2010년 8월 6일 금요일
사이트를 변경해야 할 때가 있습니다. URL 삭제에 관한 이전 게시물에서 살펴보았듯이 사이트에서 페이지를 완전히 차단하거나 삭제하는 경우도 있고 페이지의 일부분만 변경하거나 특정 텍스트를 삭제하는 경우도 있습니다. 페이지가 크롤링되는 빈도에 따라 이러한 변경사항이 Google 검색결과에 반영되기까지 다소 시간이 걸릴 수 있습니다. 이 블로그 게시물에서는 Google 검색결과에 이미 삭제된 이전 콘텐츠가 표시될 때 취할 수 있는 단계를 다룹니다. 이러한 콘텐츠는 '스니펫' 또는 검색결과와 연결되어 캐시된 페이지라는 형태로 표시될 수 있습니다. 이전 콘텐츠에 민감한 정보가 포함되어 있어서 바로 삭제해야 한다면 이러한 조치를 취하면 되고, 웹사이트를 정상적으로 업데이트할 때는 반드시 이렇게 하지 않아도 됩니다.
예를 들어 다음과 같은 가상의 검색결과를 살펴보겠습니다.
| 월터 E. 코요테 | < 직함 |
|
Acme Corp 최고 개발 책임자, 1948~2003: 잠재력을 증명한 기밀 프로젝트인 |
< 스니펫 |
| www.example.com/about/waltercoyote - 캐시됨 | < URL + 캐시된 페이지 링크 |
스니펫(또는 연결 및 캐시된 페이지)에 표시되는 콘텐츠를 변경하려면 먼저 실제(실시간) 페이지의 콘텐츠를 변경해야 합니다. 페이지에 공개적으로 표시되는 콘텐츠가 변경되지 않는 한, Google의 자동 프로세스에서는 계속해서 검색결과에 원본 콘텐츠의 일부를 표시하기 때문입니다.
페이지의 콘텐츠가 변경되면 다음의 여러 가지 옵션을 사용하여 이러한 변경사항을 검색결과에 표시할 수 있습니다.
-
Googlebot이 페이지를 다시 크롤링하고 색인을 다시 생성할 때까지 대기: 이는 대부분의 콘텐츠는 Google에서 이런 방식으로 자연스럽게 업데이트됩니다. Googlebot이 현재 해당 페이지를 얼마나 자주 크롤링하느냐에 따라 업데이트되기까지 시간이 상당히 오래 걸릴 수도 있습니다. Googlebot이 페이지를 다시 크롤링하고 색인을 재생성하면 이전 콘텐츠는 일반적으로 표시되지 않습니다. 현재 콘텐츠로 대체되기 때문입니다. Googlebot이 문제가 있는 페이지를 크롤링하지 못하는 것이 아니라면(robots.txt에 의해 차단됨 또는 서버에 제대로 액세스할 수 없음) 특별히 취해야 할 조치는 없습니다. 이러한 프로세스는 완전히 자동화되어 있으며 외부 요인에 좌우되므로 일반적인 경우라면 크롤링 및 색인 생성 속도를 높이는 것은 불가능합니다.
-
Google의 공개 URL 삭제 도구를 사용하여 다른 사용자의 웹페이지에서 삭제된 콘텐츠의 삭제를 요청할 수 있습니다. 이 도구를 사용할 때는 수정된 페이지의 URL을 정확하게 입력하고 '콘텐츠가 페이지에서 삭제됨' 옵션을 선택한 다음 페이지에서 완전히 삭제된 하나 이상의 단어를 지정하세요.
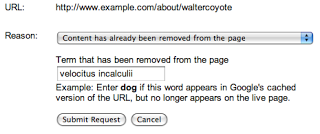
입력한 단어 중 하나도 페이지에 표시되지 않을 수도 있습니다. 페이지의 한 부분에서 삭제된 단어라 하더라도 페이지의 다른 부분에 단어가 계속 표시되면 요청이 거부됩니다. 페이지의 어느 부분에도 더 이상 표시되지 않는 단어를 선택해야 합니다. 위의 예에서 'top secret velocitus incalculii capturing device'를 삭제했다면 '내 프로젝트'와 같은 단어가 아닌 해당 문구를 제출해야 합니다. 하지만 페이지에 'top' 또는 'device'라는 단어가 계속 있으면 요청이 거부됩니다. 요청이 수행될 가능성을 최대한 높이려면 페이지에 더 이상 표시되지 않는다고 확신하는 단어를 입력해 보는 것이 가장 쉬운 방법입니다.
요청이 처리되고 제출한 단어가 더 이상 페이지에 표시되지 않음이 확인되면 검색결과에 더 이상 미리보기가 표시되지 않으며 저장된 페이지도 보이지 않게 됩니다. 제출한 단어가 더 이상 미리보기에 표시되지 않더라도 페이지의 제목과 URL은 계속 표시되며, 단어가 삭제된 콘텐츠와 관련된 검색결과(velocitus incalculii와 같은 검색어)에 계속 표시될 수 있습니다. 하지만 페이지가 다시 크롤링되고 색인이 다시 생성되고 나면 Google 검색결과에 새 스니펫과 캐시된 페이지가 표시될 수 있습니다.
Google은 페이지를 확인하여 단어가 삭제되었는지 확인합니다. 페이지가 더 이상 존재하지 않고 서버가 적절한
404또는410HTTP 결과 코드를 반환하여 Google에서 페이지를 볼 수 없는 경우 페이지 전체 삭제를 요청하는 것이 낫습니다. - Google 웹마스터 도구의 URL 삭제 도구를 사용하여 웹사이트에서 페이지 정보를 삭제해 달라고 요청합니다. 문제의 웹사이트에 액세스할 수 있으며 Google 웹마스터 도구에서 웹사이트 소유권을 확인한 경우 URL 삭제 도구(사이트 구성 > 크롤러 액세스)로 이동하여 페이지가 다시 크롤링될 때까지 스니펫과 캐시된 페이지를 삭제해 달라고 요청할 수 있습니다. URL 삭제 도구를 사용할 때는 페이지의 정확한 URL만 제출하면 되며, 삭제된 단어를 지정하지 않아도 됩니다. 요청이 처리되면 Google에서 스니펫과 캐시된 페이지를 검색결과에서 삭제합니다. 페이지의 제목 및 URL은 계속 표시되며, 삭제된 콘텐츠와 관련된 검색어의 검색결과에도 계속 페이지가 표시될 수 있습니다. 하지만 페이지가 다시 크롤링되어 색인이 생성되면 검색결과에 업데이트된 스니펫과 캐시된 페이지(새 콘텐츠 기반)가 표시될 수 있습니다.
Google은 페이지의 콘텐츠뿐 아니라 URL에 대한 인바운드 링크와 같은 다른 외부 요인도 고려하여 항목의 색인을 생성하고 순위를 지정합니다. 이로 인해 페이지가 다시 크롤링되고 색인이 다시 생성된 후에도 페이지에 더 이상 존재하지 않는 콘텐츠의 URL이 검색결과에 계속 표시될 수 있습니다. URL 삭제 도구를 통해 검색결과에서 스니펫과 캐시된 페이지를 삭제할 수는 있지만, 검색결과의 제목이 변경되거나 삭제되지는 않습니다. 또한 표시되는 URL이 변경되거나 현재 또는 이전 콘텐츠에 따라서 페이지가 특정 검색어에 대하여 표시되지 않도록 차단하지도 않습니다. 해당 콘텐츠를 완전히 삭제하는 것이 중요한 경우 URL이 Google 검색결과에서 완전히 삭제되기 위한 요구사항을 충족하는지 확인해야 합니다.
HTML이 아닌 콘텐츠 삭제
변경된 콘텐츠가 (X)HTML이 아닌 경우(예: 이미지, 플래시 파일 또는 PDF 파일이 변경된 경우) 캐시 삭제 도구를 사용할 수 없습니다. 따라서 이전 콘텐츠가 더 이상 검색결과에 표시되지 않는 것이 중요한 경우 가장 빠른 해결책은 이전 URL이 404 HTTP 결과 코드를 반환하도록 파일의 URL을 변경하고 URL 삭제 도구를 사용하여 이전 URL을 삭제하는 것입니다. 또는 Google에서 사용자의 정보를 자연적으로 새로고침하도록 선택한 경우 HTML이 아닌 콘텐츠의 미리보기(예: PDF 파일의 빠른 보기 링크)의 경우 재크롤링 후 업데이트하는 시간이 더 오래 걸릴 수 있음에 유의해야 합니다.
스니펫 또는 캐시된 버전이 표시되는 것을 사전에 방지
웹마스터는 삭제 도구를 사용하지 않고도 robots meta 태그를 사용하여 스니펫이나 캐시된 버전이 표시되는 것을 사전에 방지할 수 있습니다. 스니펫은 사용자가 관련 검색결과를 더 빠르게 인식할 수 있도록 해주며, 서버에서 예기치 않은 이벤트가 발생하더라도 사용자는 캐시된 페이지를 통해 콘텐츠를 볼 수 있습니다. 따라서 이 방법을 기본적인 접근방식으로 사용하지 않는 것이 좋습니다. 하지만 'nosnippet' robots meta 태그를 사용하여 스니펫이 표시되지 않게 하거나 'noarchive' robots meta 태그를 사용하여 페이지의 캐시가 저장되지 않도록 차단할 수는 않습니다. 기존 페이지 및 알려진 페이지의 robots 메타 태그가 변경되면 Googlebot이 페이지를 다시 크롤링하고 색인을 생성해야 변경사항이 검색결과에 표시됩니다.
이 블로그 게시물이 페이지 업데이트에 관한 URL 삭제 도구 프로세스를 좀 더 확실하게 파악하는 데 도움이 되기를 바랍니다. 다음 블로그 게시물에서는 소유하지 않은 콘텐츠의 삭제를 요청하는 방법을 알아보겠습니다. 다음 게시물을 기대해 주세요!
언제나 그렇지만 웹마스터 도움말 포럼에 의견과 질문을 올려 주시기 바랍니다.
이 시리즈의 다른 게시물
마지막으로 온라인에 표시되는 내 정보 관리하기를 읽어보는 것도 좋습니다.
