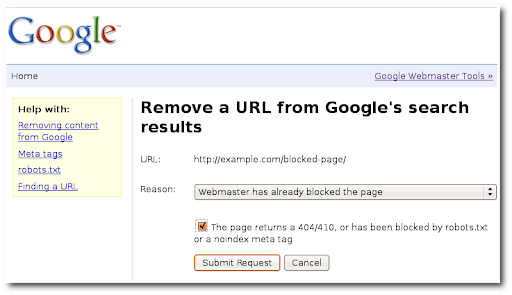
有时,网站所有者会声称他们屏蔽或移除了某个网页,但从技术上来讲,他们并没有这样做。如果对方声明某个网页已被屏蔽,您可以按照以下方法仔细检查:查看该网站的 robots.txt 文件,确认该网页是否被列入了禁止名单。
User-agent: * Disallow: /blocked-page/
检查网页的是否已遭屏蔽的另一个位置是网页的 HTML 源代码本身。您既可以访问该网页,也可以在浏览器中选择“查看网页源代码”。HTML head 部分中是否有 noindex 元标记?
<html> <head> <title>blocked page</title> <meta name="robots" content="noindex"> </head> ...
如果他们通知您该网页已被移除,您可以使用 HTTP 响应测试工具(例如适用于 Firefox 浏览器的 Live HTTP Headers 插件)进行确认。启用此插件后,您可以在 Firefox 中请求任何网址,测试 HTTP 响应是否确实为 404 Not Found 或 410 Gone。
内容已从网页中移除
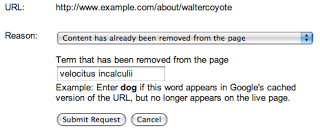
确认您要求移除的内容在网页已不复存在后,您可以使用“Content has been removed from the page”选项请求移除缓存。这种移除操作通常称为“缓存”移除,可确保 Google 的搜索结果不会包含旧网页的缓存副本或版本,也不会包含旧版网页中的任何文本摘要。您只能从 Google 搜索结果中访问目前已更新的网页(其中的内容已被移除)。不过,由于来自外部网站的入站链接仍存在,因此更新后的网页仍可能会根据与旧内容相关的字词进行排名。对于缓存移除请求,系统会要求您输入“已从网页中移除的字词”。请务必输入当前实际网页中未找到的字词,以便我们的自动化流程可以确认该网页已更改,否则请求将被拒绝。“网址移除说明”系列的第 2 部分中详细介绍了缓存移除方式。
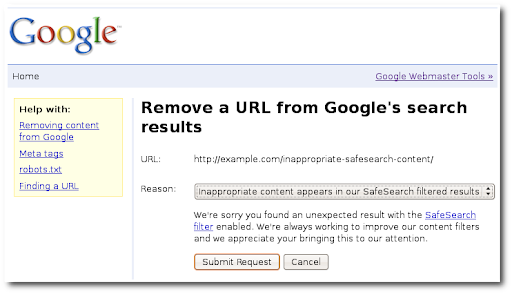
移除安全搜索过滤搜索结果中显示的不当网页或图片
Google 推出了安全搜索过滤器,旨在提供搜索结果来排除可能令人反感的内容。如果您发现某些内容应被安全搜索滤除,可以请求将来从安全搜索过滤结果中排除这些内容。使用“通过安全搜索过滤的结果中包含不当内容”选项提交移除请求。
如果您在使用公开网址移除工具时遇到任何问题,或者有未在此处解决的问题,请将其发布到网站站长帮助论坛,或访问我们的帮助中心查看更详细的移除说明。如果您要在论坛中发帖,请务必使用网址缩短服务来分享指向您要移除的内容的所有链接。
此系列中的其他博文
最后,您可能还想了解如何管理可在线获取的哪些信息。
