Thứ Hai, ngày 3 tháng 5 năm 2010
Trong bài cuối cùng này thuộc chuỗi nội dung về việc xoá URL, hãy cùng thảo luận về việc theo dõi các yêu cầu xoá của bạn, cũng như thời điểm không nên sử dụng công cụ xoá URL của Google. Nếu chưa, bạn nên đọc các bài đăng trước đó trong loạt bài này:
- Phần I: Xoá URL và thư mục
- Phần II: Xoá và cập nhật nội dung lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm
- Phần III: Xoá nội dung mà bạn không sở hữu
- Phần IV: Theo dõi yêu cầu và những nội dung không nên xóa
Bạn cũng có thể tìm hiểu cách quản lý những thông tin hiện có về bạn trên mạng.
Tìm hiểu trạng thái của yêu cầu
Yêu cầu xoá sẽ xuất hiện trong danh sách yêu cầu của bạn sau khi bạn gửi. Bạn có thể kiểm tra trạng thái của các yêu cầu bất cứ lúc nào để xem liệu nội dung đã bị xoá hay chưa, hay yêu cầu vẫn hoặc đang chờ xử lý hay đã bị từ chối.
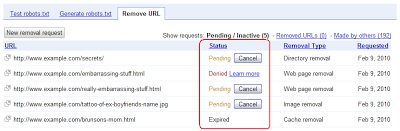
Nếu một yêu cầu bị từ chối, bạn sẽ thấy đường liên kết "Tìm hiểu thêm" bên cạnh yêu cầu đó để giải thích lý do yêu cầu cụ thể đó bị từ chối. Vì mỗi loại yêu cầu xoá lại có những điều kiện riêng, nên lý do khiến yêu cầu cụ thể bị từ chối cũng có thể khác biệt. Đường liên kết "Tìm hiểu thêm" sẽ giúp bạn tìm ra những điều cần thay đổi để yêu cầu của bạn thành công. Ví dụ: có thể bạn cần thay đổi để URL đó đáp ứng các yêu cầu đối với hình thức xoá bạn đã yêu cầu; hoặc nếu không thể làm được việc đó, có thể bạn cần yêu cầu một hình thức xoá khác (một loại yêu cầu mà URL của bạn hiện đáp ứng).
Nếu một yêu cầu được đánh dấu là "Đã xoá" nhưng bạn vẫn thấy nội dung đó trong kết quả tìm kiếm, hãy kiểm tra những điều sau:
-
URL xuất hiện trong kết quả tìm kiếm có phải là URL giống hệt với URL mà bạn đã gửi để xoá không? Việc nội dung giống hoặc tương tự nhau xuất hiện trên nhiều URL trên một trang web là việc khá phổ biến. Có thể bạn đã xoá thành công một URL, nhưng vẫn thấy những URL khác có chứa nội dung đó.
Giải pháp: Yêu cầu xoá (các) URL khác có liên quan. Hãy xem bài viết trong Trung tâm trợ giúp của chúng tôi về cách chọn đúng URL để yêu cầu xoá/chặn.
-
Xin lưu ý rằng các URL có phân biệt chữ hoa chữ thường, vì vậy, yêu cầu xoá
https://www.example.com/embarrassingstuff.htmlkhông giống với yêu cầu xoáhttps://www.example.com/EmbarrassingStuff.htmlGiải pháp: Yêu cầu xoá (các) URL khác có liên quan. Hãy xem bài viết trong Trung tâm trợ giúp của chúng tôi về cách chọn đúng URL để yêu cầu xoá/chặn.
-
Khi một yêu cầu được đánh dấu là "Đã xoá", điều này có thể mang nhiều ý nghĩa khác biệt tuỳ thuộc vào loại yêu cầu mà bạn gửi. Nếu bạn yêu cầu xoá toàn bộ một URL, thì trạng thái "Đã xoá" có nghĩa là toàn bộ URL đó không còn xuất hiện trong kết quả tìm kiếm của chúng tôi. Nếu bạn yêu cầu xoá phiên bản trong bộ nhớ đệm của một URL, thì "Đã xoá" có nghĩa là phiên bản lưu trong bộ nhớ đệm đã bị xoá và sẽ không xuất hiện trong kết quả tìm kiếm nữa; nhưng bản thân URL đó vẫn có thể xuất hiện.
Giải pháp: Kiểm tra kỹ loại yêu cầu xoá bằng cách xem cột "Loại xoá". Nếu bạn yêu cầu xoá nội dung trong bộ nhớ đệm nhưng lại muốn xoá toàn bộ URL, hãy đảm bảo rằng URL đó đáp ứng các yêu cầu về việc xoá toàn bộ, sau đó gửi một yêu cầu mới để xoá hoàn toàn URL.
Những trường hợp không nên sử dụng công cụ xoá URL
-
Để dọn sạch nội dung thừa, chẳng hạn như các trang
404cũ. Công cụ này dành cho những URL cần xoá ngay, chẳng hạn như những dữ liệu bí mật vô tình bị lộ. Nếu bạn mới thay đổi nội dung trên trang web và chỉ có một số URL lỗi thời trong chỉ mục, thì các trình thu thập dữ liệu của Google sẽ nhận ra điều này khi chúng tôi thu thập lại dữ liệu trên các URL của bạn và những trang đó sẽ tự biến mất khỏi kết quả tìm kiếm theo thời gian. Bạn không cần yêu cầu xoá ngay thông qua công cụ này. -
Để xoá lỗi thu thập dữ liệu khỏi tài khoản Công cụ quản trị trang web. Công cụ xoá này sẽ xoá URL khỏi kết quả tìm kiếm của Google chứ không xoá URL khỏi tài khoản Công cụ quản trị trang web của bạn. Hiện tại, bạn không có cách nào để xoá URL khỏi báo cáo này theo cách thủ công; chúng sẽ tự nhiên biến mất theo thời gian khi chúng tôi ngừng thu thập dữ liệu những URL liên tục
404. - Để "xây dựng lại trang web từ đầu". Nếu bạn lo lắng rằng trang web của mình có thể bị phạt, hoặc bạn muốn "xây dựng từ đầu" sau khi mua miền của một người khác, thì bạn không nên sử dụng công cụ xoá URL để xoá toàn bộ trang web rồi "bắt đầu lại". Các công cụ tìm kiếm thu thập nhiều thông tin qua các trang web khác (chẳng hạn như những người liên kết đến bạn, hoặc những từ mà họ dùng để mô tả trang web của bạn) và sử dụng thông tin này để giúp bạn hiểu trang web của bạn. Ngay cả khi chúng tôi có thể xoá mọi thông tin mà chúng tôi hiện biết về trang web của bạn, thì rất nhiều trang web như vậy sẽ hoạt động trở lại giống như khi chúng tôi thu thập lại dữ liệu trên tất cả những trang web khác giúp chúng tôi hiểu được trang web của bạn và đưa trang web đó vào ngữ cảnh Nếu lo lắng rằng miền của mình có một số dấu hiệu không hợp lệ trong quá khứ, bạn nên gửi một yêu cầu xem xét lại để cho chúng tôi biết vấn đề khiến bạn lo lắng cũng như những gì đã thay đổi (chẳng hạn như việc bạn mua miền từ người khác hoặc bạn đã thay đổi một số khía cạnh nhất định của trang web).
-
Để "tạm dừng" hoạt động của trang web sau khi bị tấn công. Nếu trang web của bạn bị tấn công và bạn muốn loại bỏ những URL không hợp lệ đã được lập chỉ mục, thì bạn có thể sử dụng công cụ xoá URL để xoá mọi URL mới do tin tặc tạo ra, ví dụ:
https://www.example.com/buy-cheap-cialis-skq3w598.html. Bạn không nên xoá toàn bộ trang web hoặc xoá những URL mà rốt cuộc bạn muốn Google lập chỉ mục. Thay vào đó, bạn chỉ cần dọn dẹp trang web và cho phép chúng tôi thu thập lại dữ liệu trên trang web của bạn để chúng tôi có thể lập chỉ mục lại nội dung mới đã được dọn dẹp càng sớm càng tốt. Bài viết này cung cấp thêm thông tin chi tiết về cách xử lý hành vi tấn công. -
Để giúp hệ thống lập chỉ mục đúng "phiên bản" của trang web của bạn. Khi yêu cầu xoá
https://www.example.com/tattoo.htmlđược chấp nhận,http://www.example.com/tattoo.htmlcũng sẽ được xoá. Điều này cũng đúng đối với các phiên bản có www và không có www của URL hoặc trang web. Lý do là cùng một nội dung như vậy thường có sẵn tại từng URL trong số này và chúng tôi nhận thấy hầu hết quản trị viên trang web và người tìm kiếm không muốn những trang trùng lặp như vậy xuất hiện trong kết quả tìm kiếm. Tóm lại, bạn không nên dùng công cụ xoá URL làm công cụ chuẩn hoá. Công cụ này không giữ phiên bản bạn mong muốn mà sẽ xoá tất cả phiên bản (http/https và có/không có www) của một URL.
Chúng tôi hy vọng loạt bài này đã giải đáp được thắc mắc của bạn về việc xoá nội dung khỏi kết quả tìm kiếm trên Google và giúp bạn khắc phục mọi vấn đề có thể phát sinh. Hãy tham gia Diễn đàn trợ giúp của chúng tôi nếu bạn vẫn còn thắc mắc.
