2010 年 8 月 6 日,星期五
可能会发生变化 - 有时,正如我们在之前发布的关于网址移除的博文中所见,您可能会彻底屏蔽或移除自己网站上的某个网页。有时,您可能只能更改网页的某些部分,或移除某些文本。这些更改可能需要一段时间才能体现在我们的搜索结果中,具体取决于网页的抓取频率。在这篇博文中,我们将探讨如果我们仍在搜索结果中显示已移除的旧内容(无论是“摘要”形式,还是从搜索结果链接至其他网页的缓存网页),您可以采取哪些措施。当旧内容中包含需要快速移除的敏感信息时,这样做很有意义;如果您只是正常更新网站,则无需执行此操作。
我们来看一个虚构的搜索结果示例:
| Walter E. Coyote | < 标题 |
|
Chief Development Officer at Acme Corp 1948-2003: worked on the top |
< 摘要 |
| www.example.com/about/waltercoyote - 缓存 | < 网址 + 指向缓存网页的链接 |
如需更改摘要(或链接的缓存页面)中显示的内容,您需要先更改实际(实时)页面上的内容。除非更改了网页的公开内容,否则 Google 的自动流程会继续在我们的搜索结果中显示部分原创内容。
网页内容发生变化后,您可以通过以下几种方式使这些更改显示在搜索结果中:
-
等待 Googlebot 重新抓取网页并将其重新编入索引:这是 Google 更新大部分内容的自然方法。有时可能需要相当长的时间,具体取决于 Googlebot 当前抓取相关网页的频率。我们重新抓取网页并将其重新编入索引后,通常不会显示旧内容,因为系统会将其替换为当前内容。如果 Googlebot 未被禁止抓取相应网页(使用 robots.txt 或因无法正确访问服务器),您无需执行任何特殊操作即可实现此目的。通常,无法加快抓取和索引编制速度,因为这些流程是完全自动化的,并依赖于许多外部因素。
-
使用 Google 的公开网址移除工具请求移除已从他人的网页中移除的内容。使用此工具时,有必要输入修改后的网页的确切网址,并选择“已从网页中移除内容”选项,然后指定已从该网页中完全移除的一个或多个字词。
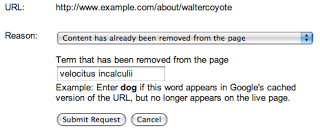
请注意,您输入的字词不能出现在相应网页上;即使某个字词已从网页的某个部分移除,如果您的字词仍出现在网页的另一部分,您的请求会被拒绝。请务必选择网页上任何位置不会再出现的一个或多个字词。在上面的示例中,如果您移除了“top secret velocitus incalculii capturing device”,则应提交这些字词,而不是“my project”。但是,如果“top”或“device”一词仍存在于网页上的任何位置,系统将拒绝该请求。为了尽可能提高成功率,最简单的方法通常是只输入一个您确定在该网页上的任何位置都不会再出现的字词。
如果您的请求已处理完毕,而且提交的字词不再出现在网页上,搜索结果将不再显示摘要,也不再提供缓存的网页。尽管摘要中不再显示这些字词,但仍会显示该网页的标题和网址;且对于已删除内容的相关搜索(例如搜索 velocitus incalculii),您可能仍会在搜索结果中发现该条目。但是,重新抓取该网页并将其重新编入索引后,我们的搜索结果中会显示新的摘要和缓存网页。
请注意,我们会查看该网页,以验证是否删除了相应的字词。如果该网页已不存在,且服务器返回了正确的
404或410HTTP 结果代码,导致我们无法查看该网页,建议您最好请求移除该网页。 - 使用 Google 网站站长工具中的网址移除工具请求从您的网站中移除网页上的信息。如果您有权访问相关网站并在 Google 网站站长工具中验证了对该网站的所有权,就可以在该网站中使用网址移除工具(依次前往“网站配置”>“抓取工具访问权限”)请求移除摘要和缓存的网页,直到 Google 重新抓取该网页。要使用此工具,您只需提交网页的确切网址即可(无需指定任何已移除的字词)。您的请求处理完毕后,我们会从搜索结果中移除摘要和缓存网页。网页的标题和网址仍然可见,不过,对于与已移除内容相关的查询,该网页仍可能会继续在搜索结果中获得排名。网页被重新抓取并重新编入索引后,搜索结果中可能会显示更新后的摘要和缓存网页(基于新内容)。
Google 会根据网页内容以及其他因素(例如指向网址的入站链接)将内容编入索引并对其进行排名。因此,即使网页已重新抓取并重新编入索引,网址也可能继续出现在网页上已不存在的内容的搜索结果中。虽然网址移除工具可以从搜索结果中移除摘要和缓存网页,但它不会更改或移除搜索结果的标题、更改显示的网址,也不会根据当前或之前的任何内容阻止网页显示在 Google 搜索结果中。如果这对您很重要,您应该确保相应网址满足从我们的搜索结果中彻底移除的要求。
移除非 HTML 内容
如果更改的内容不在 (X)HTML 中(例如,更改了图片、Flash 文件或 PDF 文件),您将无法使用缓存移除工具。因此,如果旧内容不再显示在搜索结果中,最快的方法是更改文件的网址,让旧网址返回 404 HTTP 结果代码,并使用网址移除工具移除旧网址。否则,如果您选择允许 Google 自然刷新您的信息,则请注意,在重新抓取后,非 HTML 内容的预览(例如 PDF 文件的快速查看链接)可能需要比普通 HTML 网页更长时间才会更新。
主动阻止显示摘要或缓存版本
作为网站站长,您可以使用漫游器 meta 标记主动阻止显示摘要或缓存版本,而无需使用我们的移除工具。虽然我们不建议将这种方法作为默认方法(网页摘要有助于用户更快地识别相关搜索结果,而缓存网页让用户能够在服务器不可用这种意外事件中查看您的内容),您可以使用“nosnippet”漫游器 meta 标记阻止显示摘要,或使用“noarchive”robots meta 标记禁止缓存网页。请注意,如果现有的和已知的网页上有此变化,Googlebot 将需要重新抓取这些网页并将其重新编入索引,使此变更显示在搜索结果中。
我们希望本博文能帮助您更清楚地了解适用于更新版网页的网址移除工具背后的一些流程。在下一篇博文中,我们将探讨如何请求移除不归您所有的内容;敬请期待!
与往常一样,欢迎您在我们的网站站长帮助论坛中提供反馈意见。
此系列中的其他博文
最后,您可能还想了解如何管理可在线获取的哪些信息。
