الجمعة 6 آب (أغسطس) 2010
كما رأينا في مشاركتنا السابقة حول إزالة عناوين URL، قد تتغير مجريات الأمور أحيانًا وتقرر حظر صفحة على موقعك الإلكتروني أو إزالتها تمامًا. وقد تكتفي أحيانًا بتغيير أجزاء من الصفحة، أو إزالة أجزاء معيّنة من نصها. بناءً على معدّل تكرار الزحف إلى الصفحة، قد يستغرق الأمر بعض الوقت كي تظهر هذه التغييرات في نتائج البحث لدينا. نتناول في مشاركة المدوّنة هذه الخطوات التي يمكنك اتخاذها إذا كان محرّك بحث Google لا يزال يعرض المحتوى القديم الذي أزلته، سواء كان يعرضه في شكل "مقتطف" أم على الصفحة المخزّنة مؤقتًا والتي يظهر رابط يؤدي إليها ضمن نتيجة البحث. تُعتبر هذه الخطوات مهمة إذا كان المحتوى القديم يتضمّن معلومات حساسة يجب التخلص منها سريعًا، لكنّها ليست ضرورية عند إضافة تعديلات عادية إلى موقعك الإلكتروني.
كمثال، دعنا نلقي نظرة على نتيجة البحث الوهمية التالية:
| والتر إي كويوت | < العنوان |
|
مدير التطوير في شركة Acme Corp 1948-2003: عمل على ابتكار |
< المقتطف |
| www.example.com/about/waltercoyote - نسخة مخزّنة مؤقتًا | < عنوان URL + رابط يؤدي إلى صفحة مخزّنة مؤقتًا |
لتغيير المحتوى المعروض في المقتطف (أو في الصفحة المخزّنة مؤقتًا التي تمت إضافة رابط يؤدي إليها)، ستحتاج أولاً إلى تغيير المحتوى في الصفحة الفعلية (المنشورة). ما لم يتم تغيير محتوى الصفحة المرئي للجمهور، ستواصل عمليات Google التلقائية عرض أجزاء من المحتوى الأصلي في نتائج البحث لدينا.
بعد تغيير محتوى الصفحة، نوفّر لك العديد من الخيارات لإظهار هذه التغييرات في نتائج البحث لدينا:
-
الانتظار حتى يعيد برنامج Googlebot الزحف إلى الصفحة ويعيد فهرستها: إنّها الطريقة الاعتيادية لتعديل معظم المحتوى في Google. في بعض الأحيان، قد يستغرق الأمر وقتًا طويلاً إلى حد ما، بناءً على معدّل زحف Googlebot إلى الصفحة المعنية في الوقت الحالي. بعد إعادة الزحف إلى الصفحة وإعادة فهرستها، لن يكون عادةً المحتوى القديم مرئيًا، إذ سيتم استبداله بالمحتوى الحالي. بشرط ألا يتم حظر Googlebot من الزحف إلى الصفحة المعنيّة (إما باستخدام ملف robots.txt أو بسبب عدم القدرة على الوصول إلى الخادم بشكل صحيح)، لن تضطر إلى اتخاذ أي إجراء محدّد كي يتم الزحف إلى الصفحة. بشكل عام لا يمكن تسريع عمليتَي الزحف والفهرسة، لأنّ هاتين العمليتَين مبرمَجتان تمامًا وتعتمدان على العديد من العوامل الخارجية.
-
استخدام أداة إزالة عناوين URL من Google المتاحة للجميع لطلب إزالة المحتوى الذي تمت إزالته من صفحة ويب لا تملكها: عند استخدام هذه الأداة، من الضروري إدخال عنوان URL الدقيق للصفحة التي تم تعديلها، وتحديد الخيار "تمت إزالة المحتوى من الصفحة"، ثم تحديد كلمة أو أكثر تمت إزالتها تمامًا من تلك الصفحة.
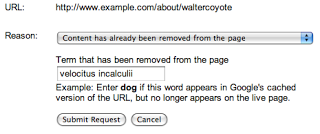
يُرجى العِلم أنّه لا يمكن أن تظهر أيّ من الكلمات التي تدخلها على الصفحة، وحتى إذا تمت إزالة كلمة من جزء واحد من الصفحة، سيتم رفض طلبك إذا استمرت هذه الكلمة في الظهور في جزء آخر من الصفحة. تأكَّد من اختيار كلمة (أو كلمات) لم تعُد تظهر في أي موضع بالصفحة. في المثال أعلاه، إذا أزلت "top secret velocitus incalculii capturing device"، يجب إرسال هذه الكلمات وليس شيئًا مثل "مشروعي". ومع ذلك، إذا كانت كلمة "top" أو "device" لا تزال تظهر في أي جزء على الصفحة، سيتم رفض الطلب. لزيادة فرص النجاح، غالبًا ما تكون أسهل طريقة هي إدخال كلمة واثق من أنّها لم تعُد تظهر في أي مكان في الصفحة.
بعد معالجة طلبك والتأكد من عدم ظهور الكلمات المرسلة في الصفحة، لن تعرض نتيجة البحث مقتطفًا، ولن تتوفر الصفحة المخزّنة مؤقتًا. سيظل عنوان الصفحة وعنوان URL الخاص بها مرئيَّين، وقد يستمر ظهور الإدخال في نتائج البحث لعمليات البحث ذات الصلة بالمحتوى الذي تمت إزالته (مثل عمليات البحث عن velocitus incalculii)، حتى إذا كانت هذه الكلمات لم تعُد تظهر في المقتطف. ومع ذلك، بعد إعادة الزحف إلى الصفحة وإعادة فهرستها، يمكن أن يظهر المقتطف الجديد والصفحة المخزّنة مؤقتًا في نتائج البحث لدينا.
يُرجى العِلم أنّنا سنحتاج إلى التأكد من إزالة الكلمات عن طريق عرض الصفحة. إذا لم تعُد الصفحة متوفرة وكان الخادم يعرض رمز نتيجة HTTP مناسبًا، سواء
404أم410، ما يجعلنا غير قادرين على عرض الصفحة، قد يكون من الأفضل لك طلب إزالة الصفحة تمامًا. - استخدام أداة إزالة عناوين URL الخاصة بأدوات مشرفي المواقع من Google لطلب إزالة المعلومات التي تظهر على إحدى صفحات موقعك الإلكتروني: إذا كانت لديك إمكانية الوصول إلى الموقع الإلكتروني المعنيّ وأكّدت ملكيتك له في أدوات مشرفي المواقع من Google، يمكنك استخدام أداة إزالة عناوين URL المتوفرة ضمن تلك الأدوات (بالانتقال إلى تصميم الموقع الإلكتروني > وصول الزاحف إلى صفحات الموقع) لطلب إزالة المقتطف والصفحة المخزّنة مؤقتًا حتى تتم إعادة الزحف إلى الصفحة. لاستخدام هذه الأداة، ما عليك سوى إرسال عنوان URL الدقيق للصفحة (لن تحتاج إلى تحديد أي كلمات تمت إزالتها). بعد معالجة طلبك، سنزيل المقتطف والصفحة المخزّنة مؤقتًا من نتائج البحث. سيظل عنوان الصفحة وعنوان URL الخاص بها مرئيَّين، وقد يتواصل ترتيب الصفحة أيضًا ضمن نتائج البحث عن العبارات المتعلقة بالمحتوى الذي تمت إزالته. بعد إعادة الزحف إلى الصفحة وإعادة فهرستها، يمكن أن تظهر نتيجة البحث مع مقتطف معدَّل وصفحة مخزّنة مؤقتًا (بناءً على المحتوى الجديد).
يعمل محرّك بحث Google على فهرسة العناصر وترتيبها ليس فقط بناءً على محتوى الصفحة، ولكن أيضًا استنادًا إلى عوامل خارجية أخرى، مثل الروابط الواردة إلى عنوان URL. لهذا السبب، من الممكن أن يستمر عنوان URL في الظهور ضمن نتائج البحث عن المحتوى الذي لم يعُد متاحًا على الصفحة، حتى بعد إعادة الزحف إلى الصفحة وإعادة فهرستها. يمكن لأداة إزالة عناوين URL إزالة المقتطف والصفحة المخزّنة مؤقتًا من نتيجة البحث، لكنّها لن تغيّر عنوان نتيجة البحث أو تزيله، أو تغيّر عنوان URL المعروض، أو تمنع الصفحة من الظهور لعمليات البحث المستندة إلى أي محتوى حالي أو سابق. وإذا كان ذلك مهمًا بالنسبة إليك، عليك التأكد من أنّ عنوان URL يفي بمتطلبات الإزالة الكاملة من نتائج البحث لدينا.
إزالة المحتوى الذي ليس بتنسيق HTML
إذا لم يكن المحتوى الذي تم تغييره بتنسيق (X)HTML (على سبيل المثال، إذا تم تغيير صورة أو ملف Flash أو ملف PDF)، لن تتمكن من استخدام أداة إزالة المحتوى المخزّن مؤقتًا. لذلك، إذا كان من المهم عدم ظهور المحتوى القديم ضمن نتائج البحث، يجب الاستعانة بالحل الأسرع، وهو تغيير عنوان URL للملف كي يعرض عنوان URL القديم رمز نتيجة HTTP 404 مع استخدام أداة إزالة عناوين URL لإزالة عنوان URL القديم. بخلاف ذلك، إذا اخترت السماح لمحرّك بحث Google بإعادة تحميل معلوماتك بشكل تلقائي، يُرجى العِلم أنّ معاينات المحتوى الذي ليس له تنسيق HTML (مثل روابط العرض السريع لملفات PDF) يمكن أن تستغرق وقتًا أطول في التعديل بعد إعادة الزحف مقارنةً بصفحات HTML العادية.
منع ظهور المقتطفات أو النُسخ المخزّنة مؤقتًا بشكل استباقي
بصفتك مشرف مواقع، يتوفر لك خيار استخدام علامات meta لبرامج الروبوت لمنع ظهور المقتطفات أو النسخ المخزّنة مؤقتًا بشكل استباقي بدون استخدام أدوات الإزالة التي نوفّرها. ولا ننصح بهذا الإجراء كأسلوب تلقائي (يمكن للمستخدمين الاستفادة من المقتطف في التعرف على نتيجة البحث ذات الصلة بعملية بحثهم بشكل أسرع، في حين تمنحهم الصفحة المخزّنة مؤقتًا إمكانية عرض المحتوى الخاص بك حتى إذا حدث أمر غير متوقّع أدّى إلى عدم توفّر الخادم)، ولكن يمكنك استخدام علامة meta المسماة nosnippet والخاصة ببرامج الروبوت لمنع ظهور المقتطف، أو علامة meta المسماة noarchive والخاصة ببرامج robots من أجل إيقاف التخزين المؤقت للصفحة. يُرجى العِلم أنّه إذا تم تغيير ذلك في الصفحات الحالية والمعروفة، سيحتاج Googlebot إلى إعادة الزحف إلى هذه الصفحات وإعادة فهرستها قبل أن يصبح هذا التغيير مرئيًا في نتائج البحث.
نأمل أن تساعد مشاركة المدونة هذه في توضيح بعض العمليات ضمن أداة إزالة عناوين URL للصفحات المعدَّلة. سنتناول في مشاركة المدونة التالية الطرق المتاحة لطلب إزالة المحتوى الذي لا تملكه.
كالعادة، نرحّب بأي ملاحظات أو استفسارات من خلال منتدى مساعدة مشرفي المواقع.
المزيد من المشاركات ضمن هذه السلسلة
- الجزء الأوّل: إزالة عناوين URL والأدلة
- الجزء الثاني: إزالة المحتوى المخزّن مؤقتًا وتعديله
- الجزء الثالث: إزالة محتوى لا تملكه
- الجزء الرابع: تتبُّع الطلبات ومعرفة ما لا يجب إزالته
وأخيرًا، يمكنك أيضًا الاطّلاع على مشاركة إدارة المعلومات المتوفرة عنك على الإنترنت.
